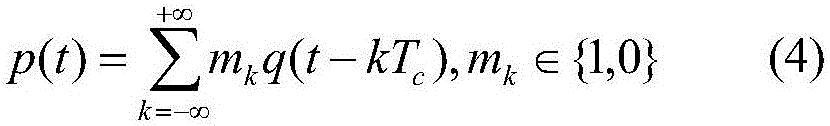M-sequence pseudo random interleaving identification method in non-cooperated condition
A recognition method, m-sequence technology, applied in the field of communication signal recognition, can solve problems such as difficulty in recognition of interleaved permutation relations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
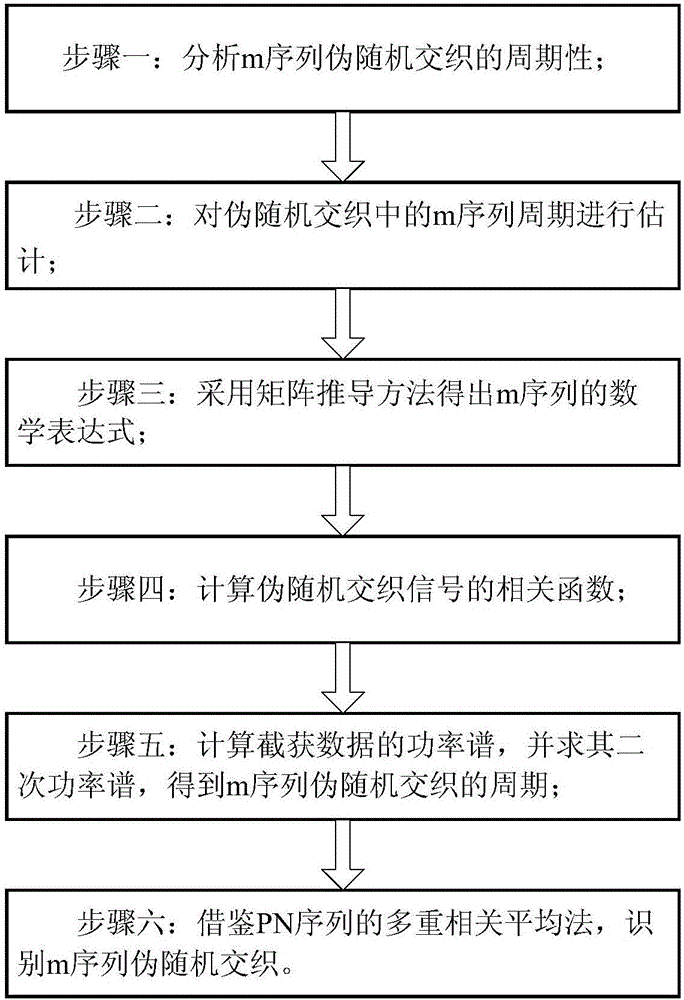
[0089] Embodiment 1: see figure 1 , an m-sequence pseudo-random interleaving identification method under a non-cooperative condition, which includes the following steps:
[0090] Step 1: analyzing the periodicity of m-sequence pseudo-random interleaving;
[0091] The structure of the m-sequence generator is a high-speed linear feedback shift register generator. By analyzing the structure of the generator, it can be obtained that the feedback connection is determined by the polynomial (1):
[0092] g(D)=1+g 1 D+g 2 D. 2 +…+g r D. r (1)
[0093] Its output is:
[0094]
[0095] where D is the unit delay variable, its power represents the delay, g i Selected from the set {0,1}, a(D) represents the initial state of the shift register;
[0096] If g(D) is a primitive polynomial, then the sequence generated by the high-speed linear feedback shift register has a maximum length, derived as follows:
[0097] Each of the possibilities loaded into the high-speed linear feed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com