Permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor assembly and permanent magnet synchronous motor
A technology for permanent magnet synchronous motors and components, which is applied to synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, etc., and can solve the problem of back electromotive force and air gap magnetic density High, application limitations of permanent magnet synchronous motors, ring magnet 3" cracking and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving back electromotive force and air gap flux density, preventing ring magnet cracking, and improving reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
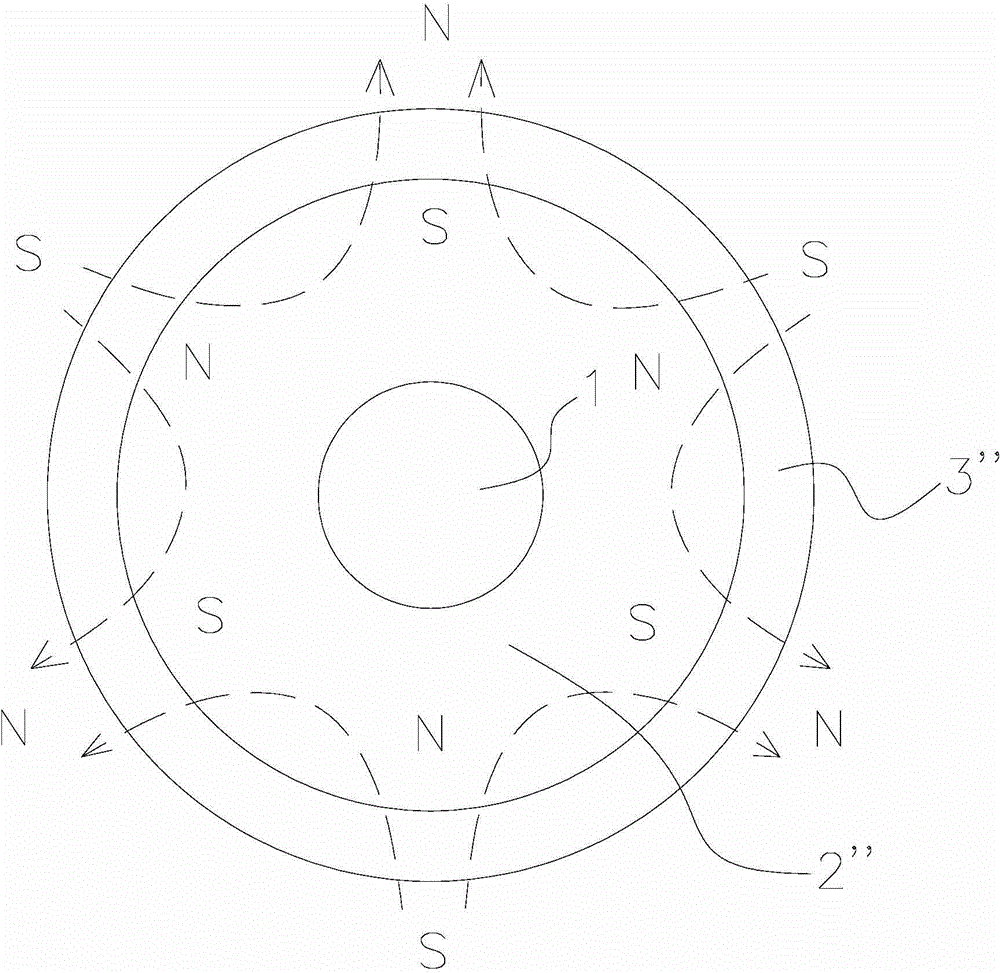
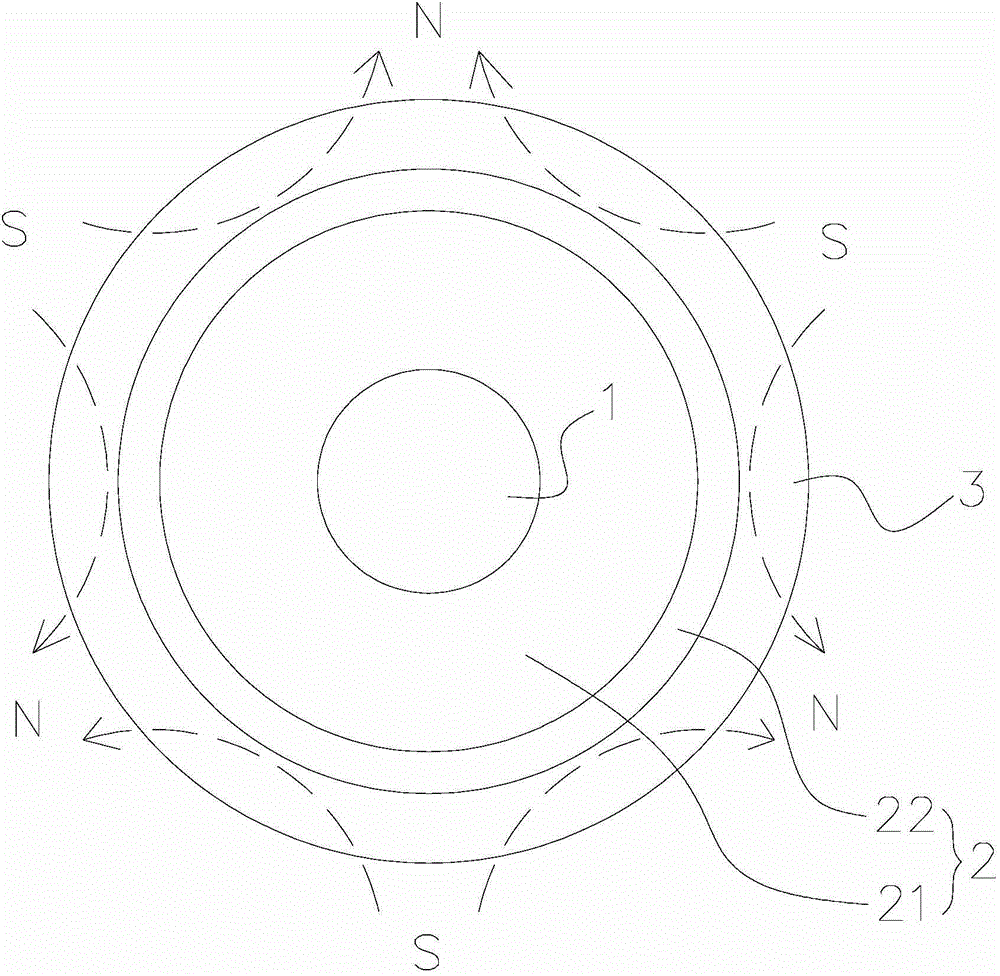
[0040] like figure 2 and image 3 As shown, it respectively shows a cross-sectional view and a longitudinal cross-sectional view of the rotor assembly of the permanent magnet synchronous motor of the present invention. Wherein, the cross-sectional view refers to a sectional view along the radial direction of the rotor assembly, and the longitudinal sectional view refers to a sectional view along the axial direction of the rotor assembly. exist figure 2 and image 3 In the preferred embodiment shown, the rotor assembly of the permanent magnet synchronous motor of the present invention includes: a rotating shaft 1 , a rotor yoke 2 and a multi-pole magnetic ring 3 .
[0041] The rotor yoke 2 is disposed around the outer periphery of the rotating shaft 1 . exist figure 2 and image 3 In the preferred example shown, the rotor yoke 2 includes a magnetically permeable portion 21 and a non-magnetically permeable portion 22 . The magnetically permeable part 21 is disposed aro...
no. 2 example
[0048] See Figure 7 , which shows a cross-sectional cross-sectional view of the rotor assembly of the permanent magnet synchronous motor of the second embodiment of the present invention. like Figure 7 As shown, the rotor assembly includes a rotating shaft 1 , a rotor yoke 2 and a multi-pole magnetic ring 3 . with the above figure 2 and image 3 The difference between the first embodiment shown in the above is that the rotor yoke part 2' only includes a non-magnetically conductive part 22' (excluding a magnetically conductive part), that is, the entire rotor yoke part 2' is made of a material that is flexible and cannot conduct magnetic fields (including but not limited to nitrile rubber material). Since the magnetic field lines of the magnetic field formed after the multi-pole magnetic ring 3 is magnetized rarely pass through the rotor yoke part in the multi-pole magnetic ring 3, the magnetic conducting part of the rotor yoke part plays a very small role. Therefore, in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com