An integral main cable saddle and single tower self-anchored cable-stayed-suspension system bridge
An integral main cable saddle and self-anchoring technology, used in bridges, bridge parts, bridge construction, etc., can solve the problems of restricted operation, heavy towers, and small internal space, avoiding stress concentration and optimizing structural force. , the effect of improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
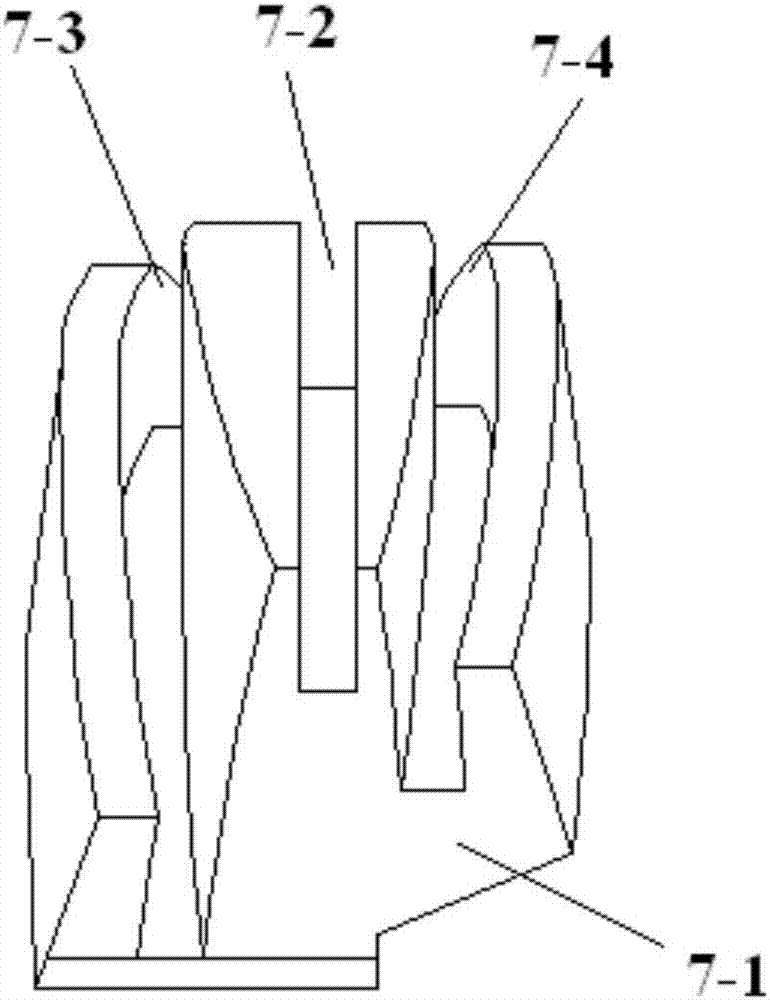
[0057] Comply with the above technical solutions, such as Figure 2 to Figure 4 As shown, the present embodiment provides an integral main cable saddle, including a saddle 7-1, and three cable grooves are processed side by side on the back of the saddle 7-1, the middle is a far section cable groove 7-2, and the far end is The two sides of the cable groove 7-2 are the middle cable groove 7-3 and the proximal cable groove 7-4;
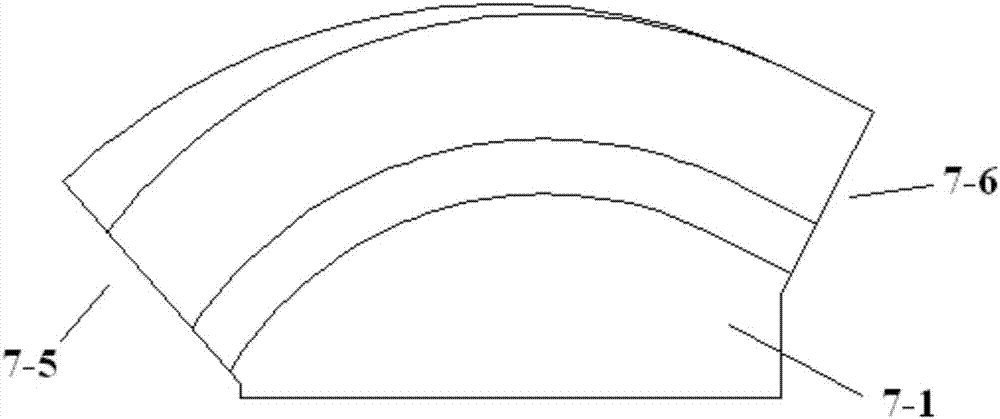
[0058] The groove bottom shape lines of the far section cable groove 7-2, the middle section cable groove 7-3 and the near section cable groove 7-4 are arcs, and the three centers of the three arcs are on the same straight line. The straight lines where the three centers of circles are located are the intersecting lines of the end face of the cable entry end 7-5 of the saddle 7-1 and the vertical plane;
[0059] The projections of the end points of the three arcs on the end face of the cable entry end 7-5 coincide in the vertical plane, and the arc radi...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Comply with the above technical solutions, such as Figure 2 to Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment provides an integral main cable saddle, the main structure is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the only difference is that in this embodiment:
[0062] The relationship between the arc radius of the middle section cable groove 7-3 and the arc radius of the far section cable groove 7-2 is:
[0063]
[0064] The relationship between the arc radius of the near section cable groove 7-4 and the arc radius of the far section cable groove 7-2 is:
[0065]
[0066] In the formula:
[0067] R 1 is the arc radius of the bottom shape line of the cable groove at the far section, R 2 is the arc radius of the bottom shape line of the cable groove in the middle section, R 3 is the arc radius of the bottom shape line of the cable groove in the near section;
[0068] H is the height of the bridge tower;
[0069] d is the distance between the anchor points of the side-span stay...
Embodiment 3
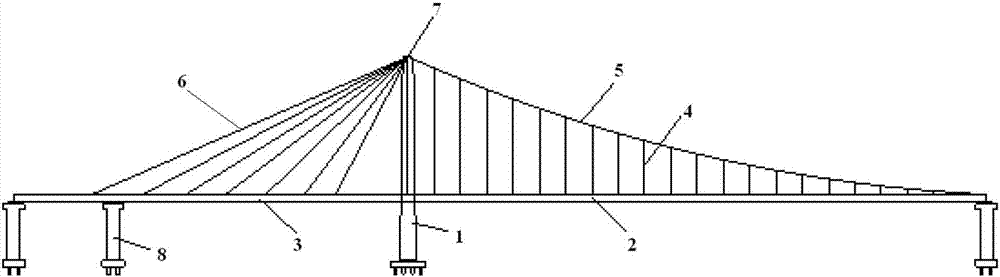
[0077] Comply with the above technical solutions, such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a single-tower self-anchored cable-stayed-suspension cooperative bridge, including a bridge tower 1, one side of the bridge tower 1 is the main span main beam 2, and the other side of the bridge tower 1 is a side span The main girder 3, the main span main girder 2 is hoisted on the main span main cable 5 by the main span sling 4, and the side span main girder 3 is suspended and hoisted by the side span stay cables 6;
[0078] Described main span main cable 5 and side-span stay cable 6 are a whole cable, bridge tower 1 top is equipped with integral main cable saddle 7, and main span main cable 5 passes through integral main cable saddle 7 and turns cable and The scatter cable is a multi-strand side-span stay cable 6;
[0079] The structure of the integral main cable saddle 7 is the same as that in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
[0080] The distance between the anchor point o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com