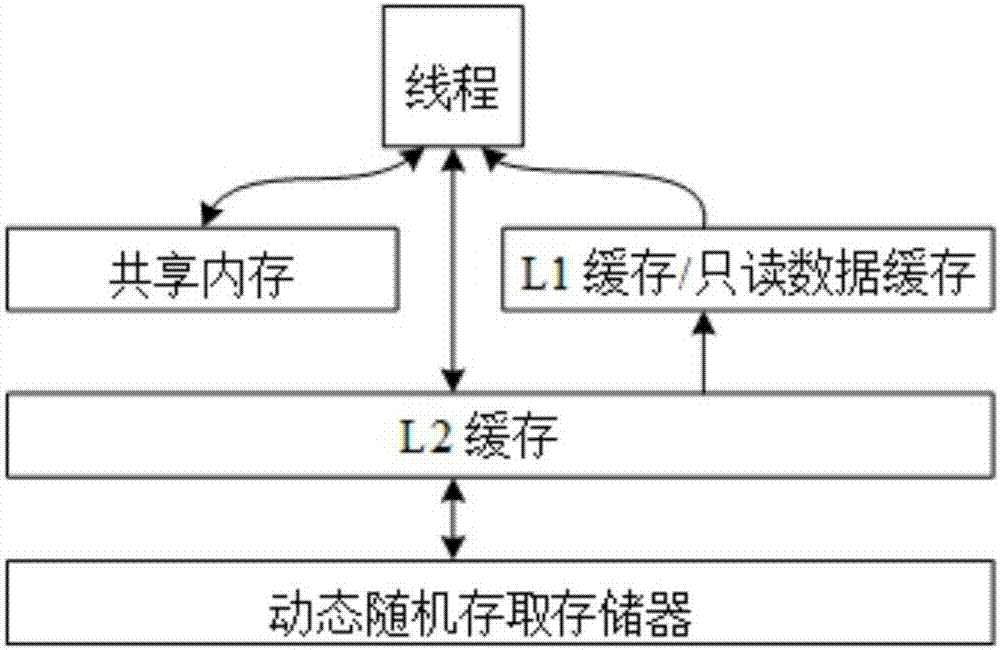
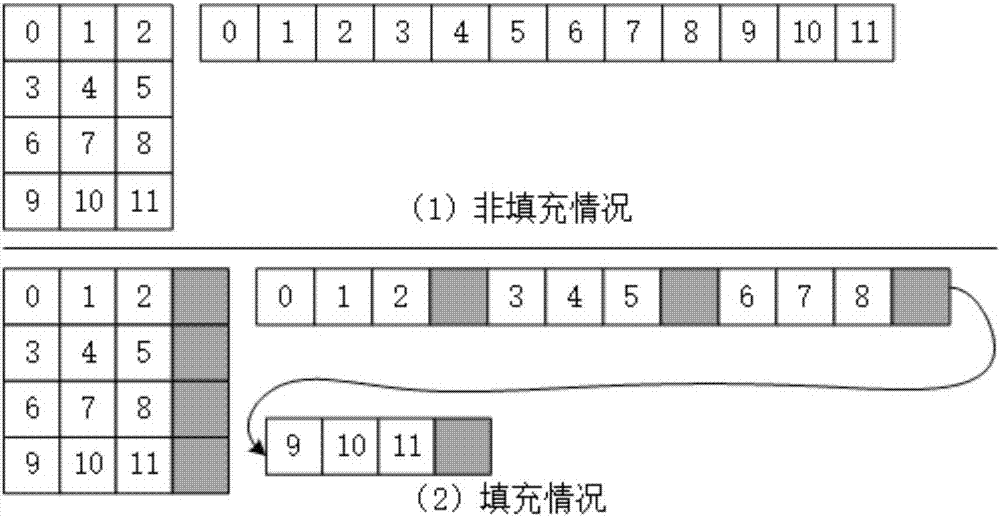
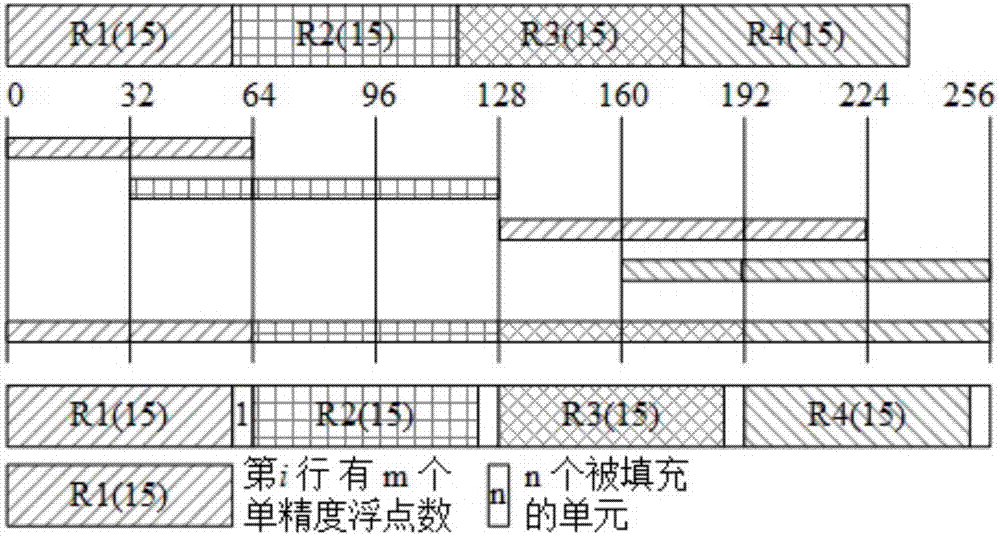
A GPU-based fast solution method for L1 minimization problem
A minimization and problem-solving technology, which is applied in the field of fast solving of GPU-based L1 minimization problems, can solve problems such as large overhead, CUBLAS does not support fusion, performance fluctuations, etc., achieve multi-level cache control optimization, and reduce global data access , the effect of high parallelism and adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] In the following description, combined with the attached Figure 1-7 The present invention is further explained in detail with specific implementation methods.
[0047] The fast iterative shrinkage threshold algorithm is an iterative shrinkage threshold algorithm, an accelerated version implemented by combining Nesterovs optimal gradient algorithm, with a non-asymptotic convergence rate O(k 2 ). The algorithm adds a new sequence {y k ,k=1,2,…}, the specific iteration steps are as follows:
[0048]
[0049] Among them, λ is a scalar weight, soft(u,a)=sign(u) max{|u|-a,0} is a soft threshold operator, y 1 =x 0 , t 1 = 1, L f is the Lipschitz constant associated with ▽f(·), which can be calculated by A T The characteristic spectrum of A is obtained (||A T A|| 2 ),▽f(y k )=A T (Ay k -b).
[0050] The invention relates to solving the L1 minimization problem, adopts a fast iterative shrinkage threshold algorithm, and the algorithm mainly involves vector operat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com