Adaptive residual feedback suppression
A feedback suppression, adaptive filter technology, applied in the prevention of acoustic wave response, sensor components, sensors, etc., can solve the problems of inability to feedback path modeling, instability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
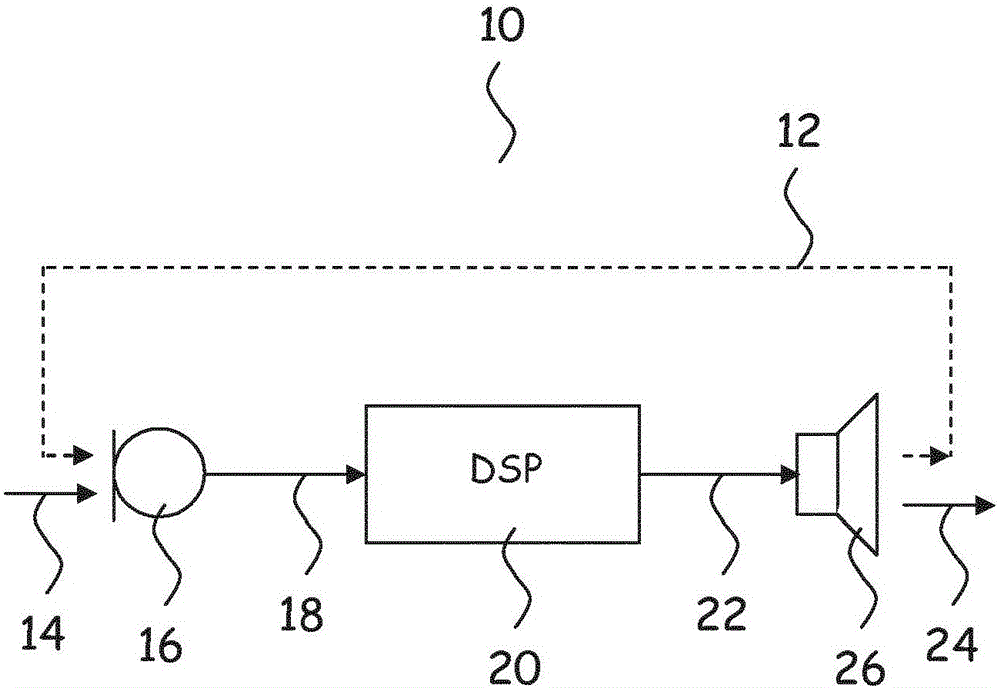
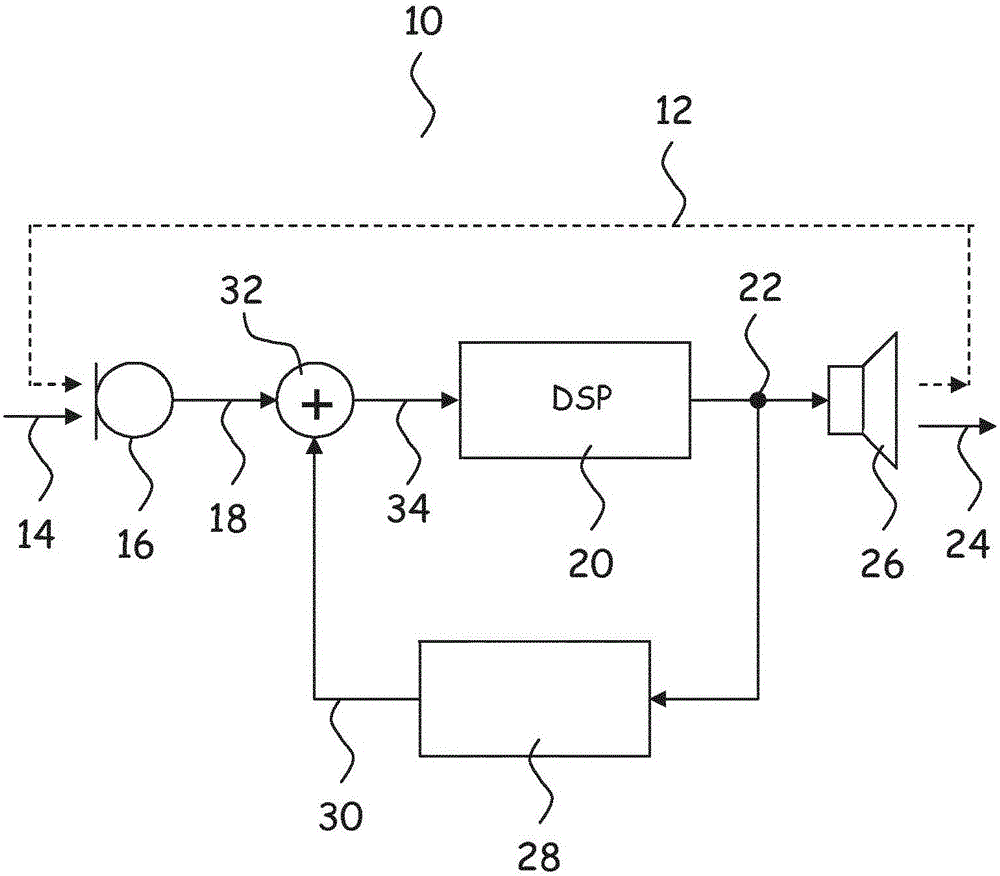
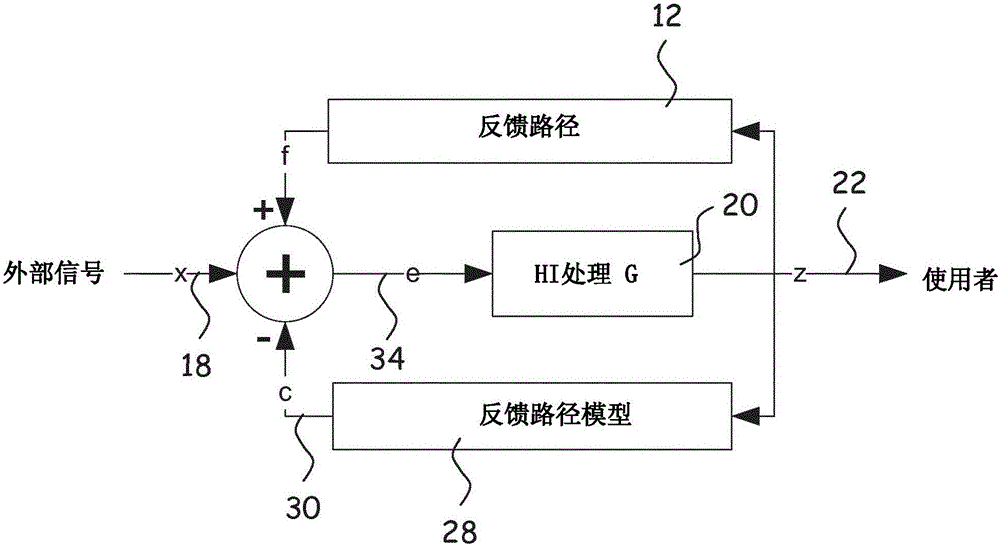
[0110] Various embodiments are described below with reference to diagrams. It should also be noted that the diagrams are only intended to help describe the embodiments. They are not intended as an exhaustive description of the invention or as a limitation on the scope of the invention. In addition, an illustrated embodiment does not require all aspects or advantages to be shown. An aspect or advantage described in conjunction with a particular embodiment is not necessarily limited to that embodiment and may be practiced in any other embodiment even if not so illustrated.
[0111] The new method and the new hearing aid according to the appended claims may be embodied in different forms not shown in the drawings and should not be construed as limited to the examples set forth herein. Like reference numerals refer to like elements throughout. Identical elements will therefore not be described in detail in connection with the description of the respective figures.
[0112] fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com