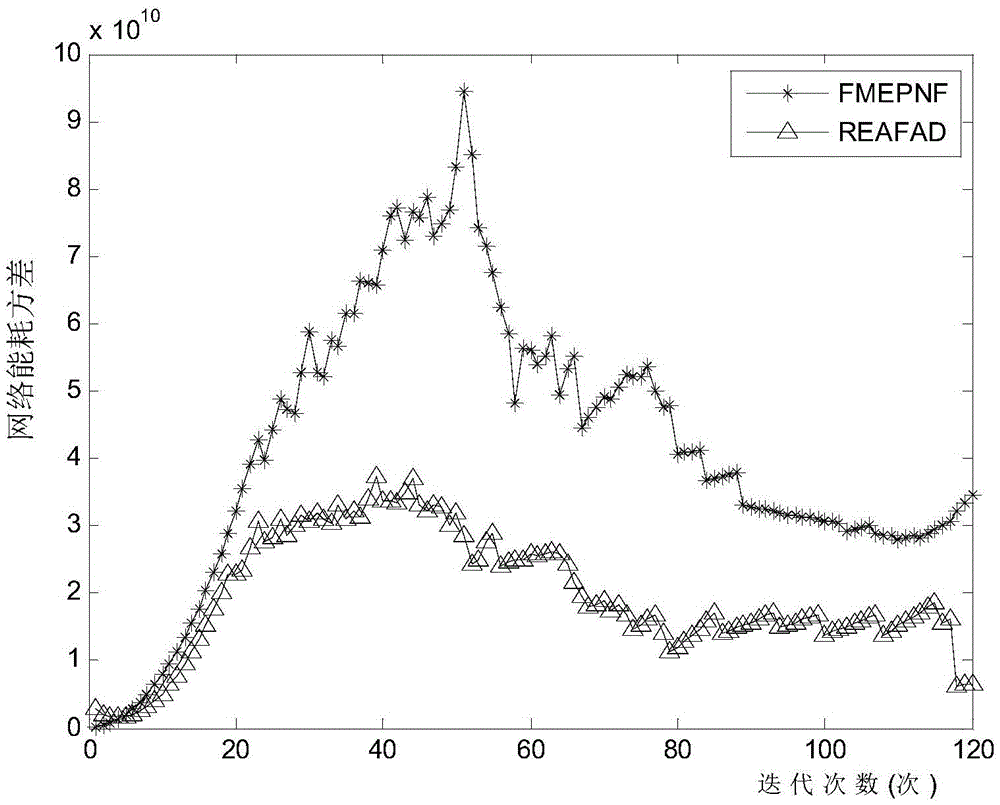
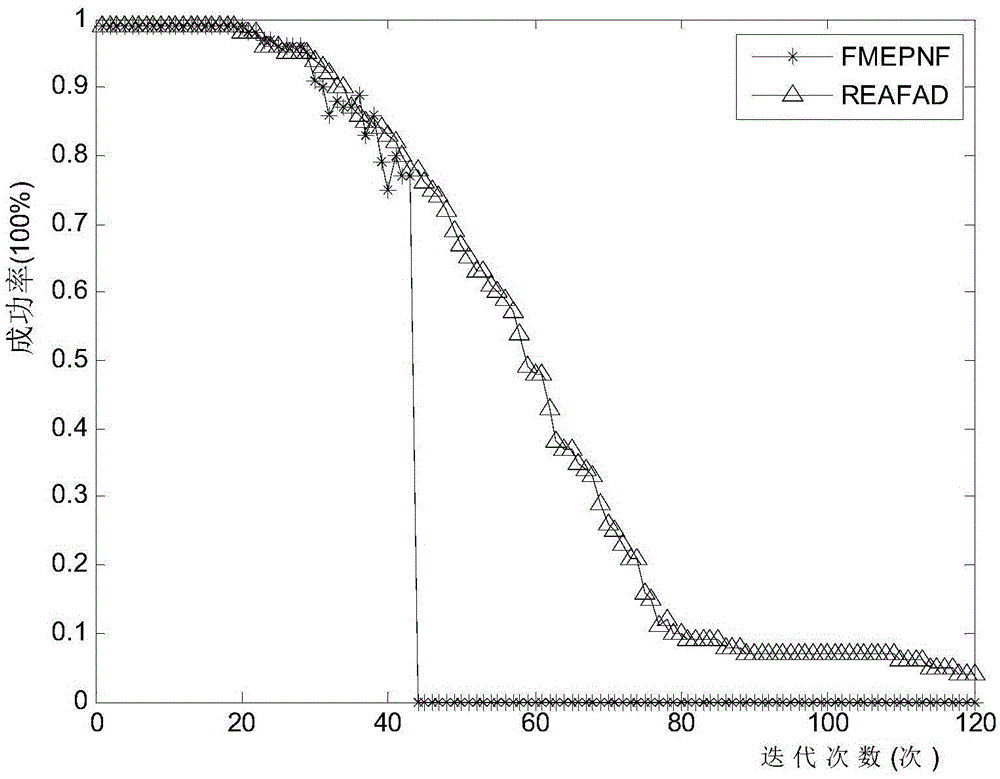
Routing algorithm for dynamically adjusting forward angle based on residual energy
A technology of residual energy and dynamic adjustment, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problem of excessive energy consumption of key nodes, achieve the effect of maintaining effective coverage, improving the uniformity of energy consumption, and balancing network energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
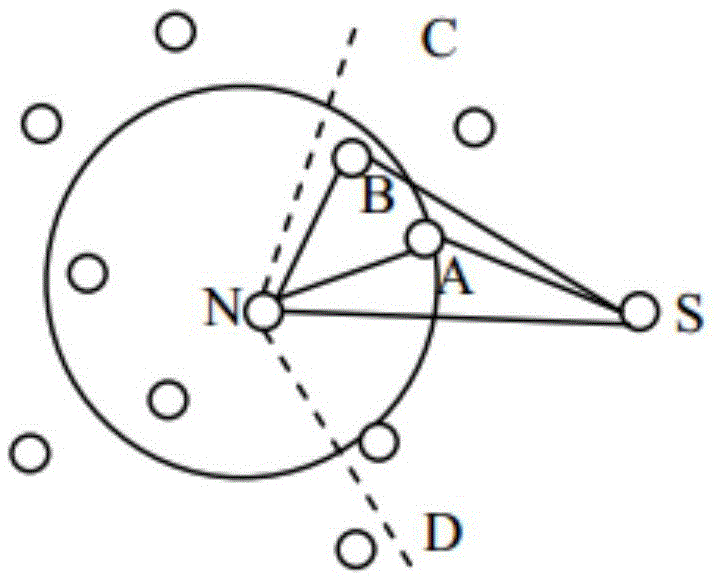
[0027] Example 1: Such as Figure 1-4 As shown, a routing algorithm that dynamically adjusts the forward angle based on the remaining energy, and a routing algorithm that dynamically adjusts the forward angle based on the remaining energy. When a node is ready to select the next hop node, the current node's forward angle range is judged Whether the remaining energy of the inner neighbor node is lower than the remaining energy threshold of the node E th :
[0028] If the remaining energy of neighboring nodes within the forward angle range of the current node is lower than the remaining energy threshold E th , The node increases the forward angle; among them, the principle of the node increases the forward angle: from the minimum forward angle A min To maximum forward angle A max , Until the maximum forward angle range, there is no meeting that the remaining energy is higher than the remaining energy threshold E th When it is a neighbor node, follow its probability transfer functi...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Such as Figure 1-4 As shown, a routing algorithm that dynamically adjusts the forward angle based on the remaining energy, and a routing algorithm that dynamically adjusts the forward angle based on the remaining energy. When a node is ready to select the next hop node, the current node's forward angle range is judged Whether the remaining energy of the inner neighbor node is lower than the remaining energy threshold of the node E th :
[0044] If the remaining energy of neighboring nodes within the forward angle range of the current node is lower than the remaining energy threshold E th , The node increases the forward angle; among them, the principle of the node increases the forward angle: from the minimum forward angle A min To maximum forward angle A max , Until the maximum forward angle range, there is no meeting that the remaining energy is higher than the remaining energy threshold E th When the neighbor node is the neighbor node, follow its probabilit...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Such as Figure 1-4 As shown, a routing algorithm that dynamically adjusts the forward angle based on the remaining energy, and a routing algorithm that dynamically adjusts the forward angle based on the remaining energy. When a node is ready to select the next hop node, the current node's forward angle range is judged Whether the remaining energy of the inner neighbor node is lower than the remaining energy threshold of the node E th :
[0053] If the remaining energy of neighboring nodes within the forward angle range of the current node is lower than the remaining energy threshold E th , The node increases the forward angle; among them, the principle of the node increases the forward angle: from the minimum forward angle A min To maximum forward angle A max , Until the maximum forward angle range, there is no meeting that the remaining energy is higher than the remaining energy threshold E th When the neighbor node is the neighbor node, follow its probabilit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com