Method for inversing sea-bottom attenuation coefficient by using modal dispersion curve energy difference
A technology of dispersion curve and attenuation coefficient, which is applied in the inversion field of seabed attenuation coefficient, can solve the problems of no inversion of seabed attenuation coefficient and insufficient use of modal dispersion curve amplitude energy information, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] Now in conjunction with embodiment, accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
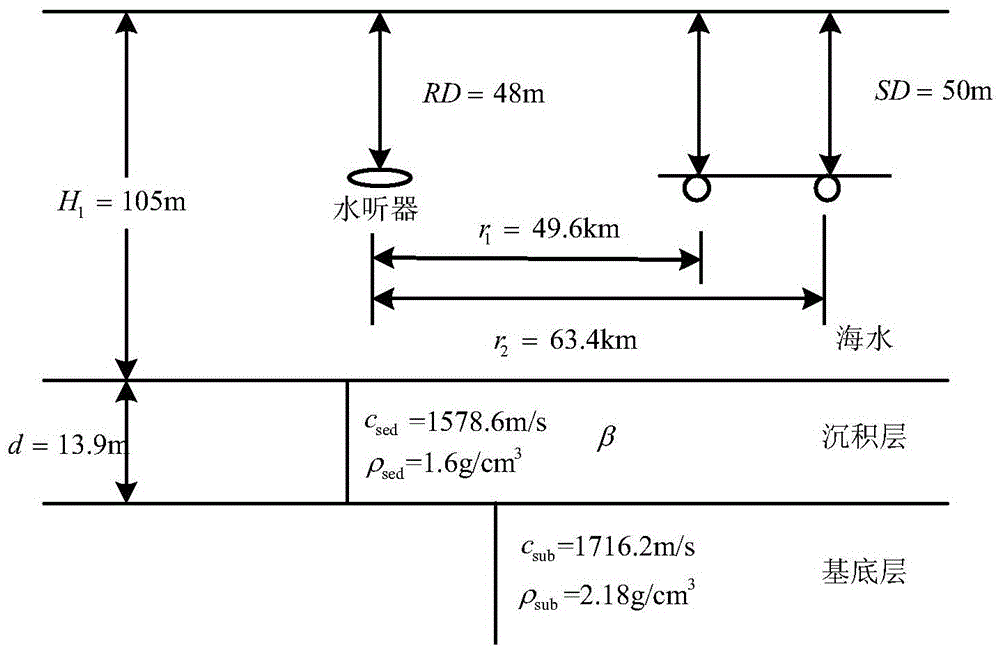
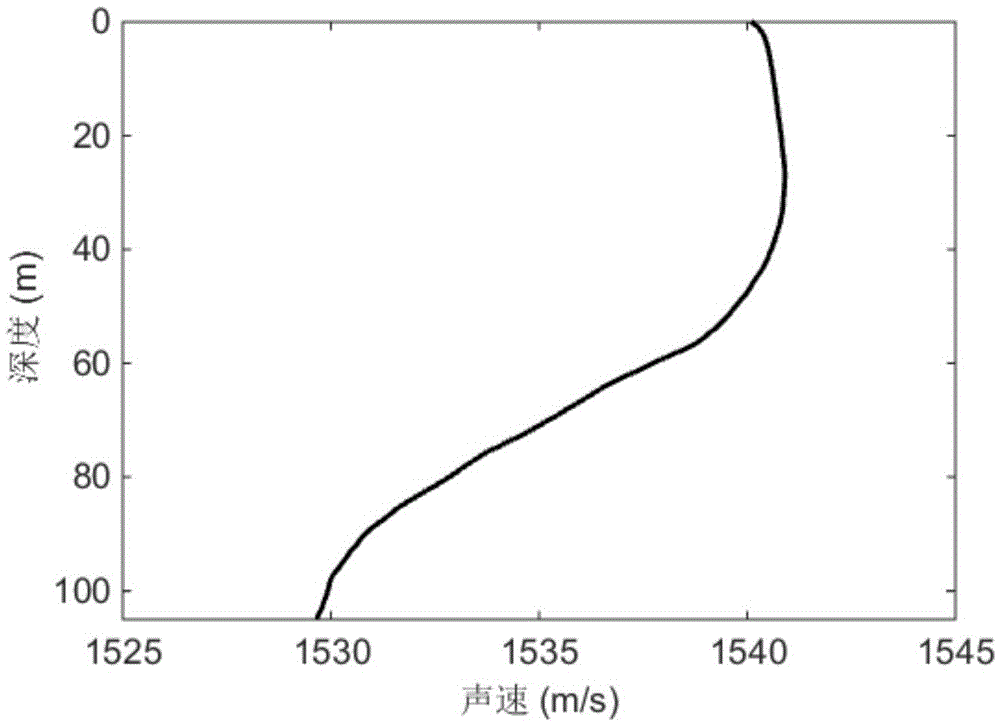
[0035] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , using a system consisting of two explosion sound sources with an initiation depth of 50m and a hydrophone to invert the seabed attenuation coefficient. The channel environment is shallow sea, the sea depth is about 105m, the sound source depth is 50m, and the receiving depth is 48m. The receiving hydrophone is 49.6km away from the first explosion sound source and 63.4km away from the second explosion sound source; the thickness of the sediment layer is 13.9m, the sound velocity of the sediment layer is 1578.6m / s, and the density of the sediment layer is 1.6g / cm 3 , the speed of sound in the base layer is 1716.2m / s, and the density of the base layer is 2.18g / cm 3 ; The shallow sea sound velocity profile is figure 2 The sound velocity profile shown.
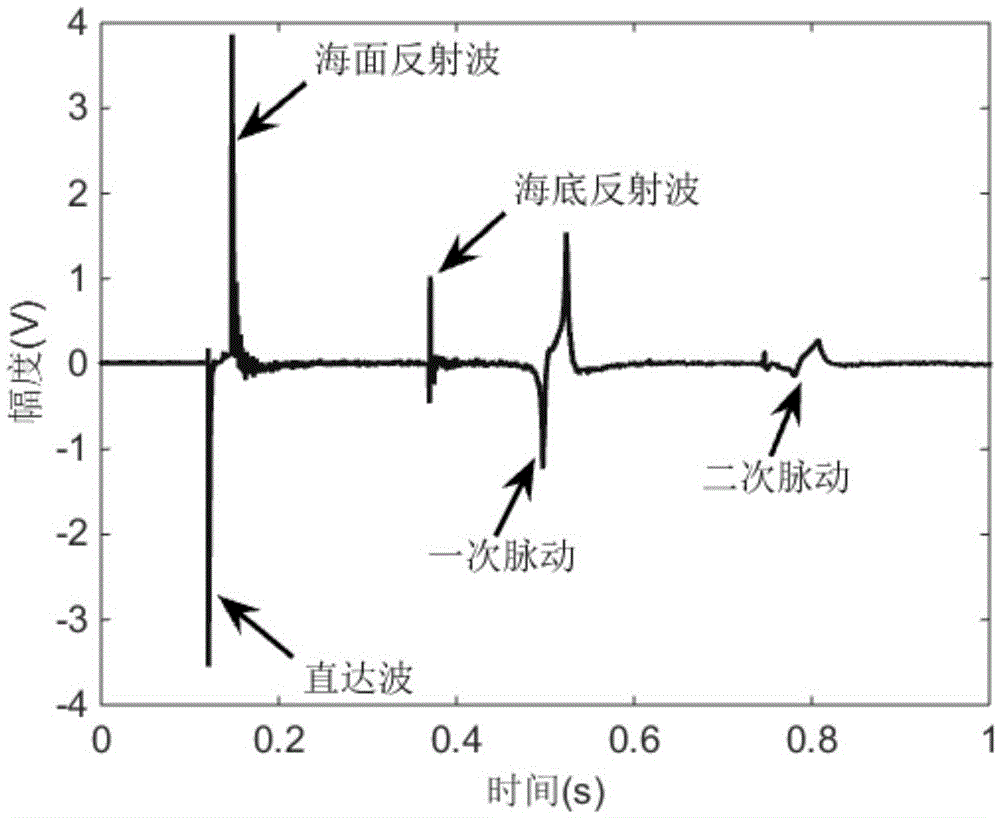
[0036] Referring to Figure 4 and Figure 5, it can be seen that the fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com