Defending method for malicious request packet of interest attacks in NDN (Named Data Networking)
An interest packet and malicious technology, applied in security devices, network traffic/resource management, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as low node work efficiency, suppression of normal requesting user network access capabilities, normal user performance constraints, etc., to ensure the overall Reliability, the effect of reducing the packet loss rate of request interest packets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The technical solution of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
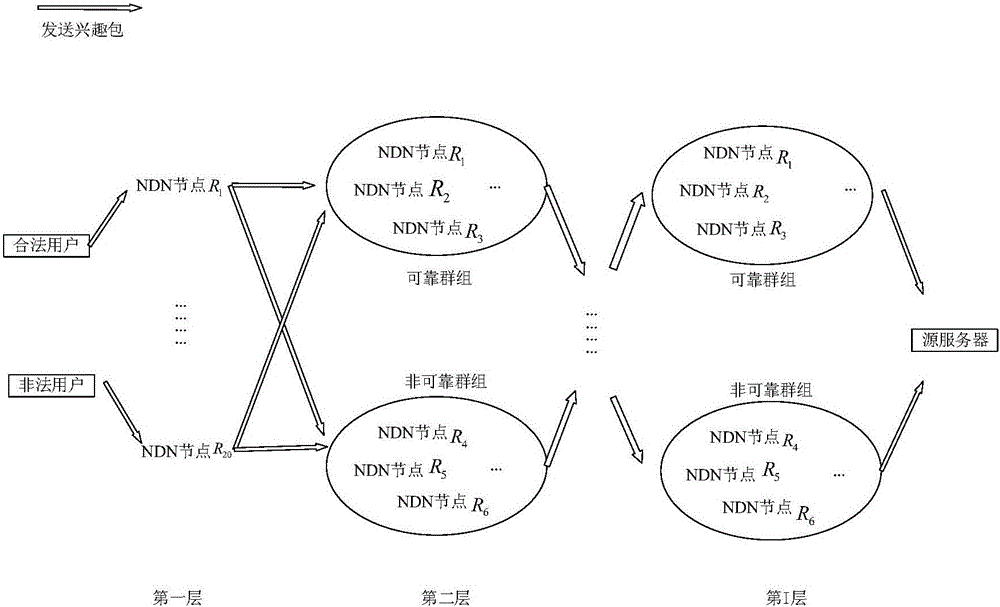
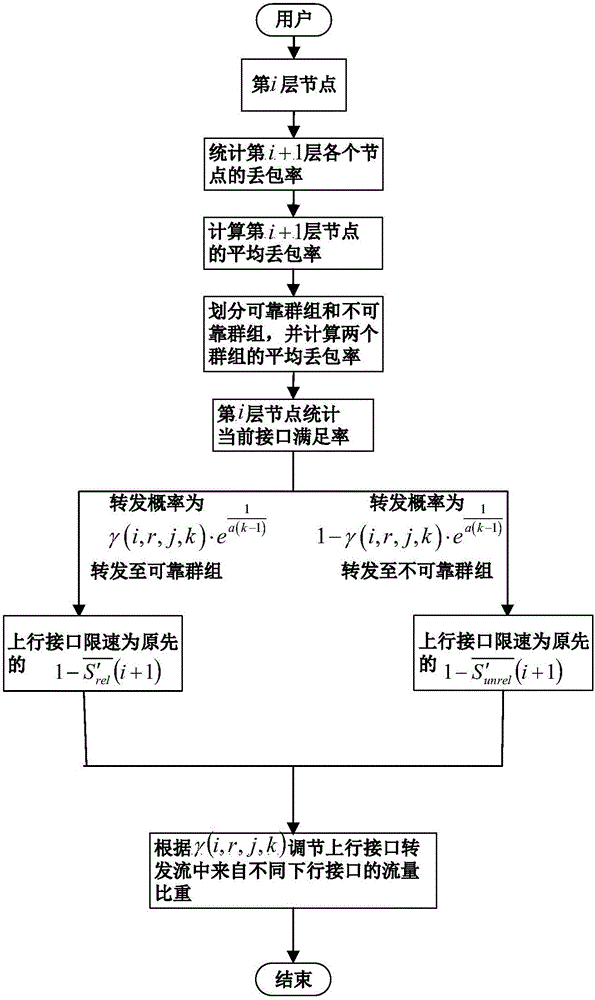
[0031] Assuming an NDN network scenario such as figure 1 As shown, the network topology is set to a 5-layer structure, each layer of the network has 20 nodes, and each node has 10 downlink interfaces. The data source can provide a total of 5000 contents, which can be divided into 50 categories according to the popularity of the contents, that is, each category contains 100 contents, and the ratio of the cache size to the total amount of network contents is 0.01. The cache replacement strategy adopts the least recent replacement strategy (LRU). The request Interest packet sent by the user obeys the Zipf-like distribution of α=1.2, and the arrival rate of the interface routing node user request Interest packet is 10 4 pieces / second, the average network round-trip delay for content acquisition is 8ms, the entry survival time of the rou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com