Abrasive scratch interference test method for diamond tool pre-repaired non-ferrous metal specimens
A technology of diamond tools and non-ferrous metals, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, and mechanical devices. It can solve the problem of failure to realize automatic adjustment and position feedback control, difficulty in achieving high-precision interference behavior testing, and failure to consider the interaction of multiple abrasive grains. Interference and other problems, achieve high-speed and high-precision scratch test, avoid large end face runout or radial runout, improve shape accuracy and surface finish
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] A test method for the continuous scratching interference behavior of a single abrasive grain on a non-ferrous metal specimen pre-repaired by a diamond tool. The device used includes:
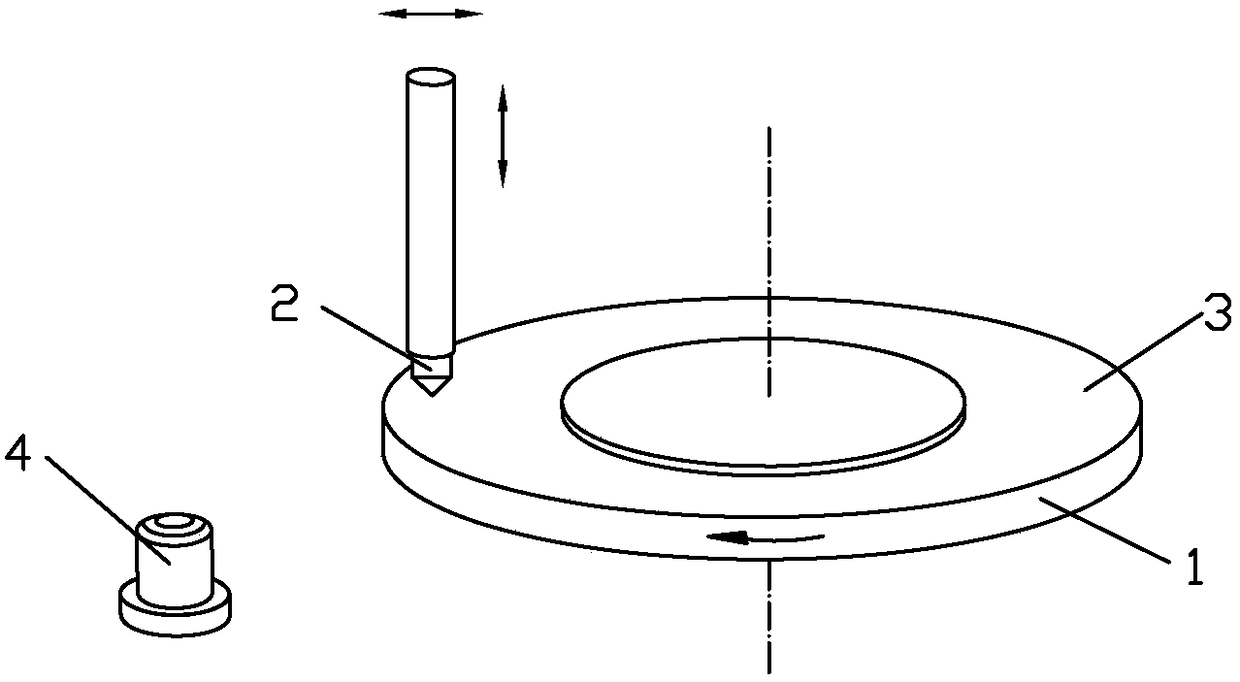
[0042] The machine tool, the disc-shaped non-ferrous metal test piece 1 is mounted on the electric spindle of the machine tool, and the test piece 1 can be rotated by the electric spindle;
[0043] A dynamic balancer, used for online dynamic balancing of the test piece 1;
[0044] The diamond single-point tool is a diamond turning tool 5, specifically a polycrystalline diamond (PCD) single-point turning tool and a single crystal diamond (ND) single-point turning tool, which are used to repair the end face of the test piece 1; the diamond turning tool 5. It is detachably attached to the bracket, and is movably attached to the machine tool through the bracket;
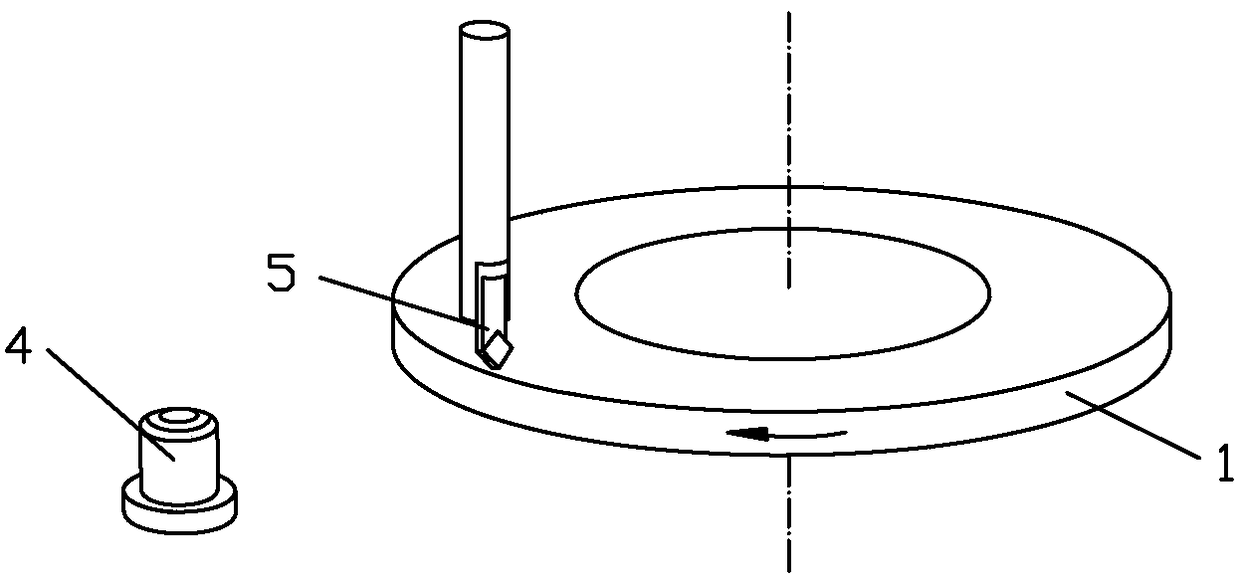
[0045] The tool head 2 is used for scratch testing; the top of the tool head 2 is fixed with a single grain of abrasive; the tool...
Embodiment 2
[0068] 1) Clamp the aluminum alloy disc-shaped test piece 1 with a diameter of 140mm on the electric spindle of the machine tool through a mechanical fixture, and the test piece 1 can be rotated by the electric spindle; use a dynamic balancer to perform online dynamic balancing on the test piece 1, so as to Reduce the vibration of the test piece 1 during high-speed rotation, so as to ensure the stable contact between the abrasive grains and the test piece 1 during the scratching process;
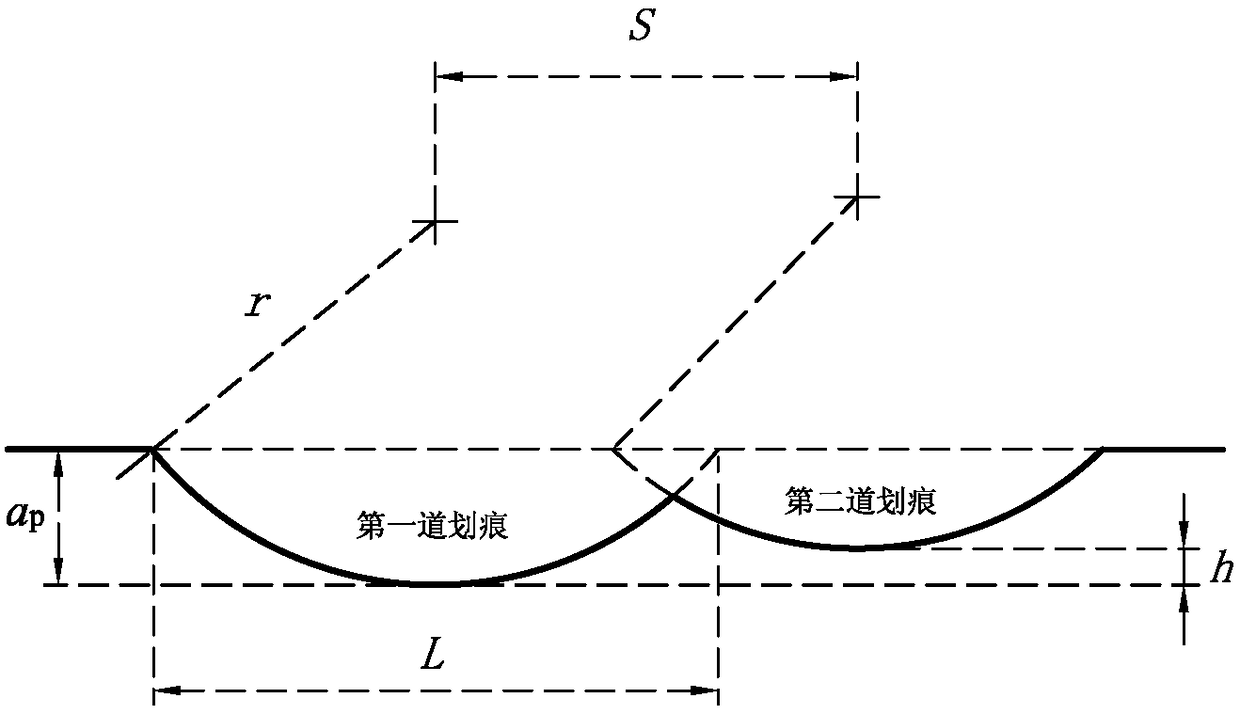
[0069] 2) Use the diamond turning tool 5 to repair the disk of the test piece 1, first use the polycrystalline diamond single-point turning tool to repair the disk, and then use the single-crystal diamond single-point turning tool to repair the disk, and form an end runout of 3 μm on the surface of the test piece 1 , the circular repairing area 3 with an average surface roughness Ra 4nm, to reduce the runout of the end face of the specimen 1, improve the surface quality, and further ensure th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com