Hyperspectral Image Classification Method Based on 3D Non-local Mean Filtering
A hyperspectral image, non-local mean technology, applied in the field of remote sensing image processing, can solve problems such as easy generation of errors, affecting classification accuracy, application of non-local mean filtering to hyperspectral data, etc., to simplify the process and improve the classification accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
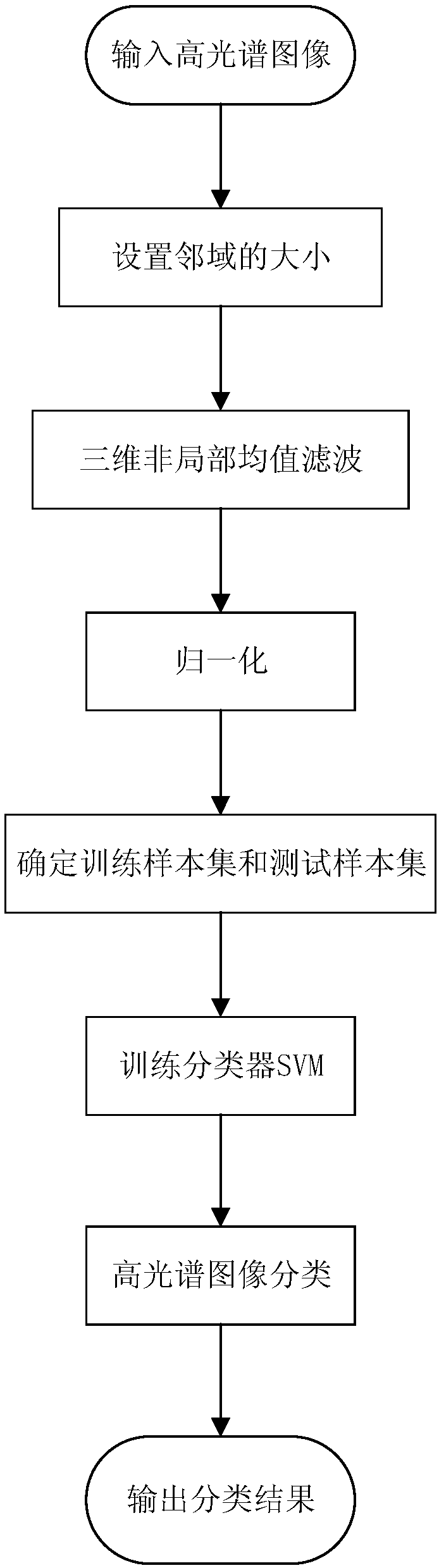
[0029] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0030] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0031] Step 1, input 3D hyperspectral image data with category labels.
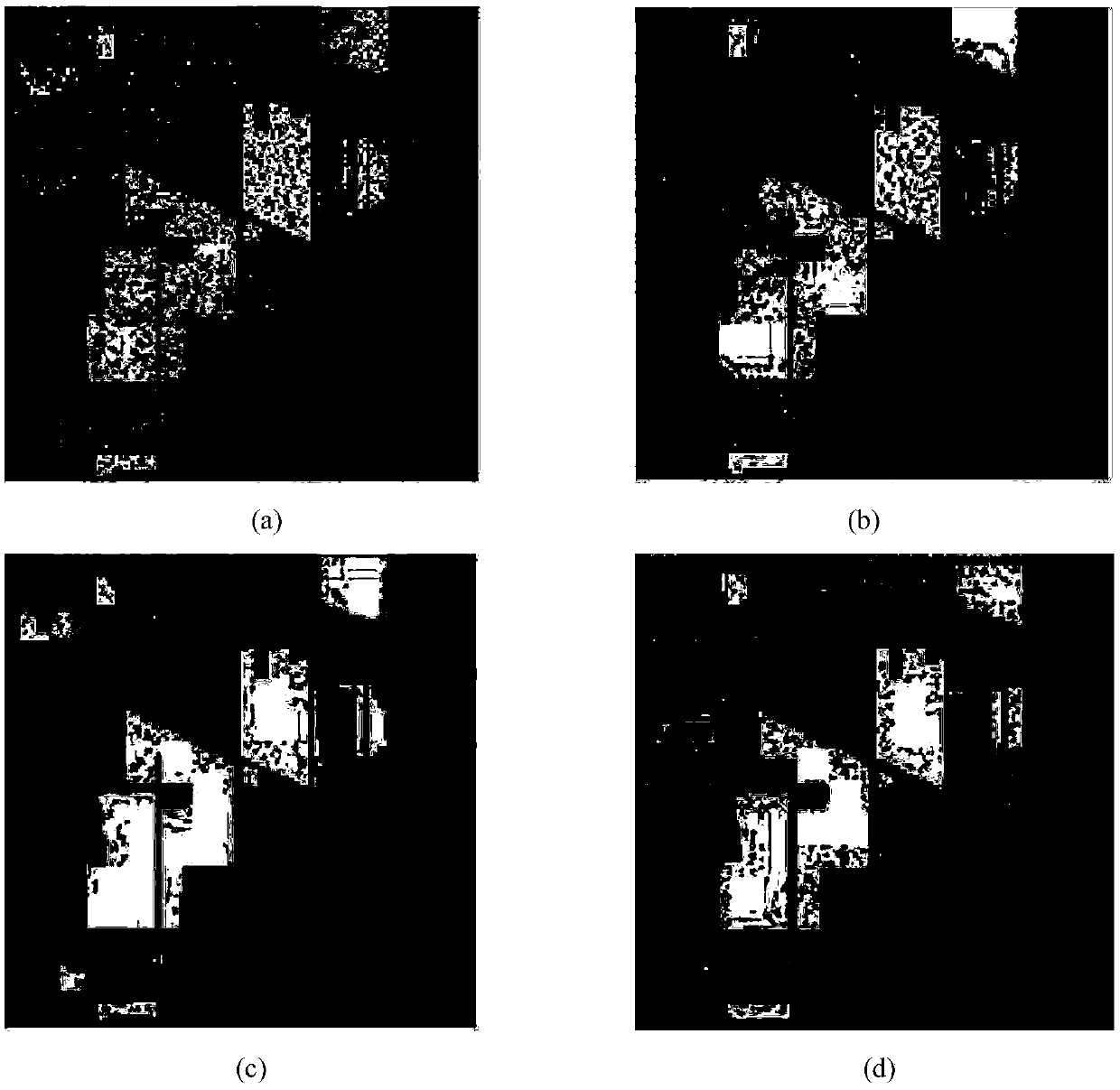
[0032] 1.1) Input the three-dimensional hyperspectral image data to be classified and its category label. The hyperspectral image contains k categories in total, each category contains several pixels, and the size of the input hyperspectral image is m×n×d, where, d represents the total number of spectral bands of the hyperspectral image, m and n represent the number of rows and columns in the two-dimensional space, respectively, and N=m×n represents the total number of pixels;
[0033] 1.2) Express the pixel set of the hyperspectral image as X=[x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x s ,...,x N ], where x s Represents the pixel of the sth point after being arranged in two-dimensional spatial columns in the hyperspectral ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com