Method for efficiently reproducing brachymeria lasus by taking corcyra cephalonica pupae as hosts
A technology of rice moth pupae and leg wasps, applied in animal husbandry, etc., to save cumbersome steps, reduce the possibility of infection, and increase the effect of parasitism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] (1) Raising instead of the host: spread a layer of feed with a thickness of 1 cm in the plastic box (the feed ingredients are calculated in parts by weight from 50 parts of corn flour, 25 parts of flour, 20 parts of wheat bran, 3 parts of white sugar, and 2 parts of yeast. ); evenly sprinkle 1mL rice moth eggs on the feed, and then use a sieve to sprinkle a layer of feed that just covers the eggs; after 15 days, feed once every 3 days, and the amount of input is the food intake of larvae for 3 days; after larvae develop to 30 days, , spread two parallel nylon ropes on the surface of the feed, with both ends of the ropes exposed, and then bury the ropes in the feed when feeding; when the larvae cocoon and pupate, put the ropes together with the cocoon block Lift them together; take the rice moth pupae with cocoons on the rope and set aside;
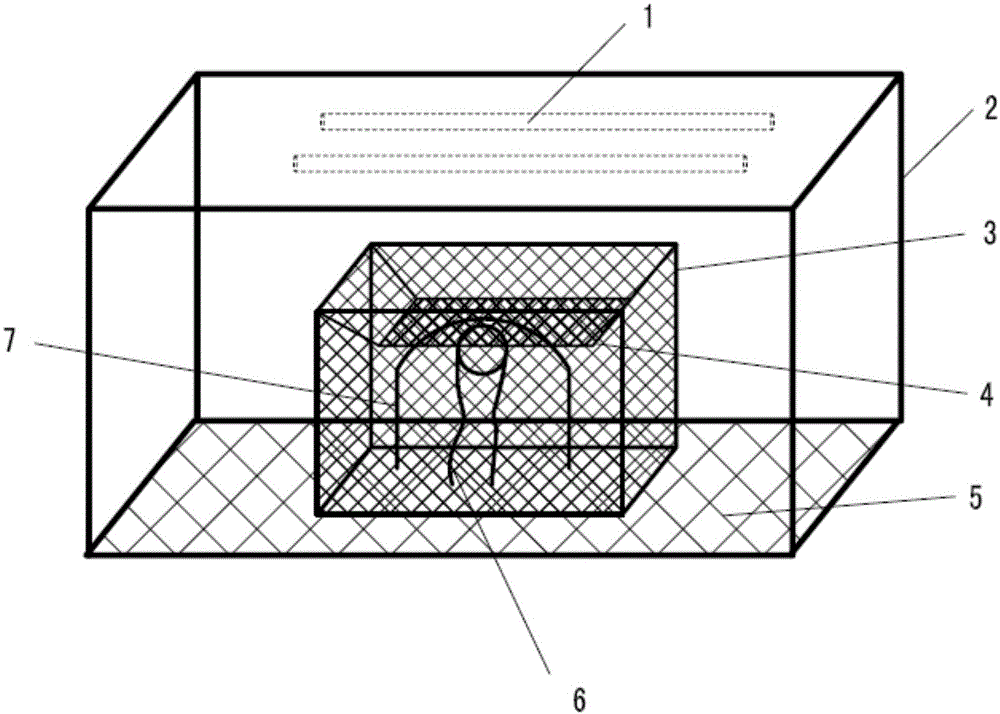
[0035] (2) Prepare numerous honeycomb cages: as figure 1 As shown, in the numerous bee chambers, the numerous bee cages 3 are pla...
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) Raising instead of the host: spread a layer of 1.5cm thick feed in a plastic box (the feed ingredients are calculated by weight by 50 parts of corn flour, 25 parts of flour, 20 parts of wheat bran, 3 parts of white sugar, and 2 parts of yeast. Sprinkle 1.5mL rice moth eggs evenly on the feed, and then use a sieve to sprinkle a layer of feed that just covers the eggs; after 15 days, feed once every 3 days, and the input amount is the food intake of larvae for 3 days; After 30 days, spread two parallel nylon ropes on the surface of the feed, and the two ends of the ropes are exposed, and when feeding thereafter, the ropes are buried in the material; Lift the cocoon block together; take the rice moth pupae with cocoons on the rope and set aside;
[0047] (2) Prepare numerous honeycomb cages: as figure 1 As shown, in the numerous bee chambers, the numerous bee cages 3 are placed on the insect racks 2 provided with lamp tubes 1 and barbed wire 5 at the top, and the nume...
Embodiment 3
[0058] (1) Raising instead of the host: spread a layer of 1-1.5 cm thick feed in a plastic box (the feed ingredients are calculated by weight by 50 parts of corn flour, 25 parts of flour, 20 parts of wheat bran, 3 parts of white sugar, and 2 parts of yeast. Sprinkle 1.3mL rice moth eggs evenly on the feed, and then use a sieve to sprinkle a layer of feed that just covers the eggs; after 15 days, feed once every 3 days, and the input amount is the food intake of larvae for 3 days; After 30 days of development, spread two parallel nylon ropes on the surface of the feed, and the two ends of the ropes are exposed, and when feeding thereafter, the ropes are buried in the material; when the larvae cocoon and pupate, the The rope is lifted together with the cocoon block; take the cocooned rice moth chrysalis on the rope and set aside;
[0059] (2) Prepare numerous honeycomb cages: as figure 1 As shown, in the numerous bee chambers, the numerous bee cages 3 are placed on the insect r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com