Multidimensional data space similarity matching method based on relation communication networks
A similarity matching, data space technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of no classification, lack of theoretical basis, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
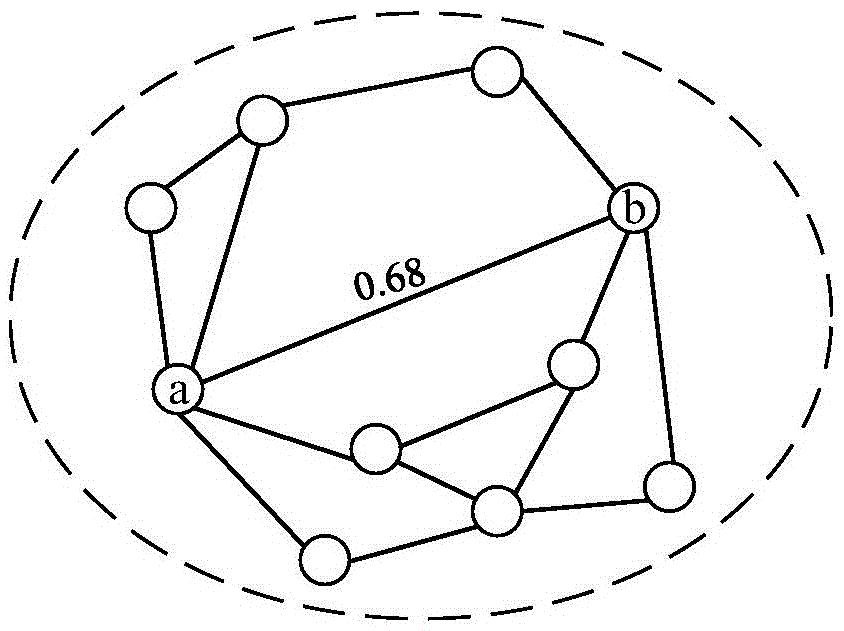
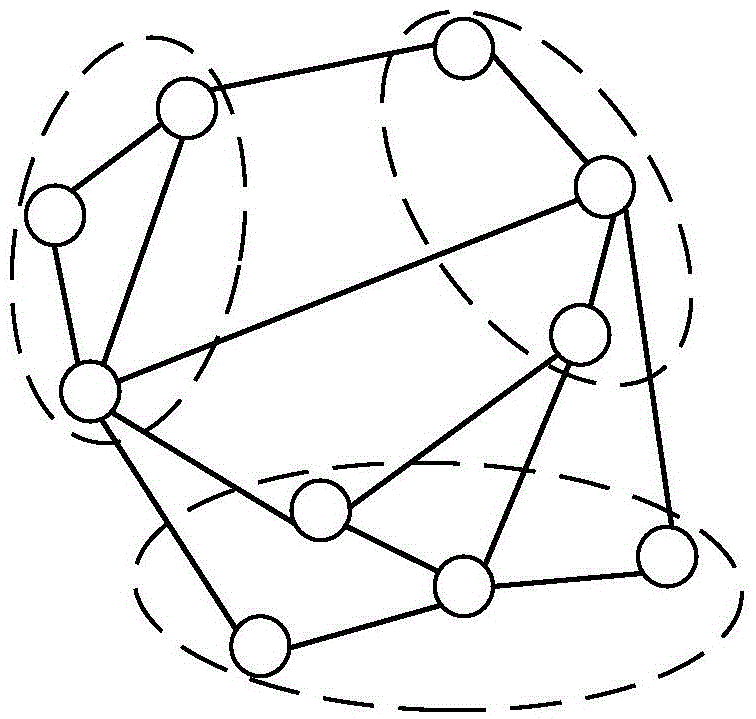
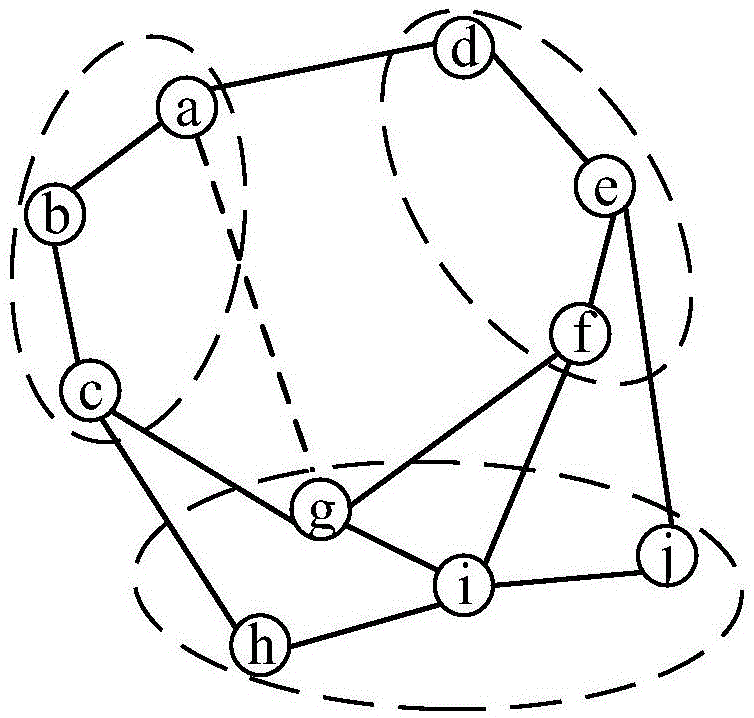
[0064] 1. In order to facilitate the description of this algorithm and highlight the advantages of this algorithm: it can calculate the similarity between data objects in the multi-dimensional data space, the key terms in the algorithm are defined as follows:
[0065] Data type T: The data type is the type of data objects that need to calculate the similarity, and the data type defines a class of data object information with the same attributes.
[0066] Data object O: A data object is a specific instance of a data type. A data object can only belong to one data type, and a data type can have pairs of data object instances.
[0067] Data space S: The data space is a collection of data object instances of the same data type. There can be multiple data object instances of the same data type in a data space, and the number of data object instances in different data spaces can be different. . S for data space t Represents, where t represents the type of data space.
[0068] Exa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com