Device and method for transferring two-dimensional layered semiconductor material to diamond anvil cell
A diamond-to-anvil, two-dimensional layered technology, applied in the field of high-voltage devices, can solve the problems of narrow sample chamber, difficulty in cutting substrates, and influence of sample materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The overall structure of the device for transferring two-dimensional layered semiconductor materials to the diamond counter-anvil of the present invention is described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
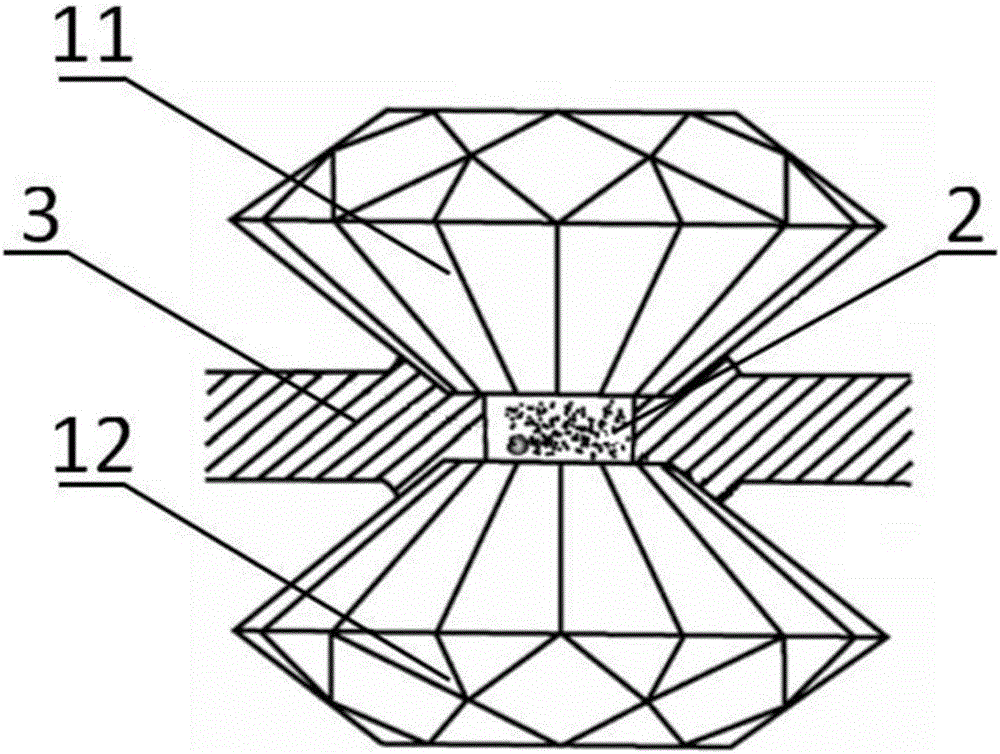
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, the diamond counter-anvil is composed of an upper anvil 11, a lower anvil 12, a sample chamber 2, and a metal spacer 3. The upper anvil 11 and the lower anvil 12 are two diamonds, and the metal spacer 3 is generally made of T-301 stainless steel. , There is also a ruby in the sample chamber 2 to calibrate the pressure.
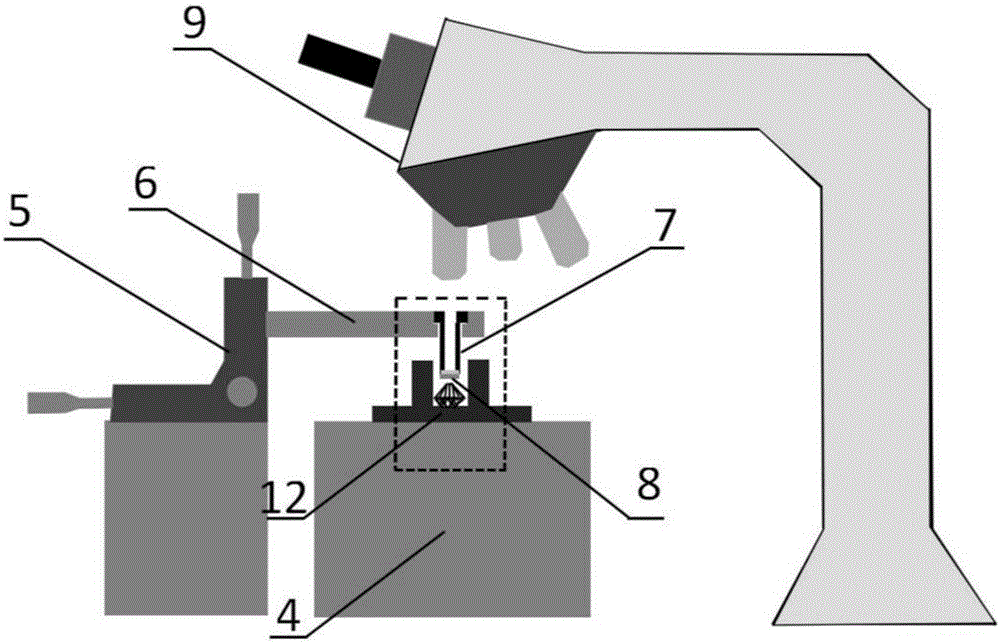
[0027] exist figure 2 Among them, the three-dimensional translation stage 5, the extension arm 6, the vertical shaft 7 and the glass plate 8 constitute the main body of the device for transferring two-dimensional layered semiconductor materials to the diamond anvil; the sample stage 4, optical microscope9.
[0028] Described three-dimensional translation platform 5 selects the three-dimensional translat...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2 transfers two-dimensional layered semiconductor material to DAC
[0030] To transfer the two-dimensional layered semiconductor material into the DAC, the sample material can be directly adhered to the anvil surface of the lower anvil 12 within the sample cavity, and then the diamond is reset so that the sample material is in the sample cavity.
[0031] The adhesive film substrate with the sample of interest is attached to the outer surface of the glass slide 8 at the bottom of the shaft 7 . Such as figure 2 , put the lower anvil 12 on the sample stage 4, use the optical microscope 9 to find the anvil surface of the lower anvil, and move the target position where the target sample is to be transferred to the center of the field of view of the optical microscope 9. The shaft 7 is first positioned above the lower anvil 12, and the adhesive film substrate with the sample is not in contact with the lower anvil 12. Adjust the focal length of the optical micros...
Embodiment 3
[0033]Example 3 Transfer of monolayer MoSe to piston cylinder DAC 2 sample
[0034] In the first step, monolayer MoSe was prepared on the adhesive film substrate by mechanical exfoliation method 2 sample. First cut the adhesive film substrate (model: Gel-Pak PF-30-X4) into 1.5cm 2 Area-sized squares, remove the front and rear protective films, and attach to a clean glass slide. Then a piece of MoSe 2 Put the body material into the tape (Nitto SPV224s), fold and tear the tape in half repeatedly until a layer of samples is evenly distributed on the tape. Cover the tape on the film substrate and tear off the tape. It can be observed that a lot of MoSe remains on the film substrate. 2 Material. Put the film substrate under the optical microscope 9 (eyepiece: 10X objective lens: 50X) to find the sample. After finding the target sample, you can directly perform Raman spectrum characterization and photofluorescence characterization on the film substrate. It is determined that t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com