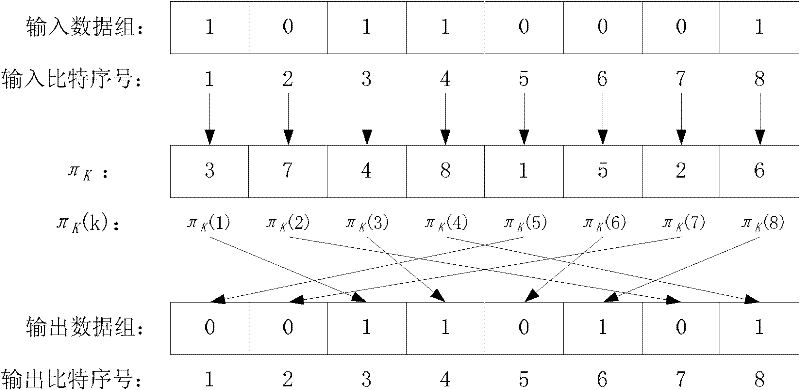
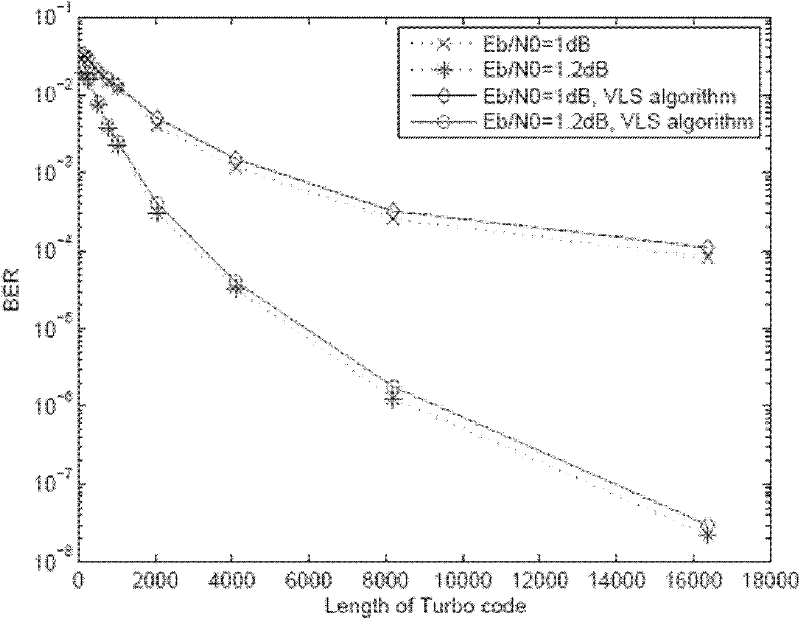
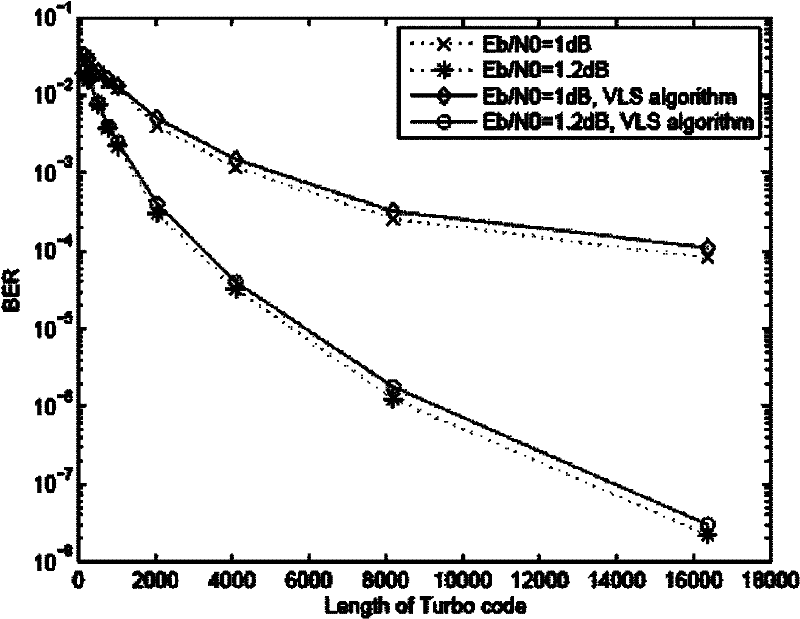
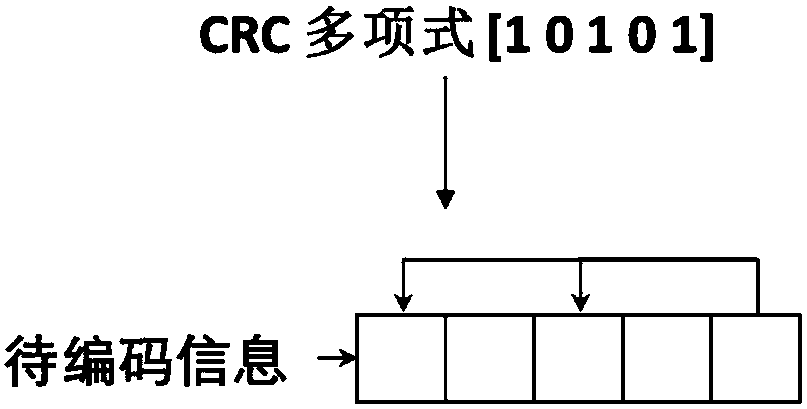
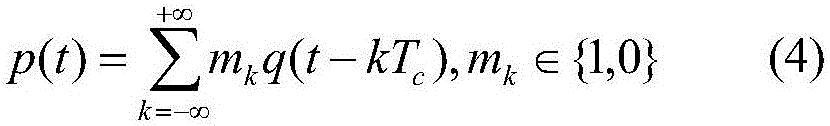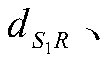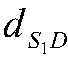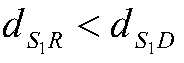Patents
Literature
70 results about "Interleave sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, an interleave sequence is obtained by merging two sequences via an in shuffle.
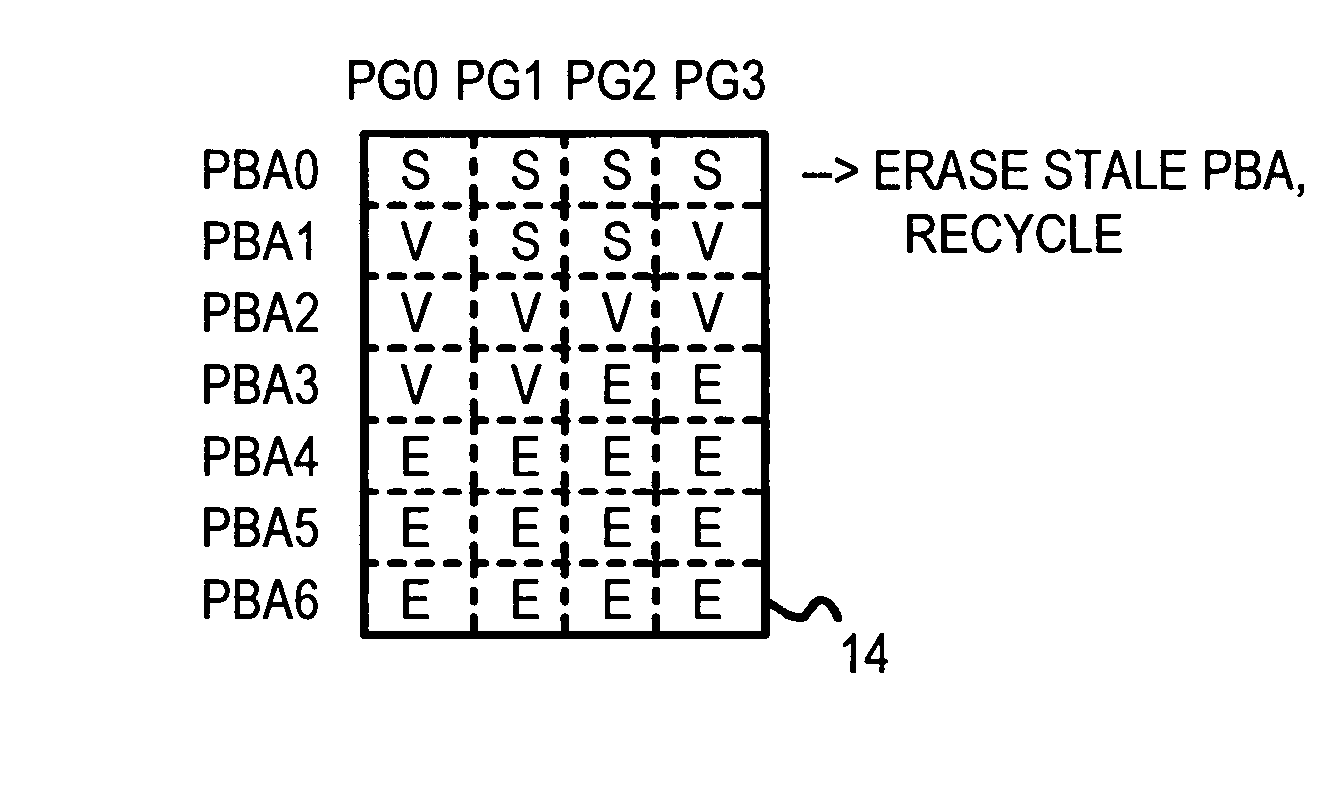
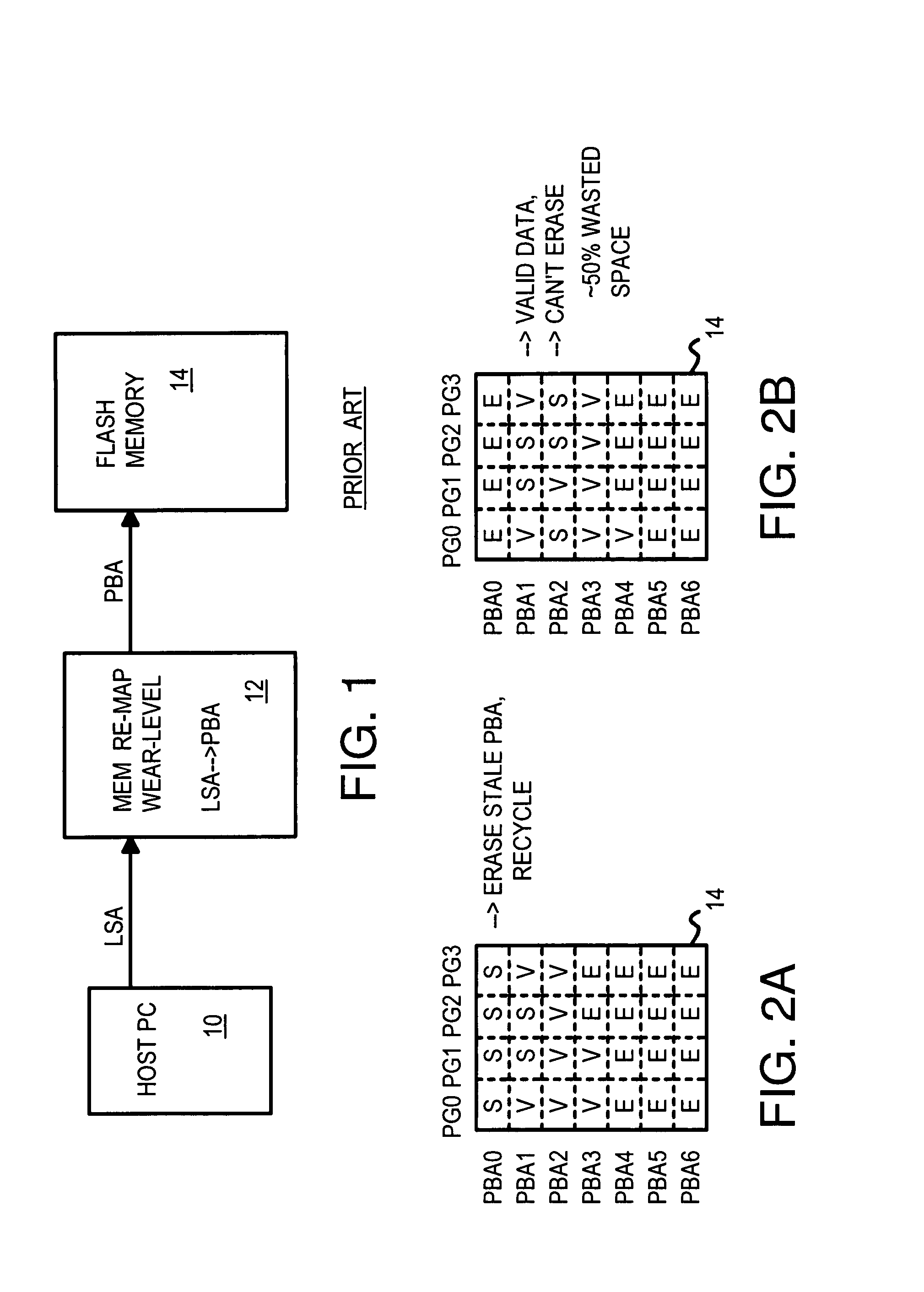
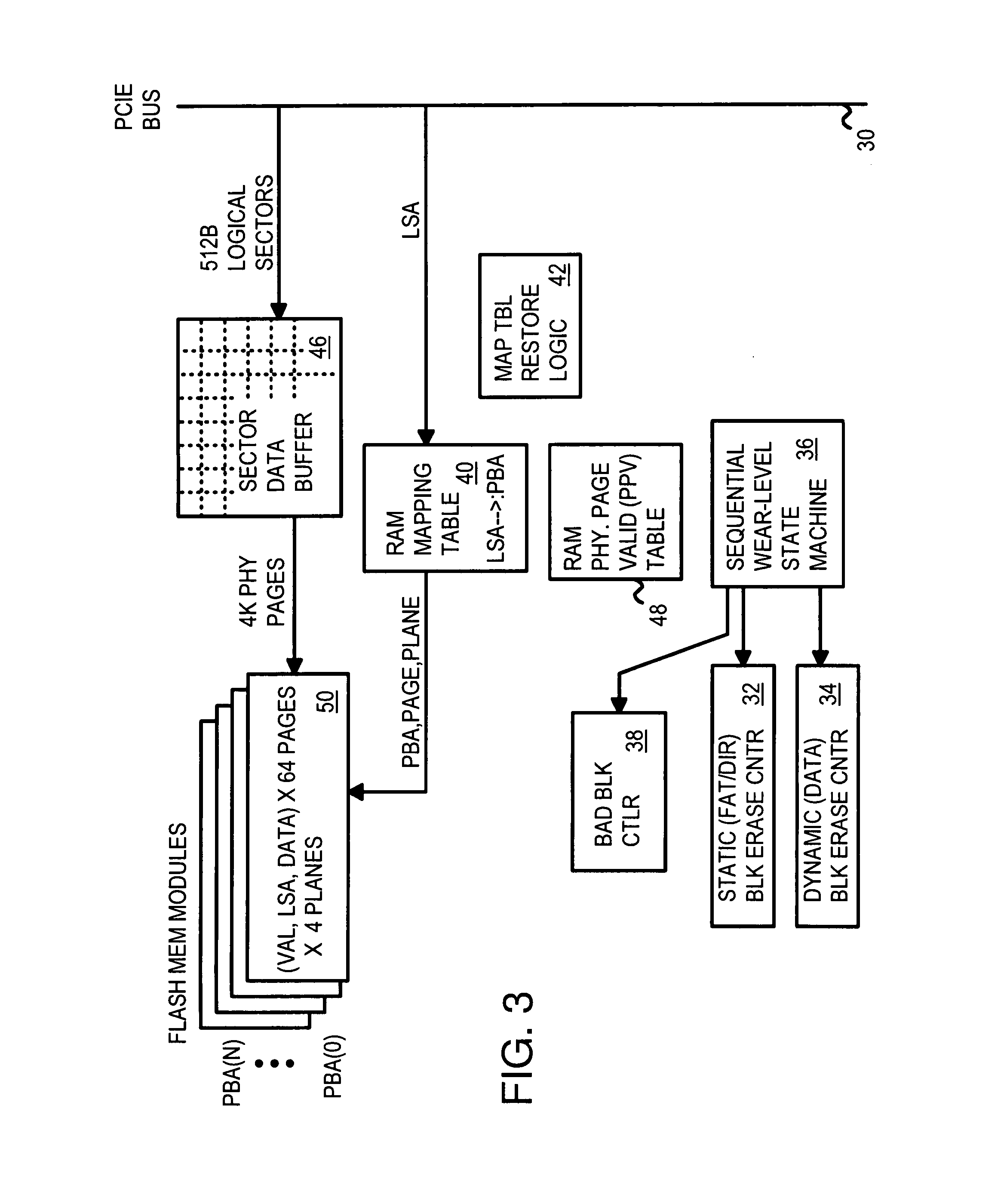
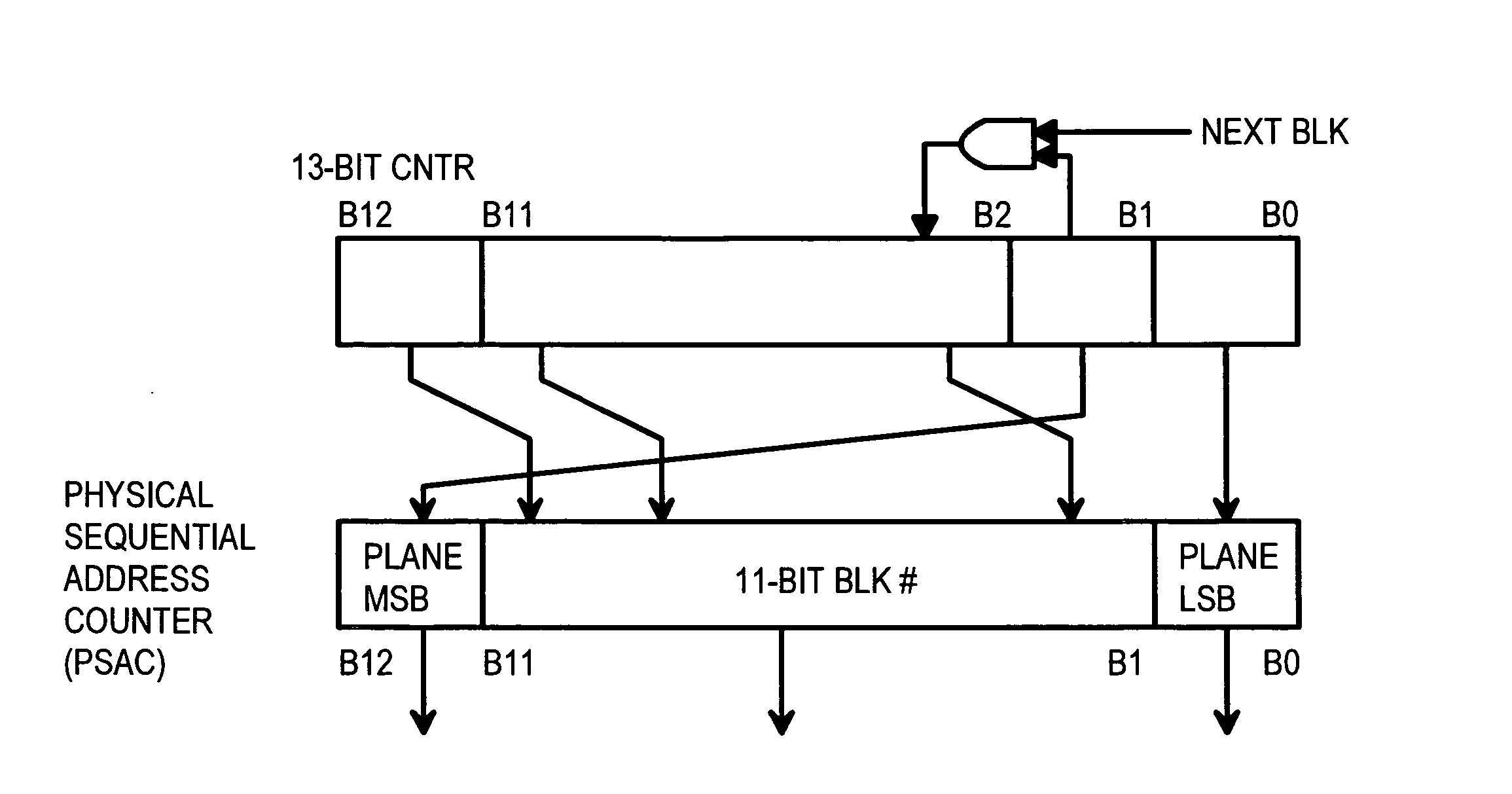
Multi-Channel Flash Module with Plane-Interleaved Sequential ECC Writes and Background Recycling to Restricted-Write Flash Chips
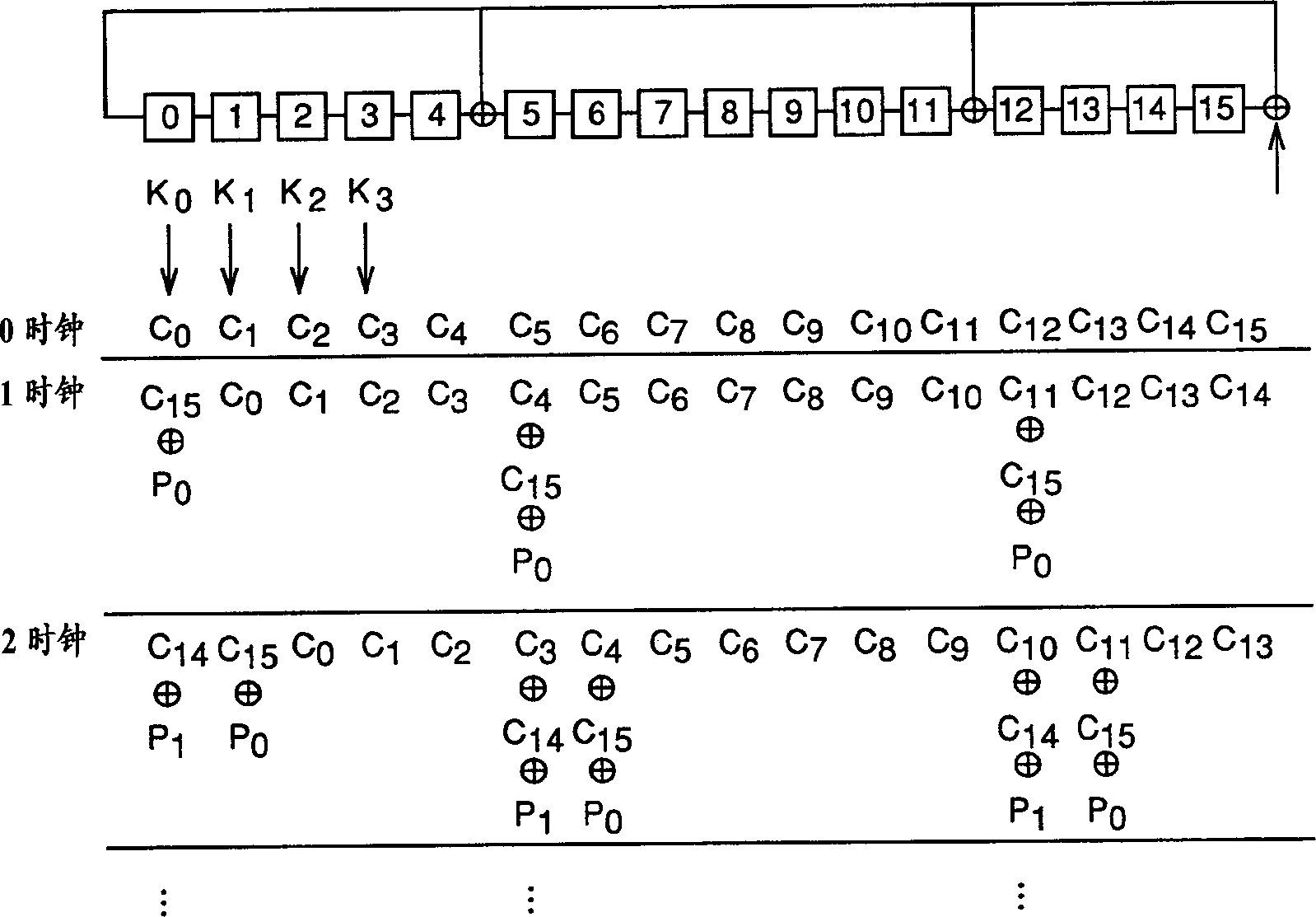
InactiveUS20080034154A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesInterleave sequenceBlock number
A RAM mapping table is restored from flash memory using plane, block, and page addresses generated by a physical sequential address counter. The RAM mapping table is restored following a plane-interleaved sequence generated by the physical sequential address counter using interleaved bits extracted from the lowest bits of the logical block index. These plane-interleave bits are split into a LSB and a MSB, with middle physical block bits between the LSB and MSB. The physical sequential address counter generates a physical block number by incrementing the plane-interleave bits before the middle physical block bits, and then relocating the MSB to above the middle physical block bits. This causes blocks to be accessed in a low-high sequence of 0, 1, 4096, 4097, 2, 3, 4098, 4099, etc. in the four planes of flash memory. Background recycling and ECC writes are also performed.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
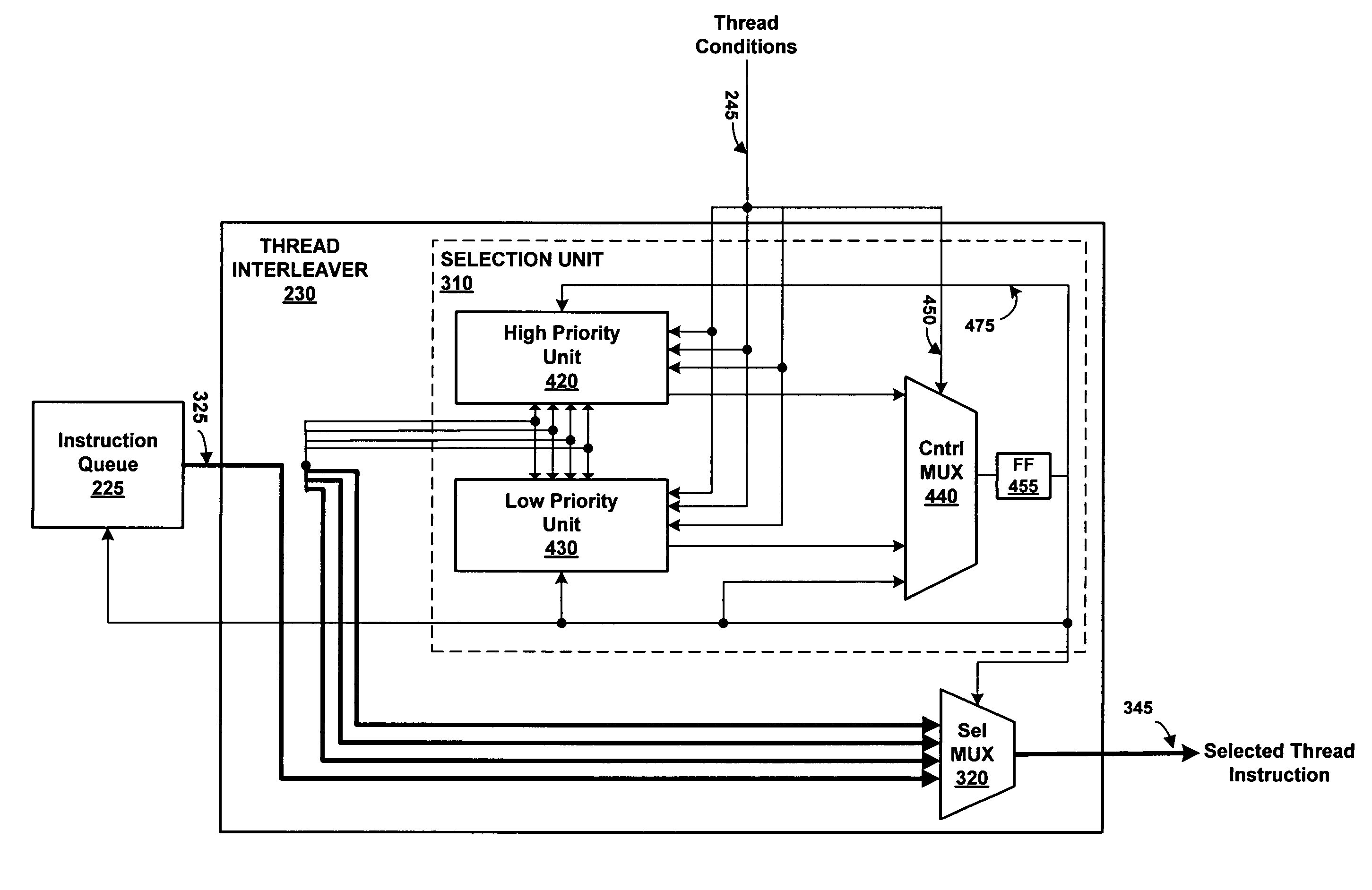
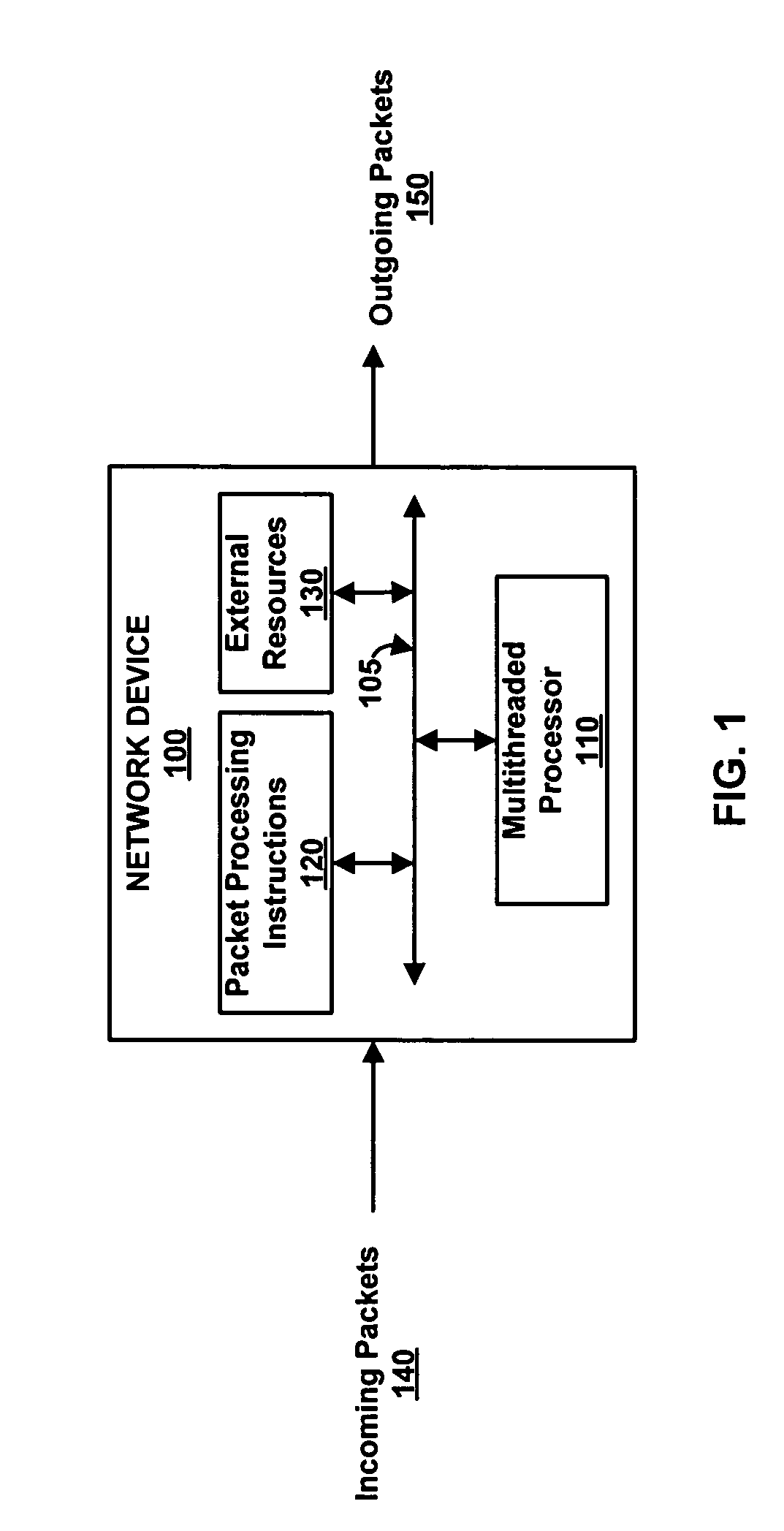
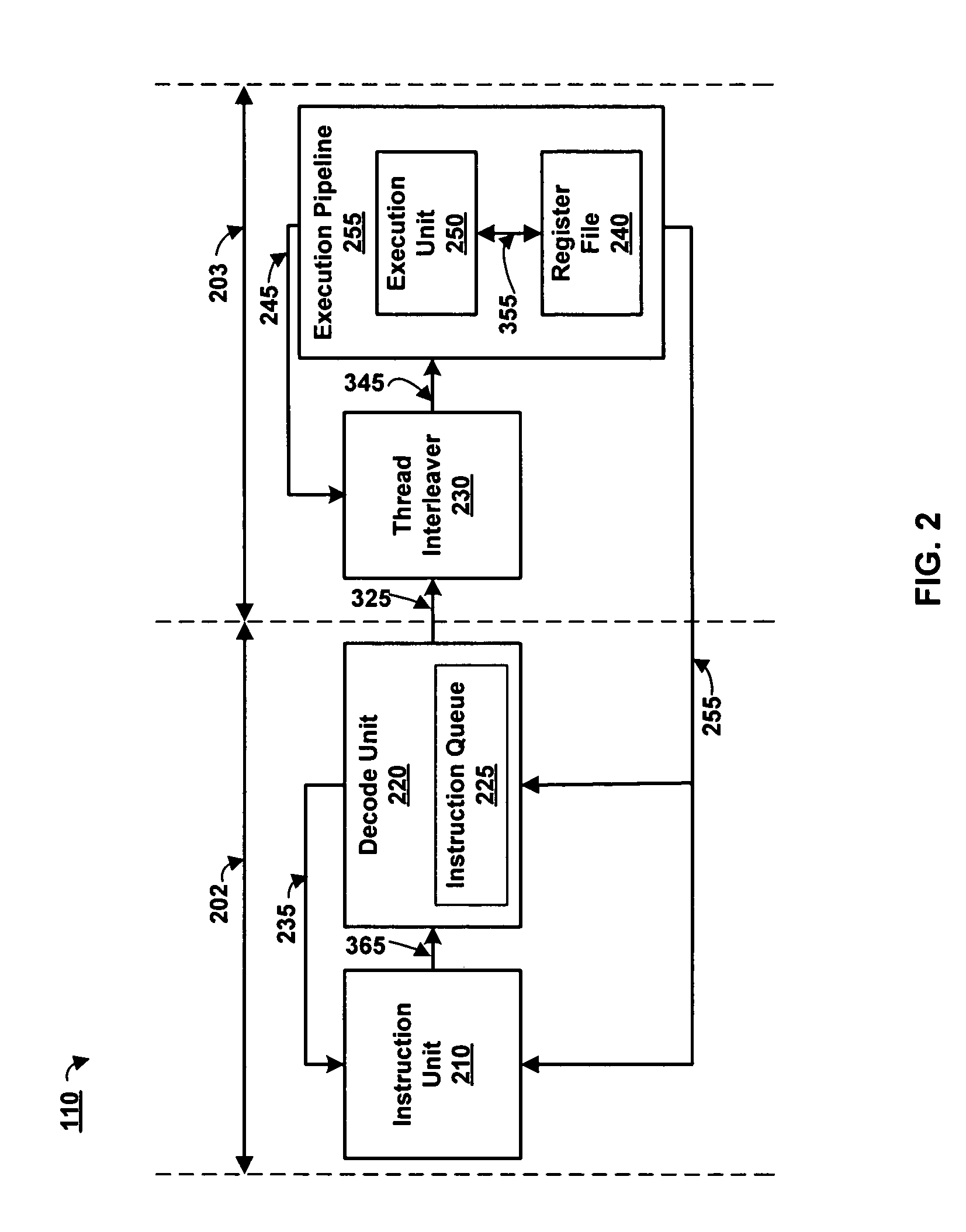
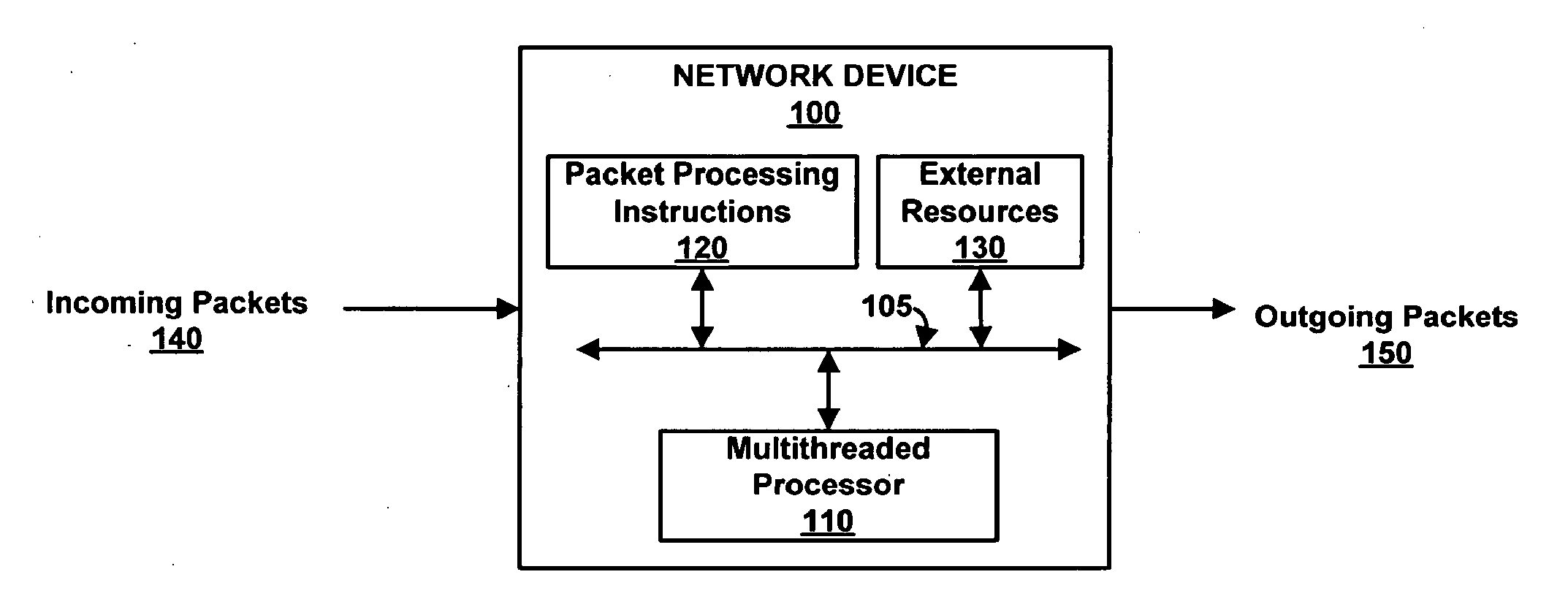
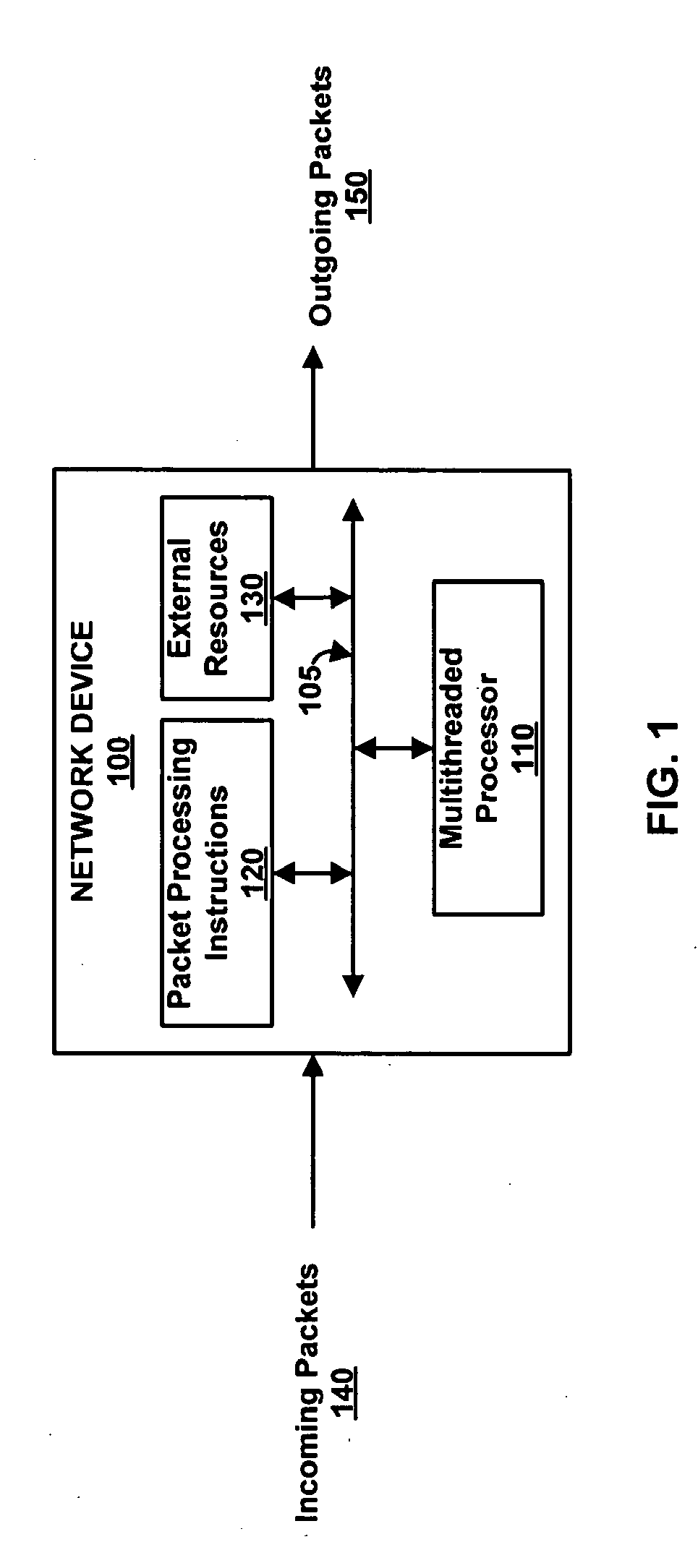
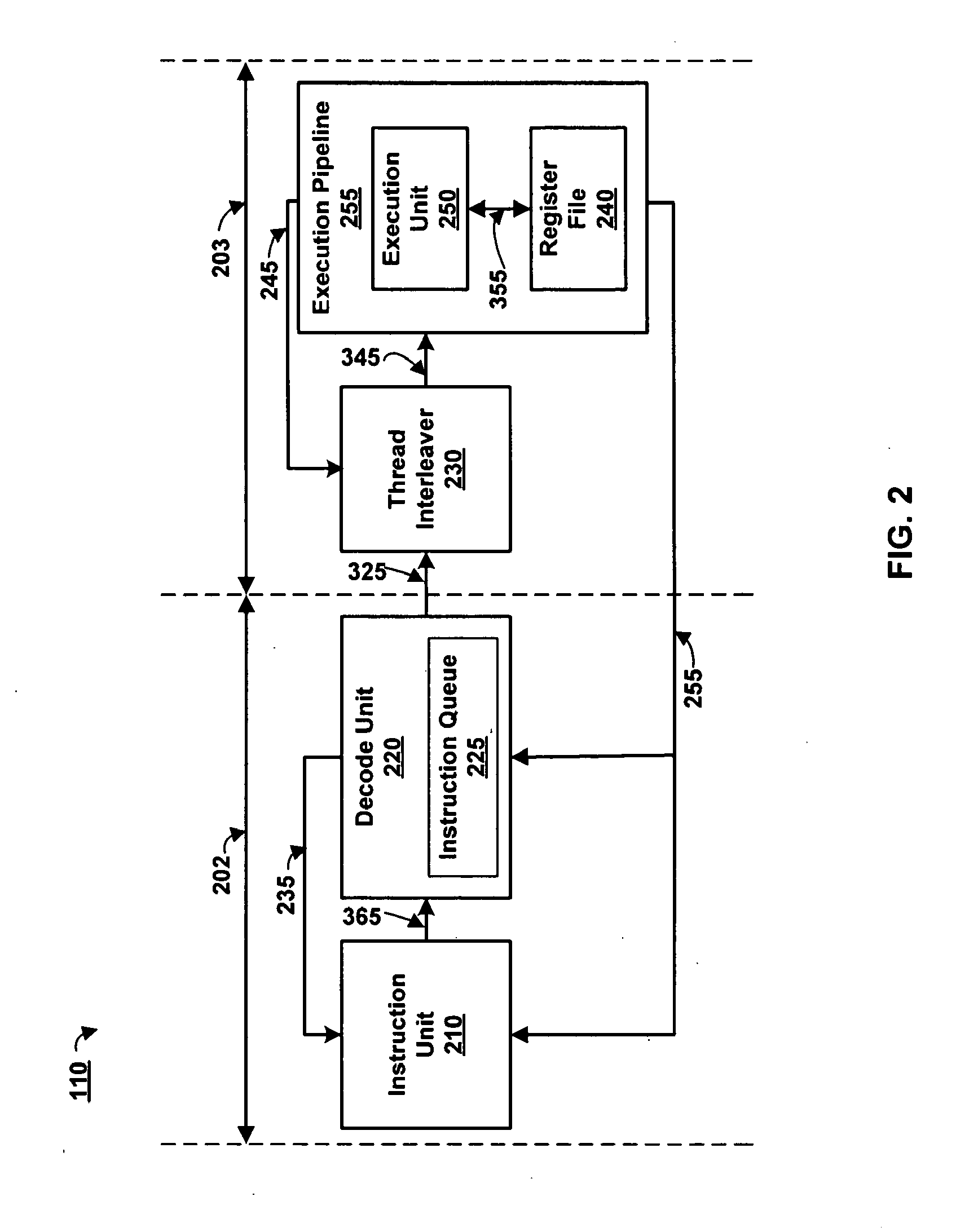
Thread interleaving in a multithreaded embedded processor
InactiveUS7360064B1Improves processor utilizationImprove performanceDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionTime conditionInstruction unit
The present invention provides a network multithreaded processor, such as a network processor, including a thread interleaver that implements fine-grained thread decisions to avoid underutilization of instruction execution resources in spite of large communication latencies. In an upper pipeline, an instruction unit determines an instruction fetch sequence responsive to an instruction queue depth on a per thread basis. In a lower pipeline, a thread interleaver determines a thread interleave sequence responsive to thread conditions including thread latency conditions. The thread interleaver selects threads using a two-level round robin arbitration. Thread latency signals are active responsive to thread latencies such as thread stalls, cache misses, and interlocks. During the subsequent one or more clock cycles, the thread is ineligible for arbitration. In one embodiment, other thread conditions affect selection decisions such as local priority, global stalls, and late stalls.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
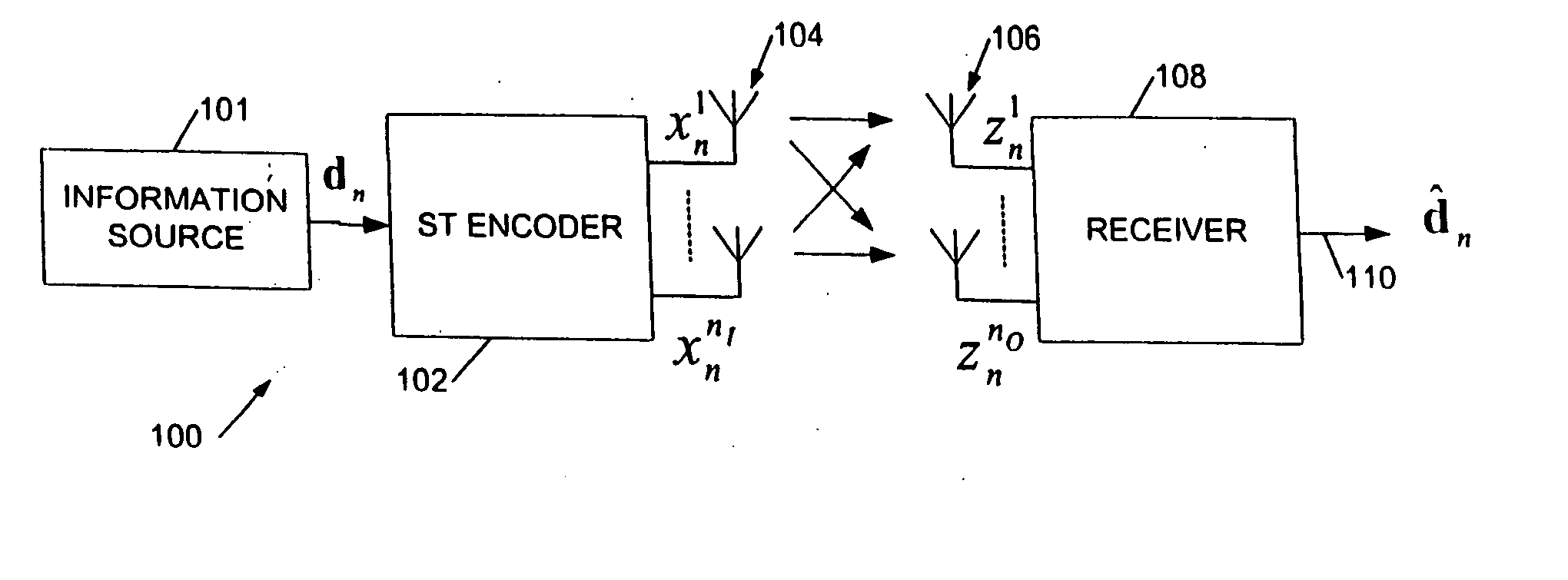
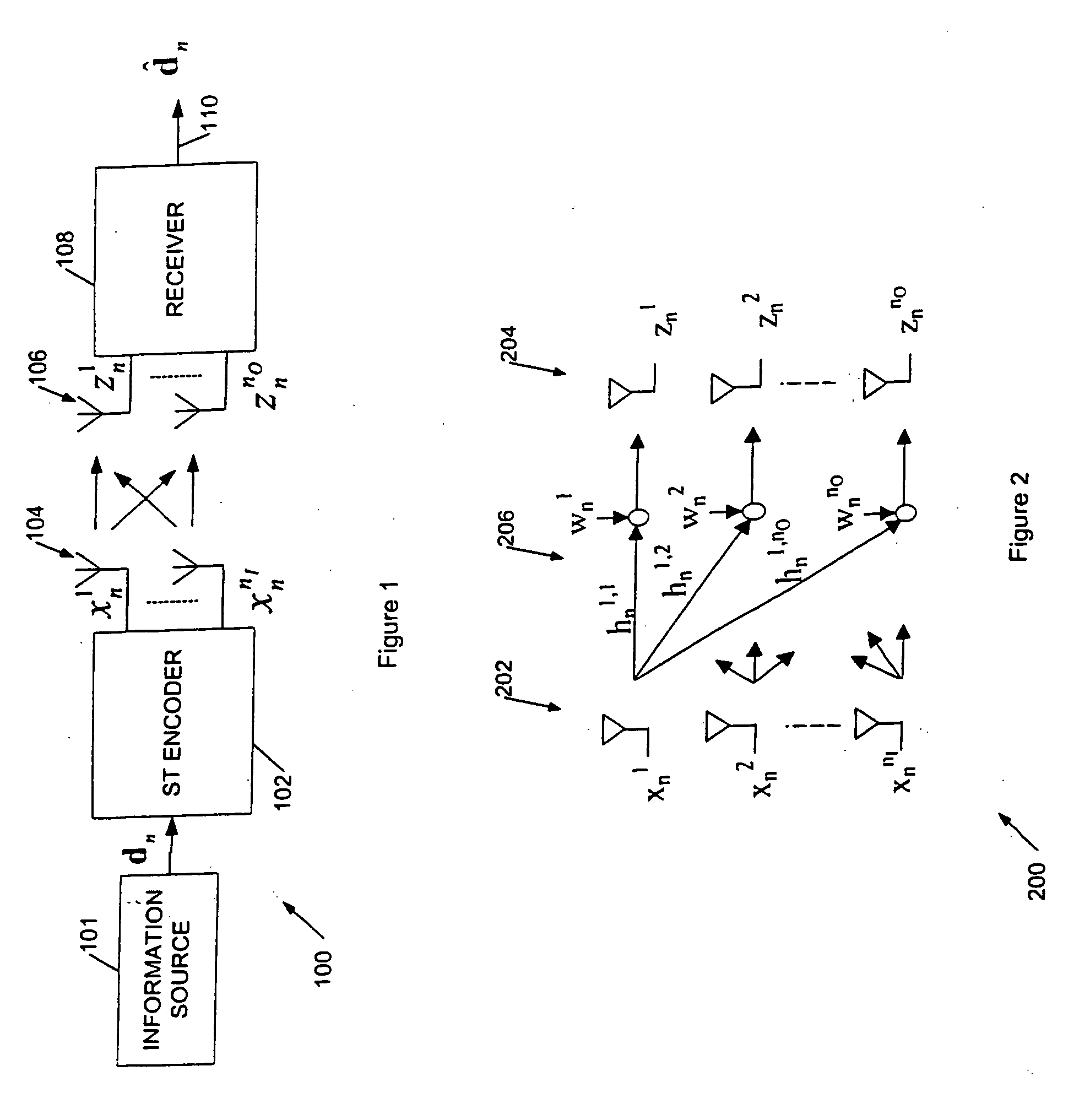
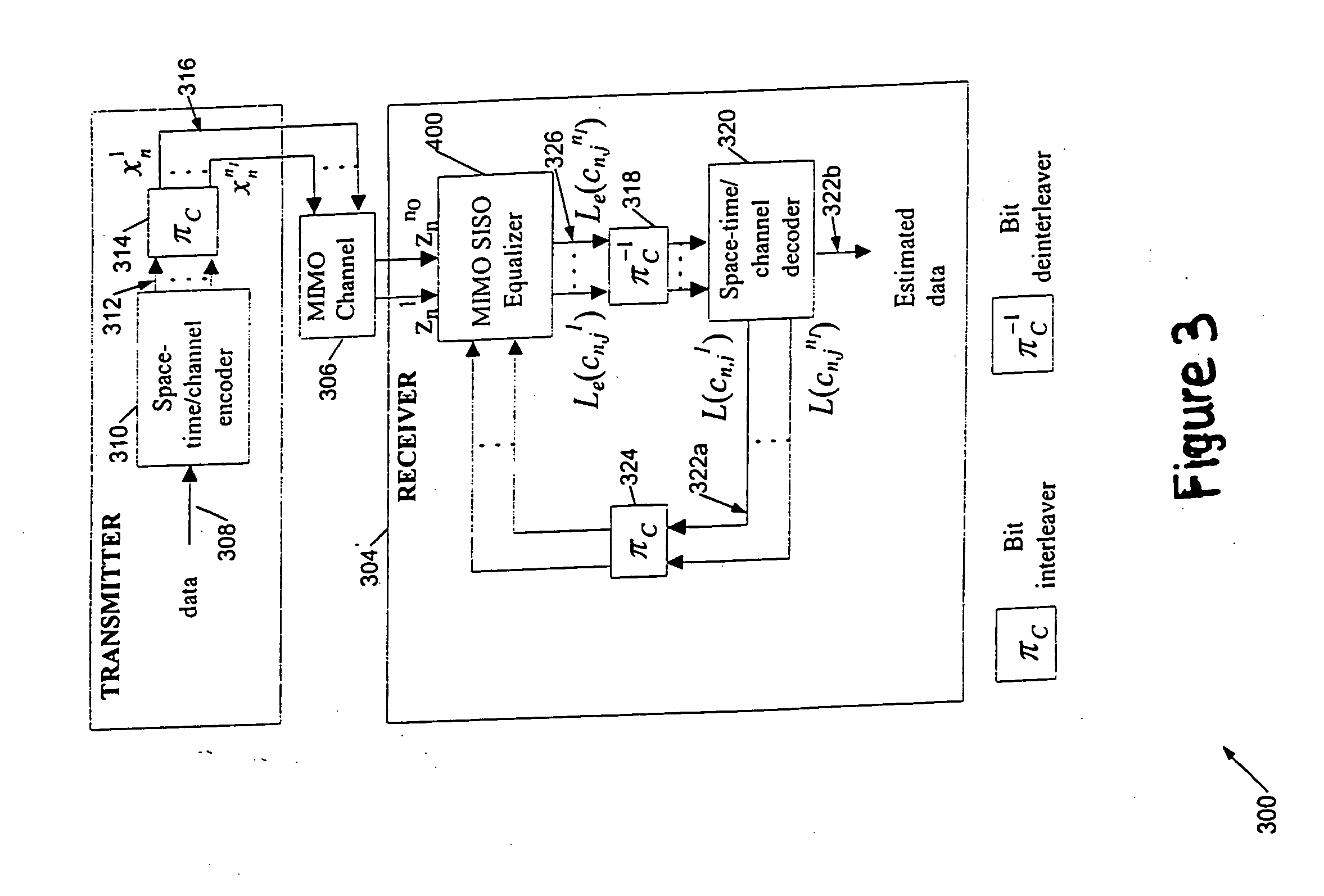
Communications apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20050128966A1Low complexity decodingImprove transfer rateMultiplex communicationRadio transmissionCommunications systemInterleave sequence
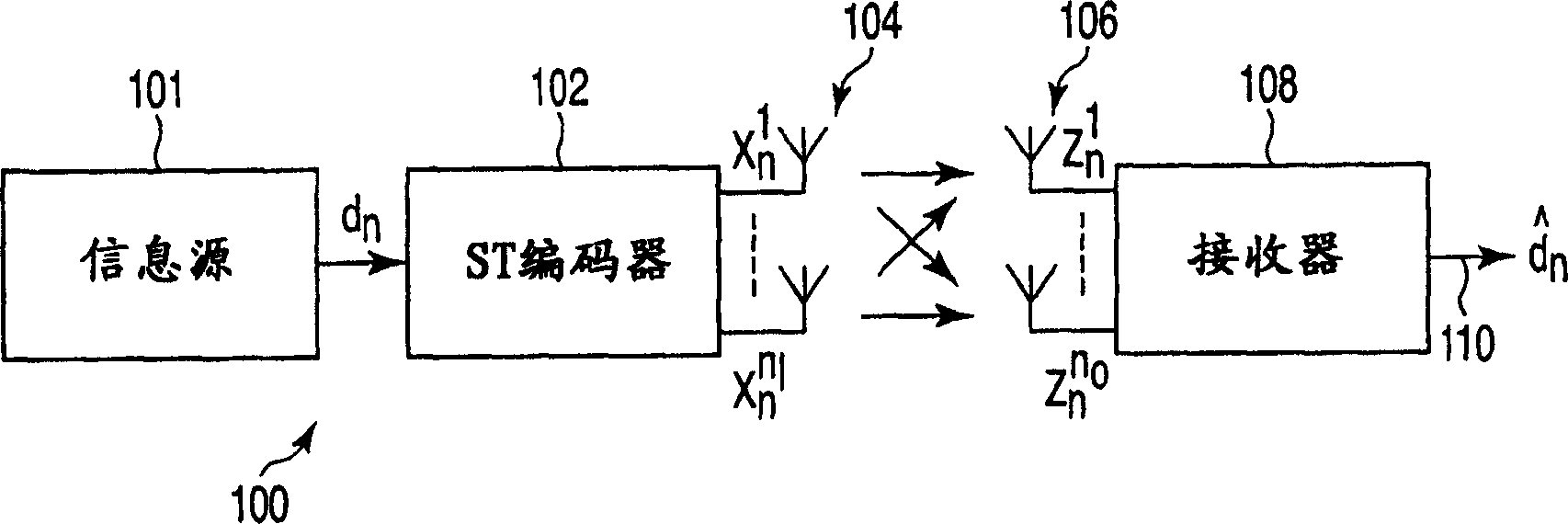
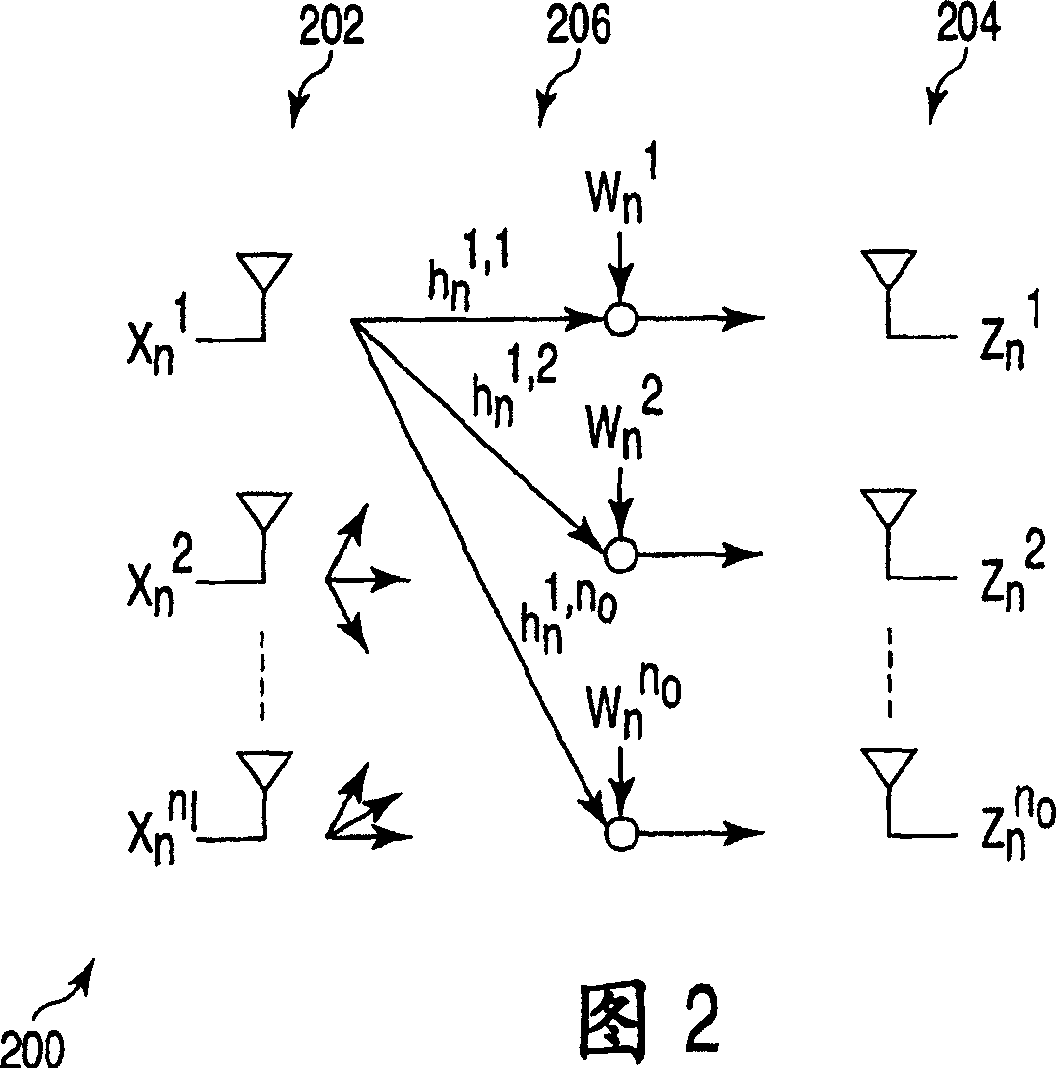
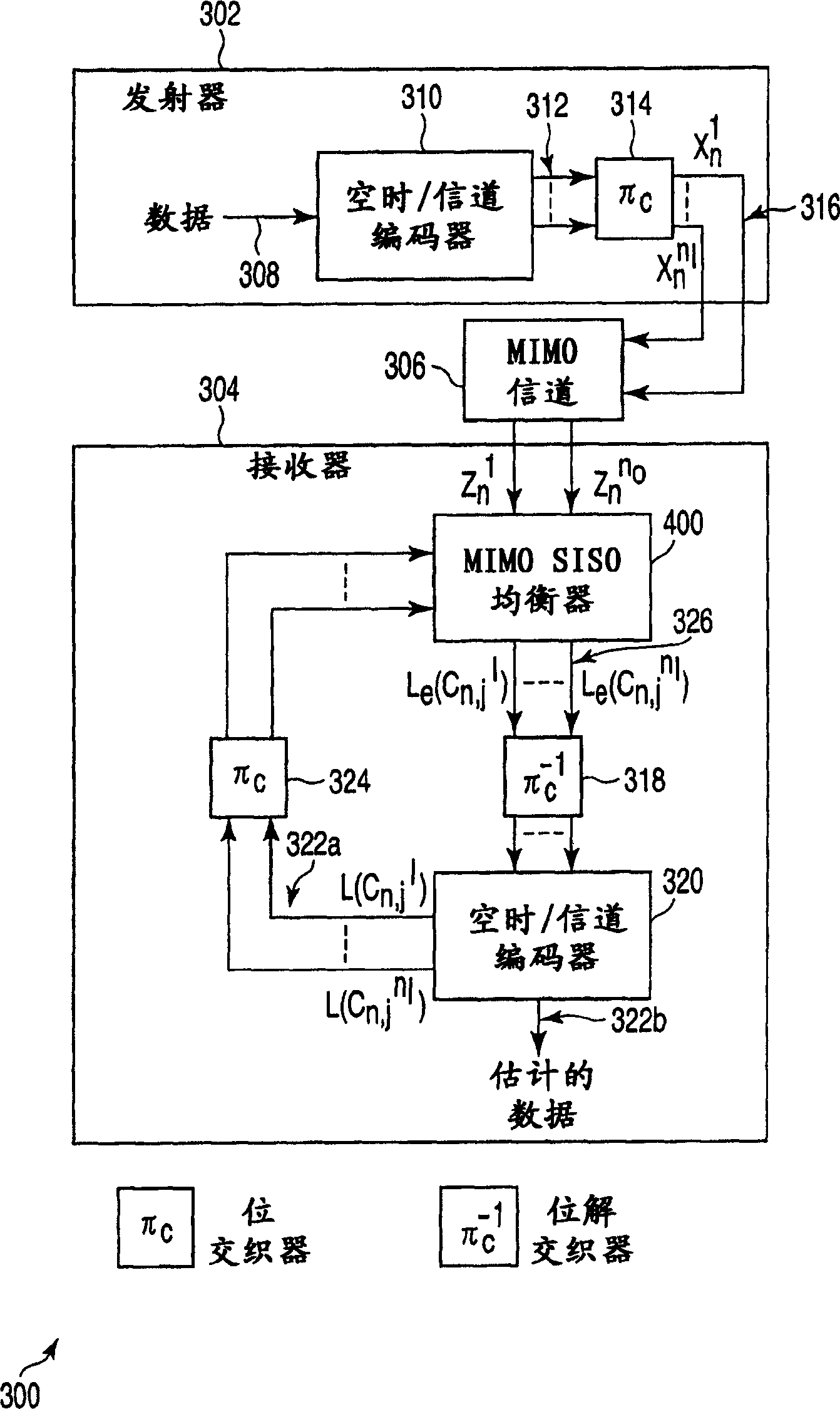
This invention relates to apparatus, methods and computer program code for transmission and reception in communication systems in which a receiver receives signals from a plurality of transmit antennas associated with a single transmitter. In particular this is related to MIMO (multiple input multiple output) and MISO (multiple input single output) channel based wireless systems. The present invention provides a method of transmitting a data sequence in a wireless communications system comprising: transmitting said data sequence from a first antenna; interleaving the data sequence; transmitting at least a part of the interleaved sequence from a second antenna spaced apart from the first antenna, the part of the interleaved sequence transmitted simultaneously with a part of the data sequence transmitted from the first antenna.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
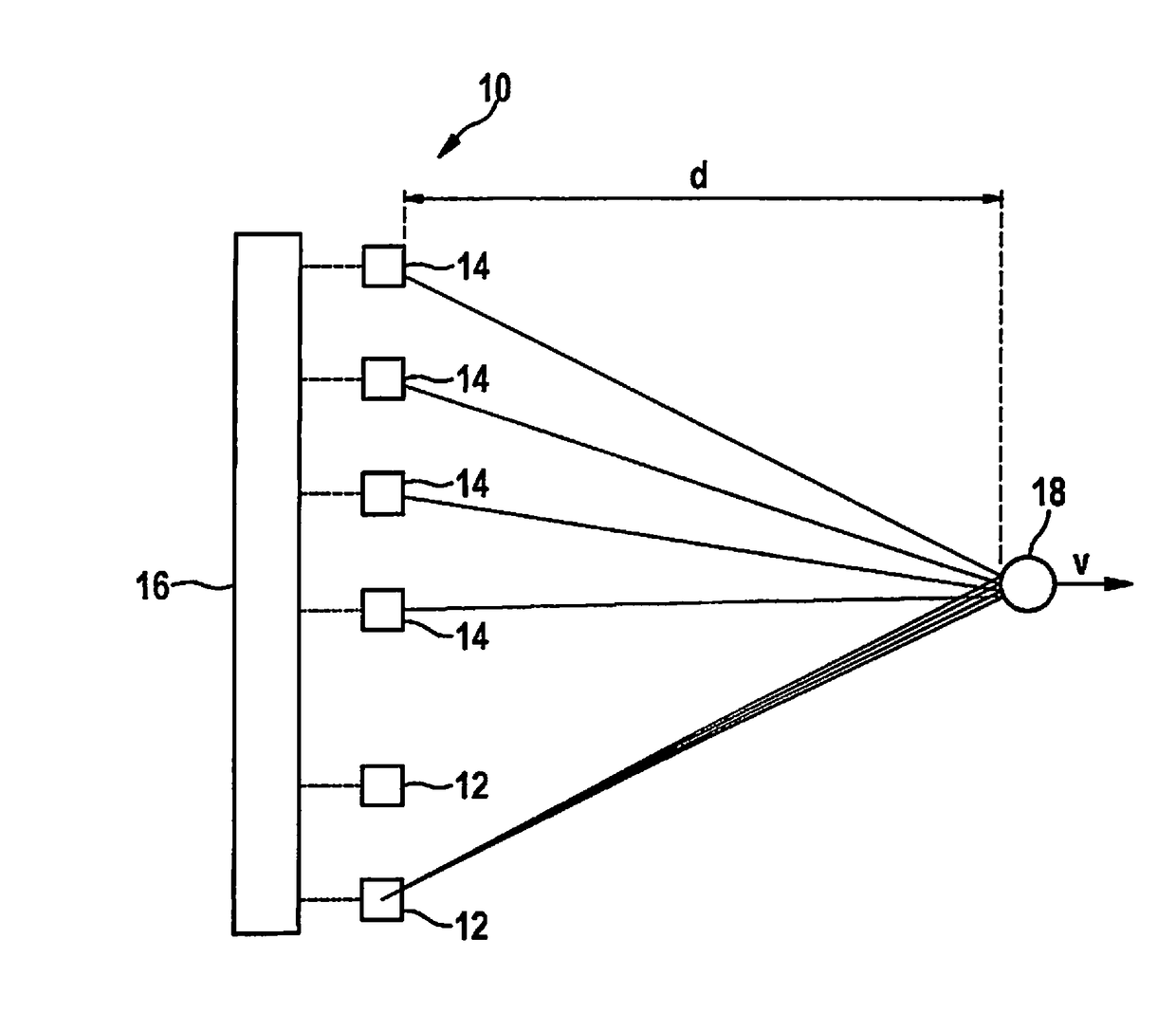
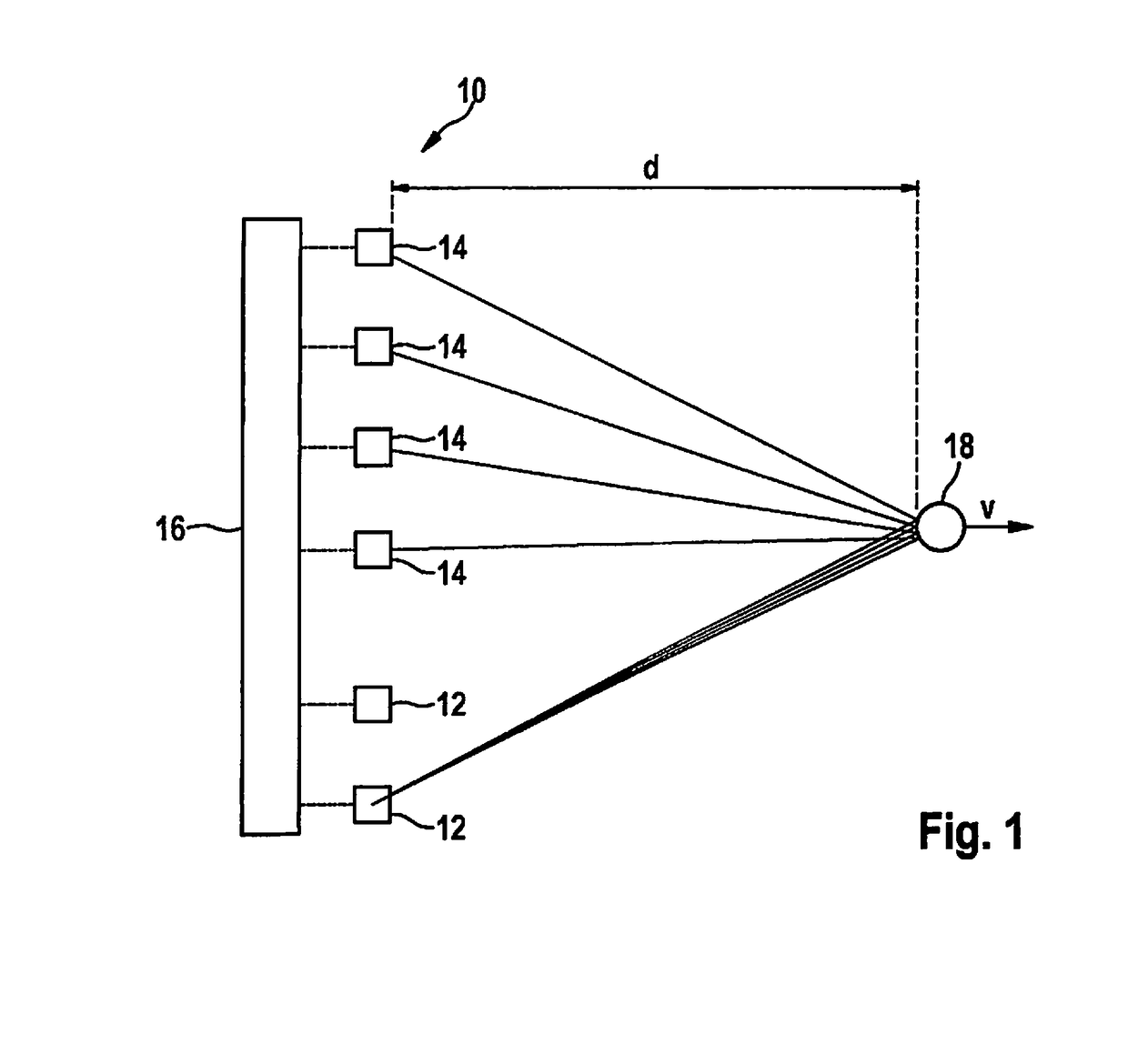
MIMO radar measurement sensor
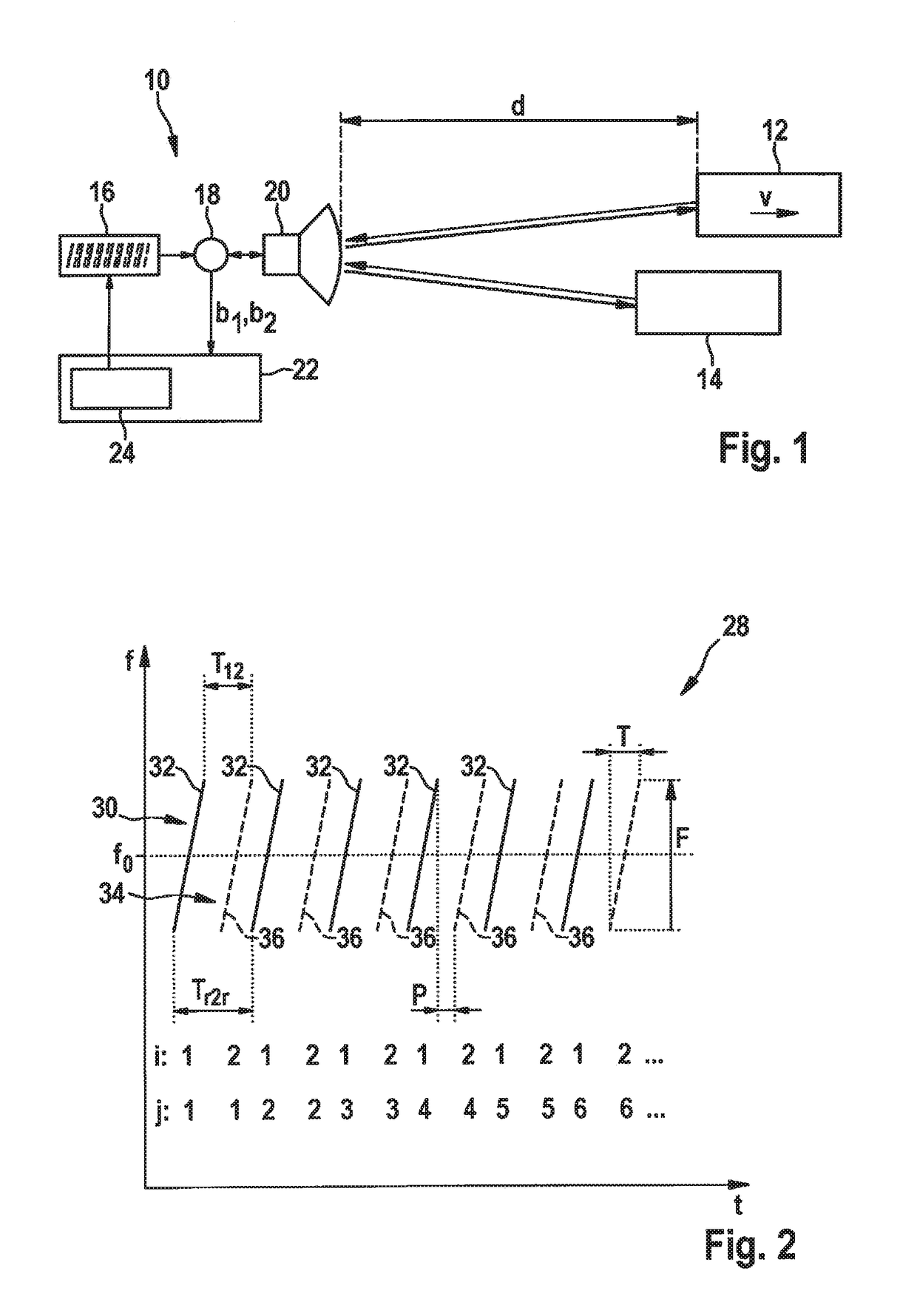
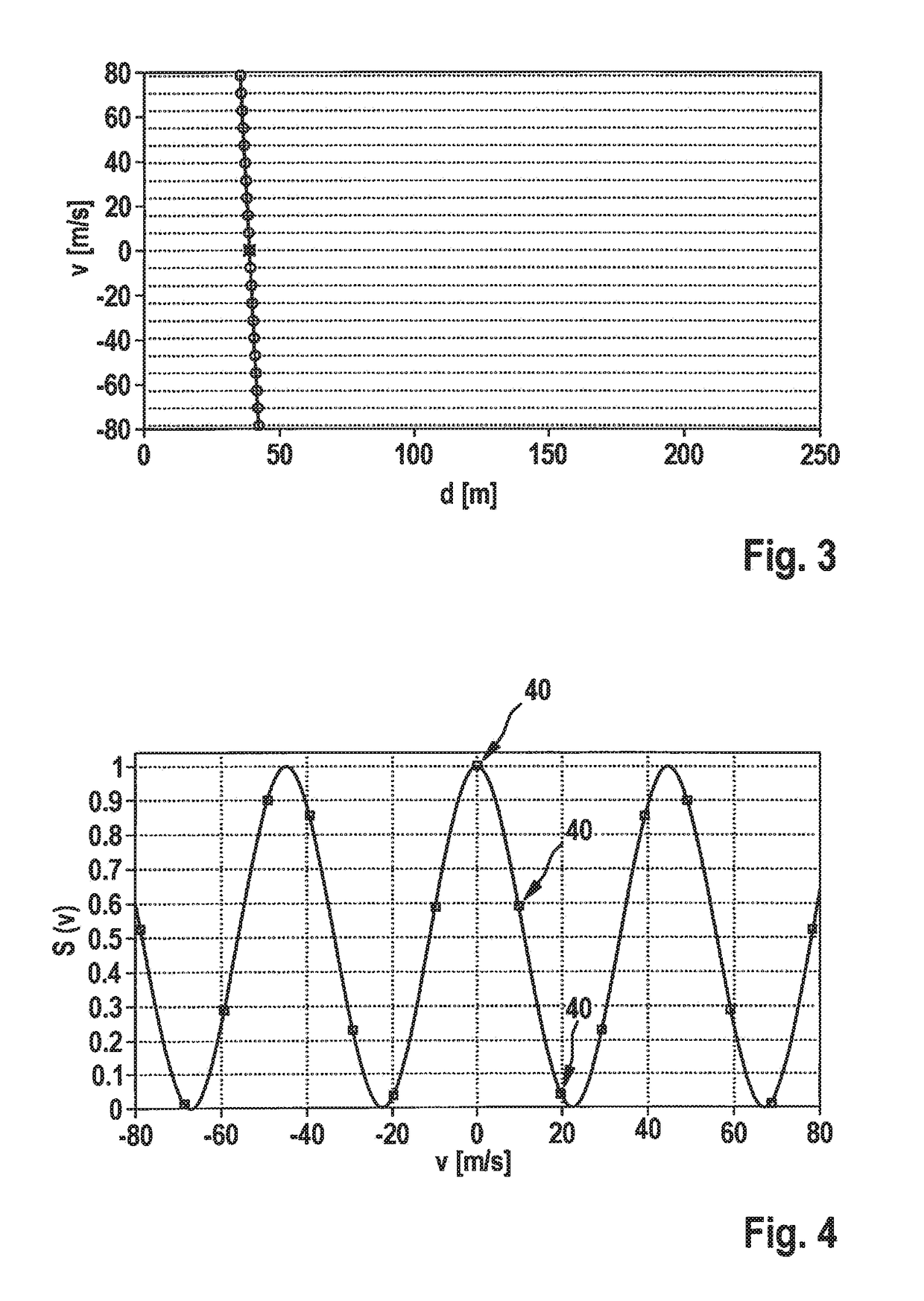
ActiveUS20170131392A1Hardware outlay is decreasedPrecise positioningRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumTransmission switching
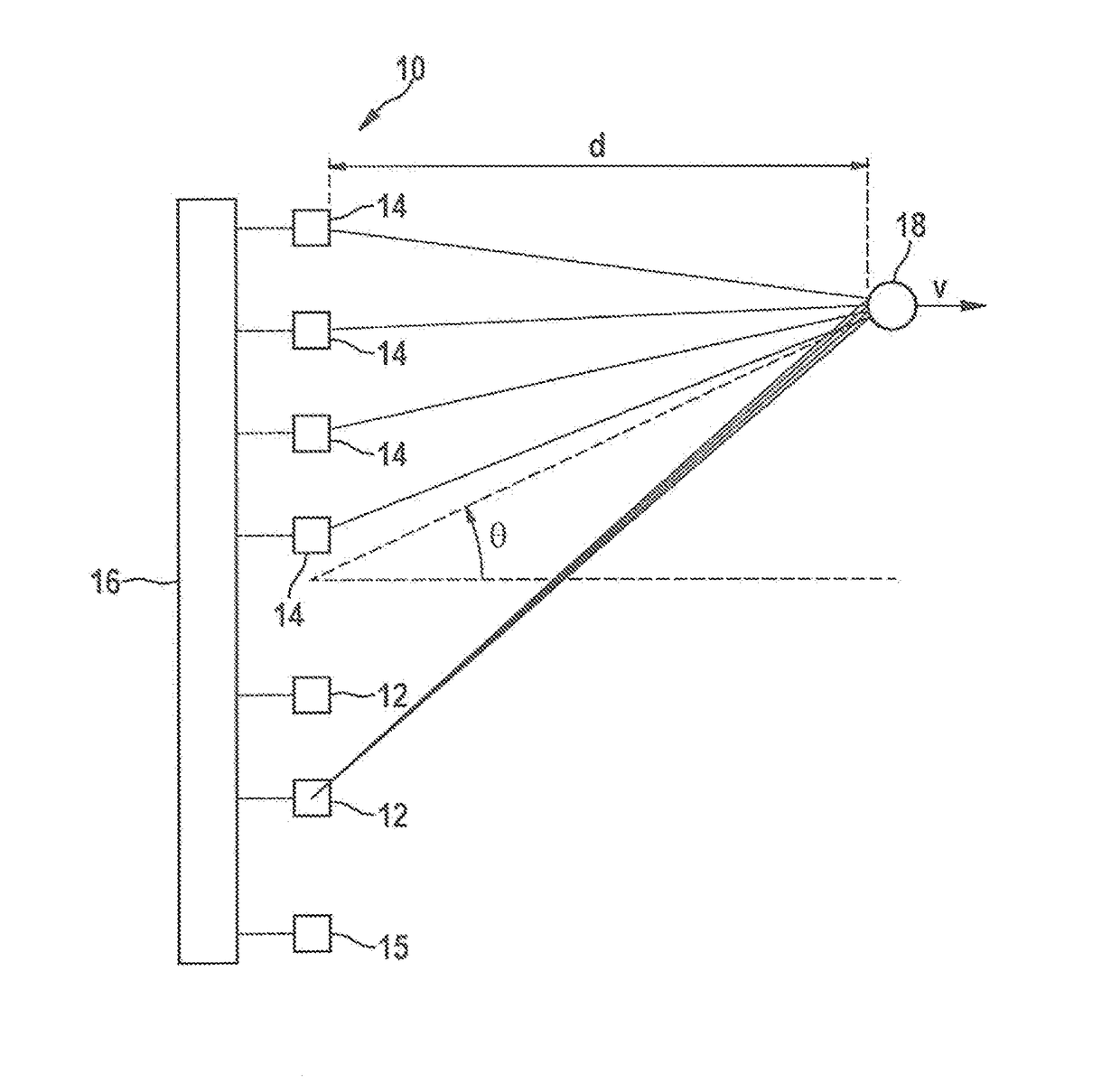
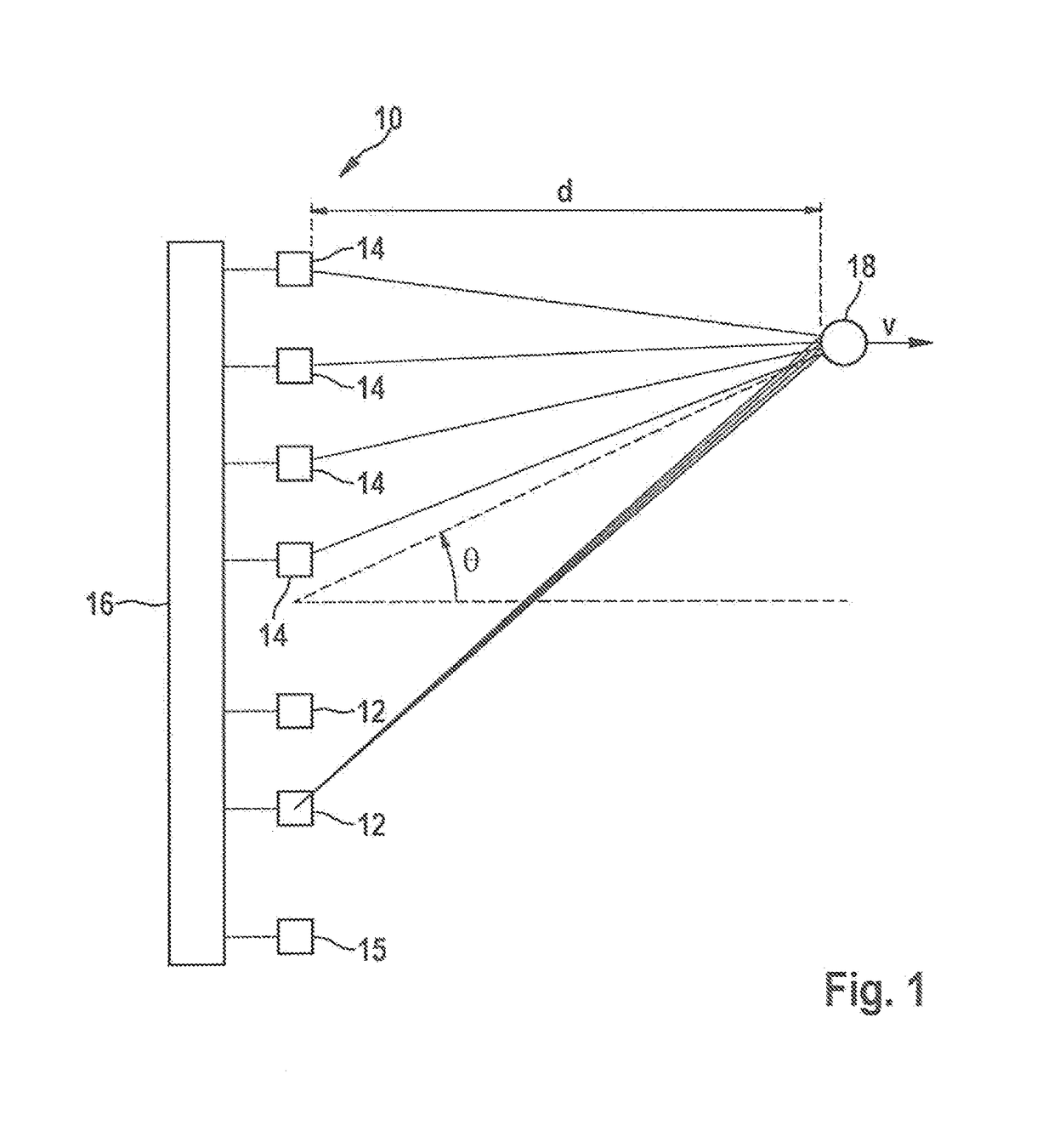
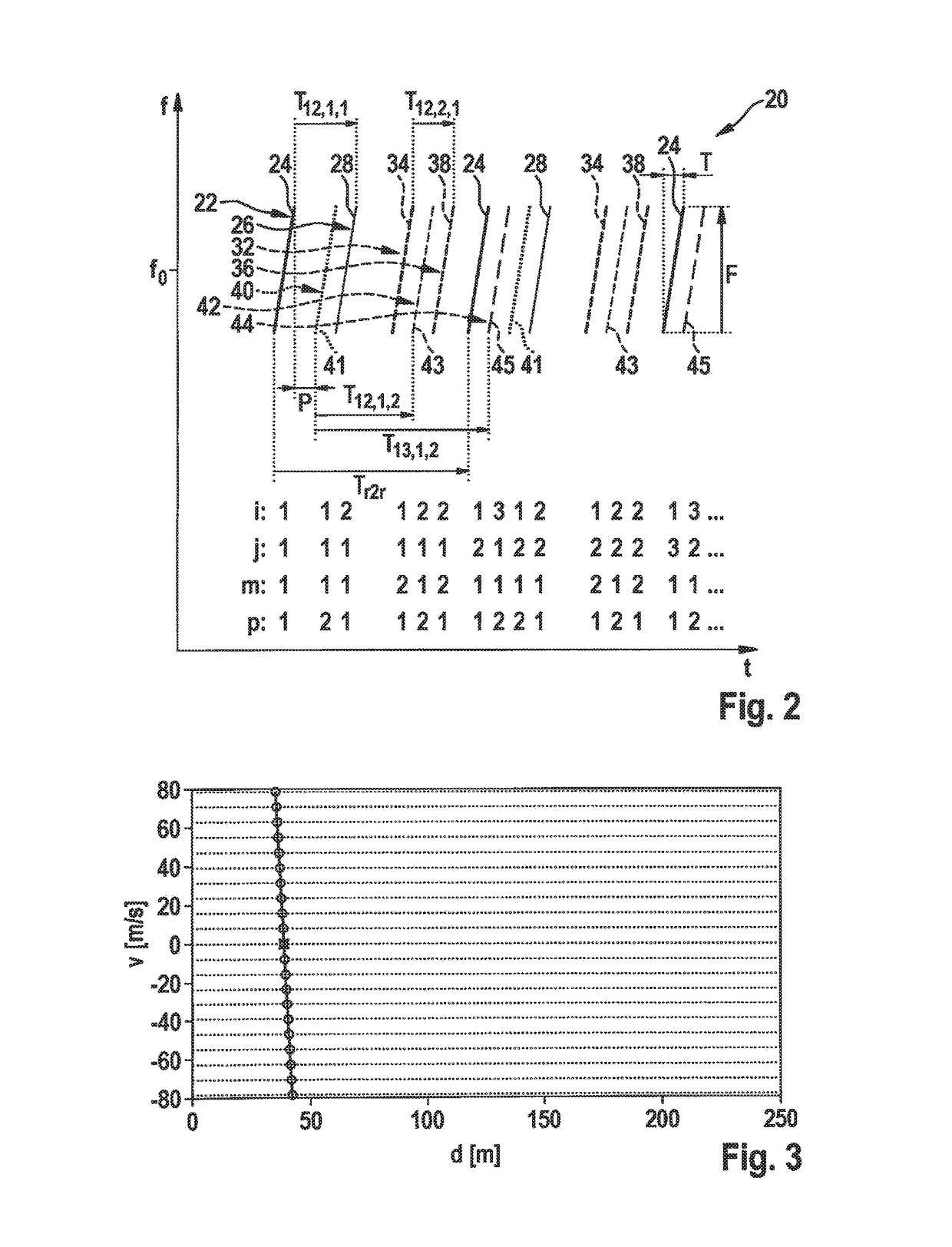
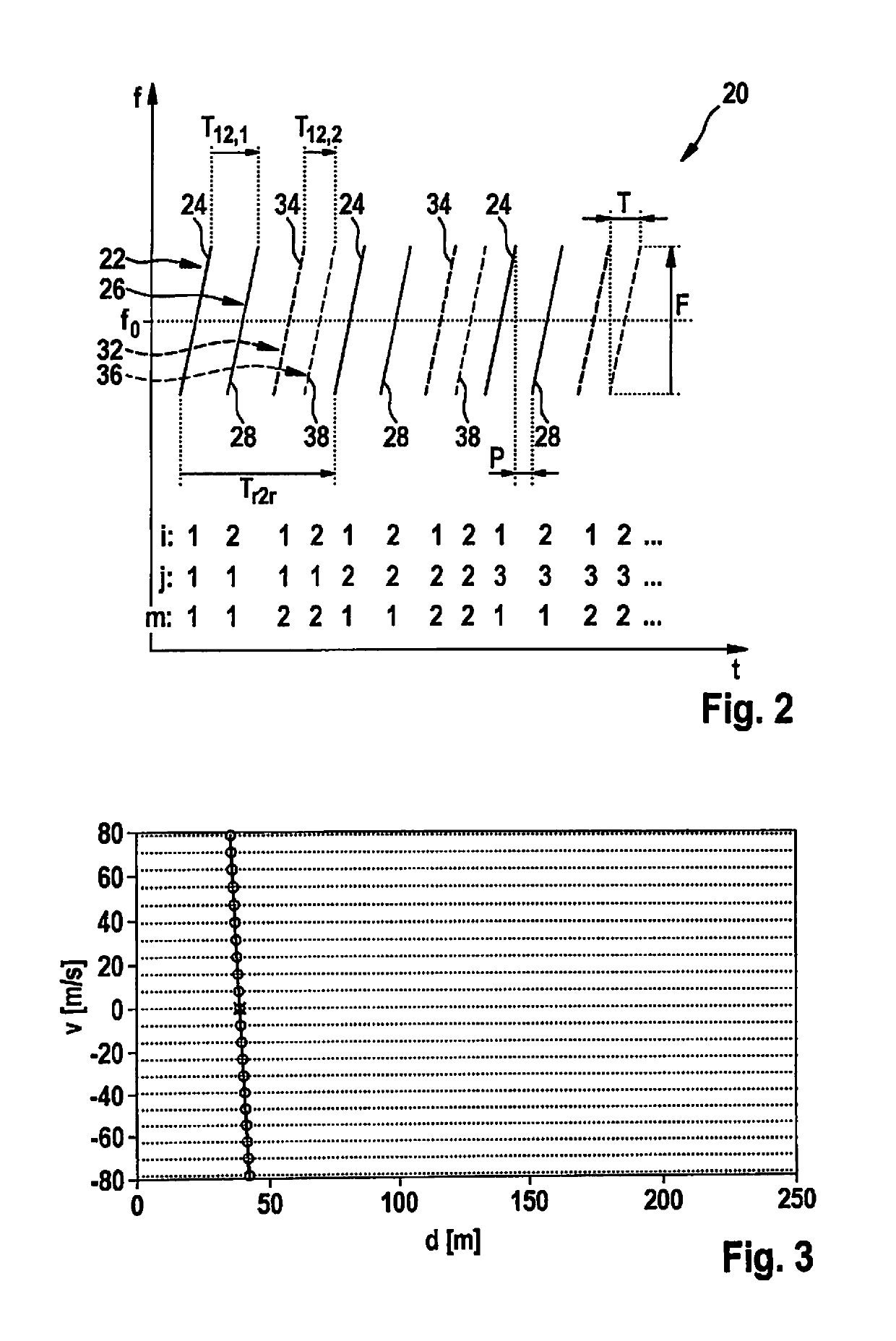
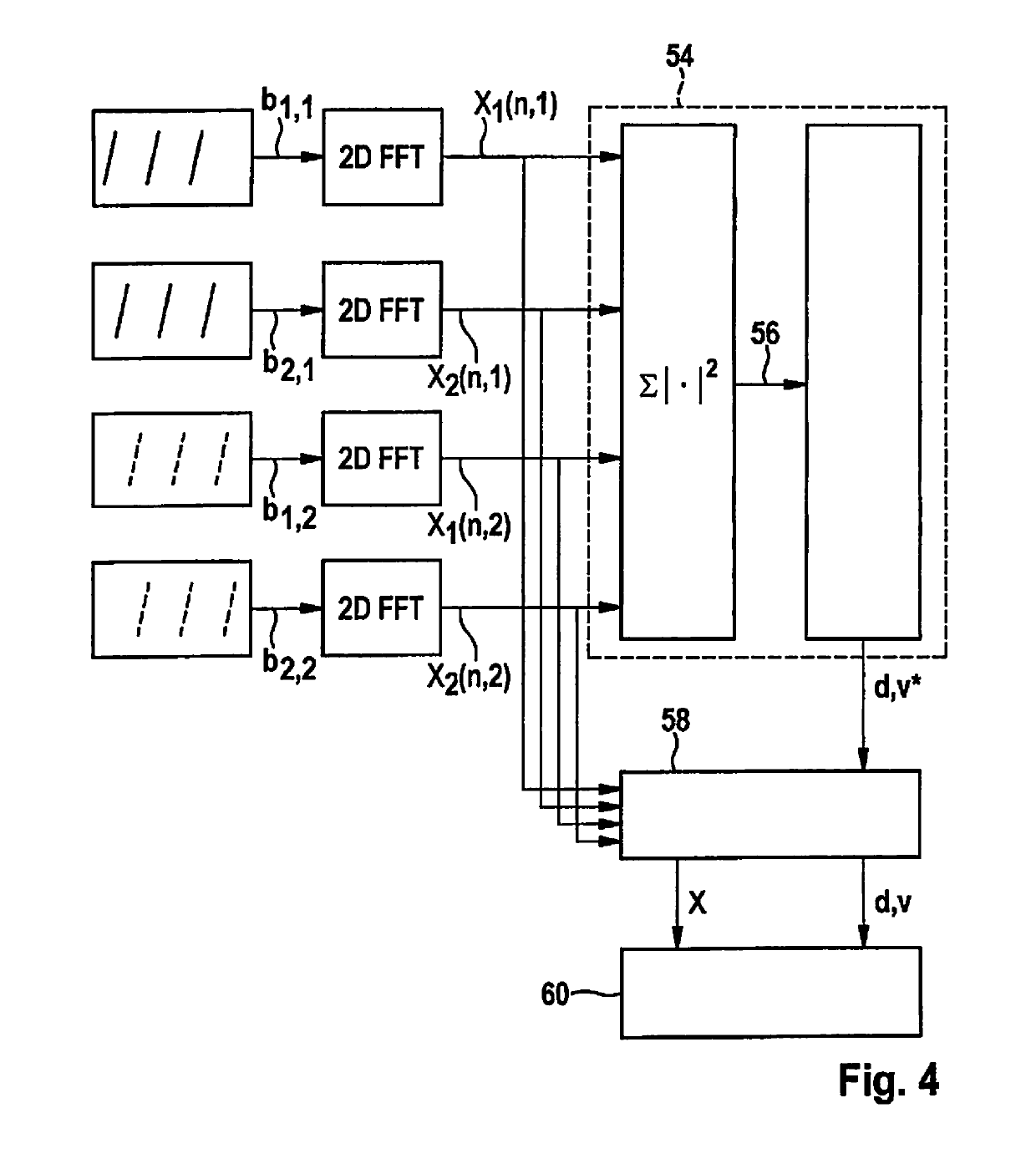
A MIMO FMCW radar sensor and a MIMO time multiplexing method for localizing a radar target, in which an FMCW radar measurement is performed with a transmitted signal whose modulation pattern encompasses, for different transmission switching states that differ in terms of the selection of antenna elements used for transmission, mutually temporally interleaved sequences of ramps; ambiguous values for the relative velocity of the radar target are determined from a position of a peak in a two-dimensional spectrum; phase relationships between spectral values of spectra are checked for agreement with phase relationships expected for several of the determined values of the relative velocity; on the basis thereof, an estimated value for the relative velocity of the radar target is selected from the determined periodic values of the relative velocity; and the angle of the radar target is determined on the basis of amplitudes and / or phase relationships between obtained baseband signals.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Thread interleaving in a multithreaded embedded processor
ActiveUS20090049279A1Improve utilizationImprove performanceDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionTime conditionInstruction unit
The present invention provides a network multithreaded processor, such as a network processor, including a thread interleaver that implements fine-grained thread decisions to avoid underutilization of instruction execution resources in spite of large communication latencies. In an upper pipeline, an instruction unit determines an-instruction fetch sequence responsive to an instruction queue depth on a per thread basis. In a lower pipeline, a thread interleaver determines a thread interleave sequence responsive to thread conditions including thread latency conditions. The thread interleaver selects threads using a two-level round robin arbitration. Thread latency signals are active responsive to thread latencies such as thread stalls, cache misses, and interlocks. During the subsequent one or more clock cycles, the thread is ineligible for arbitration. In one embodiment, other thread conditions affect selection decisions such as local priority, global stalls, and late stalls.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
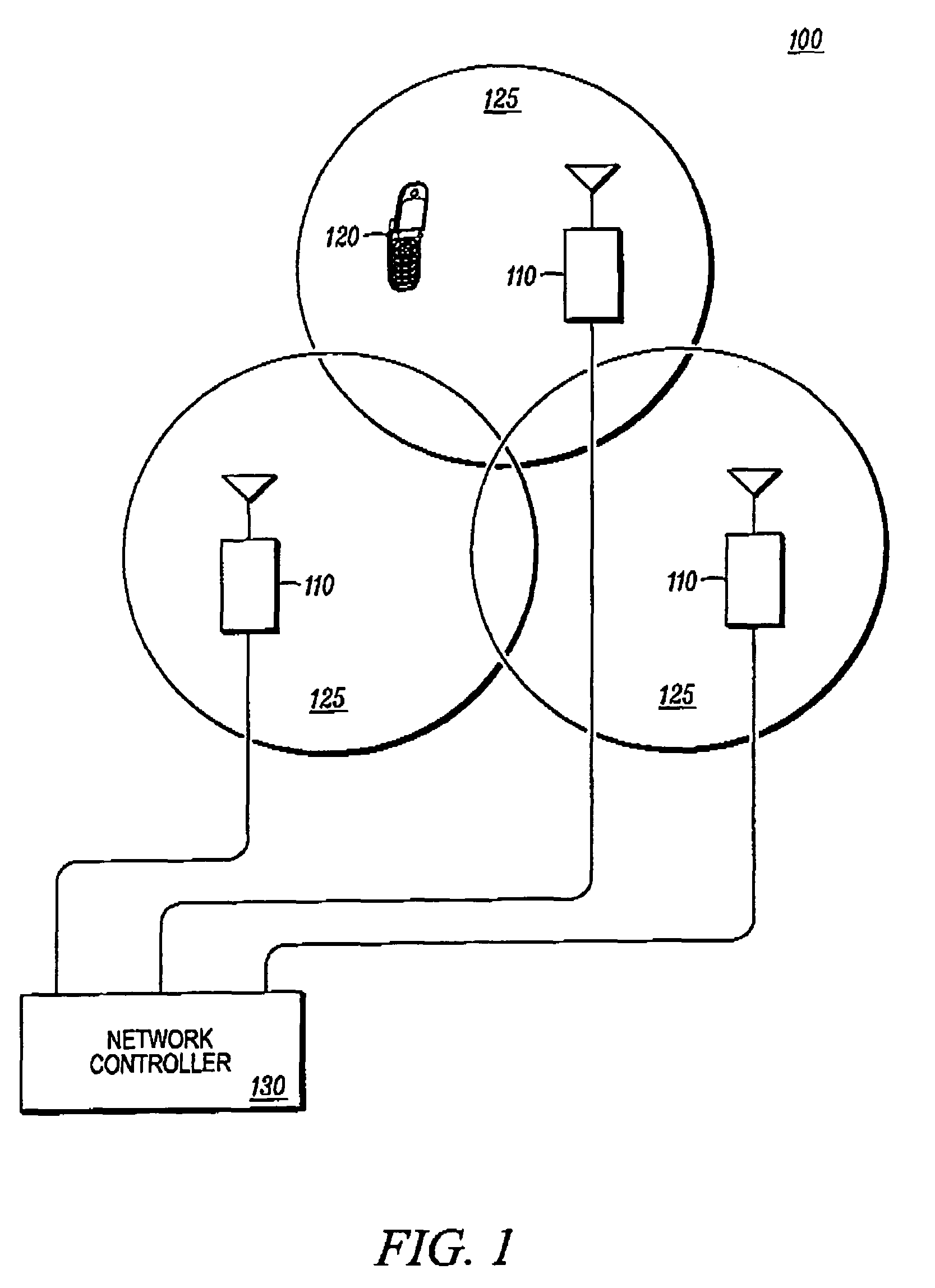
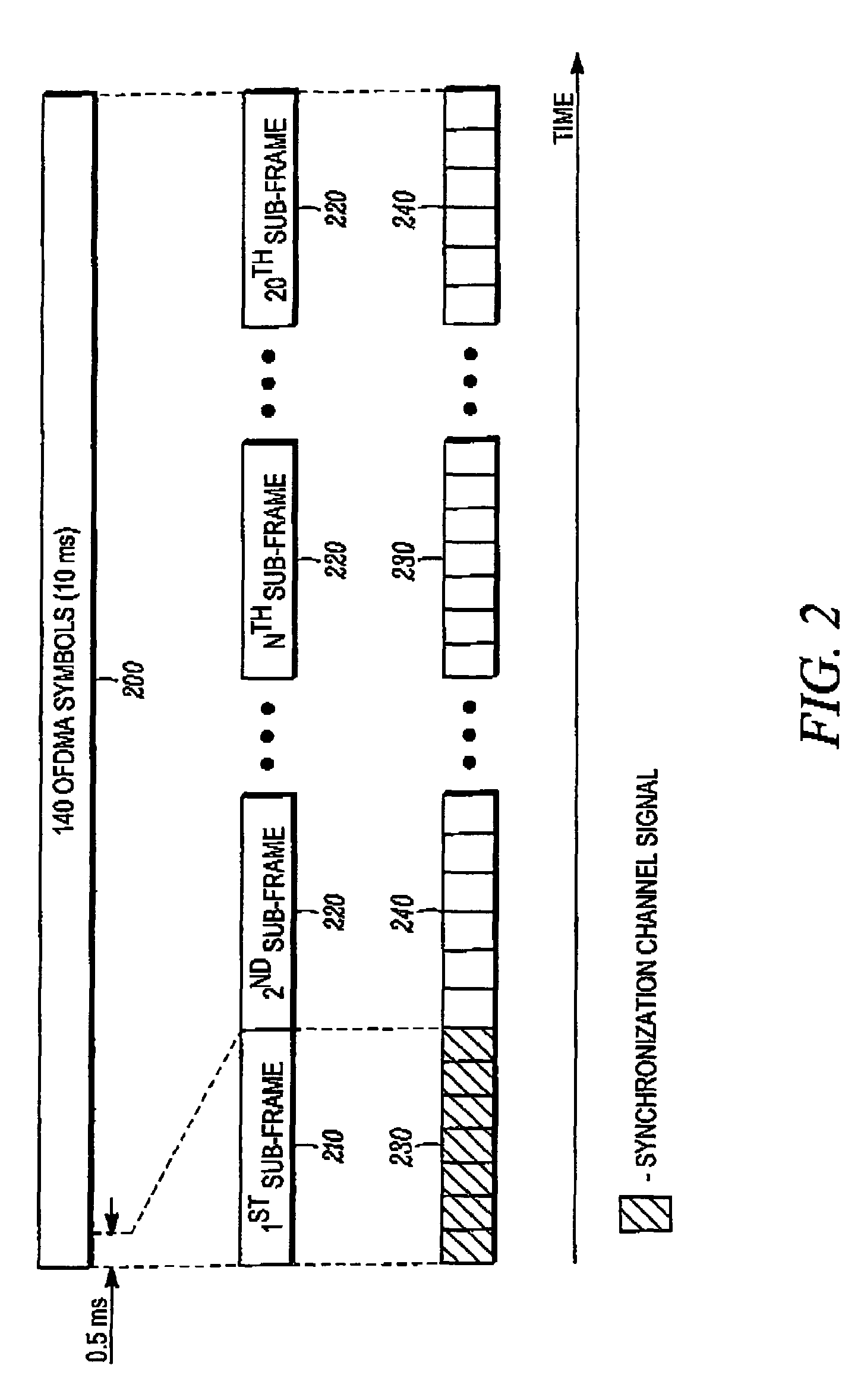
Method and apparatus for interleaving sequence elements of an OFDMA synchronization channel
A method and apparatus is provided for transmitting an orthogonal frequency domain multiple access (OFDMA) signal including a synchronization channel signal transmitted including a plurality of sequence elements interleaved in time and frequency (610, 640). The synchronization channel signal sequence elements enable an initial acquisition and cell search method with low computational load by providing predetermined time domain symmetry (702, 704) for common sequence elements in OFDMA symbol periods (620, 660) for OFDMA symbol timing detection and frequency error detection in an OFDMA system supporting multiple system bandwidths, both synchronized and un-synchronized systems, a large cell index and an OFDMA symbol structure with both short and long cyclic prefix length.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Improved communications apparatus and methods
This invention relates to apparatus, methods and computer program code for transmission and reception in communication systems in which a receiver receives signals from a plurality of transmit antennas associated with a single transmitter. In particular this is related to MIMO (multiple input multiple output) and MISO (multiple input single output) channel based wireless systems. The present invention provides a method of transmitting a data sequence in a wireless communications system comprising: transmitting said data sequence from a first antenna; interleaving the data sequence; transmitting at least a part of the interleaved sequence from a second antenna spaced apart from the first antenna, the part of the interleaved sequence transmitted simultaneously with a part of the data sequence transmitted from the first antenna.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Apparatus and method for joint and time delayed measurements of components of conjugated quadratures of fields of reflected/scattered and transmitted/scattered beams by an object in interferometry
InactiveUS20060033924A1Reduce sensitivityFast scanningInterferometersUsing optical meansPhase shiftedInterleave sequence
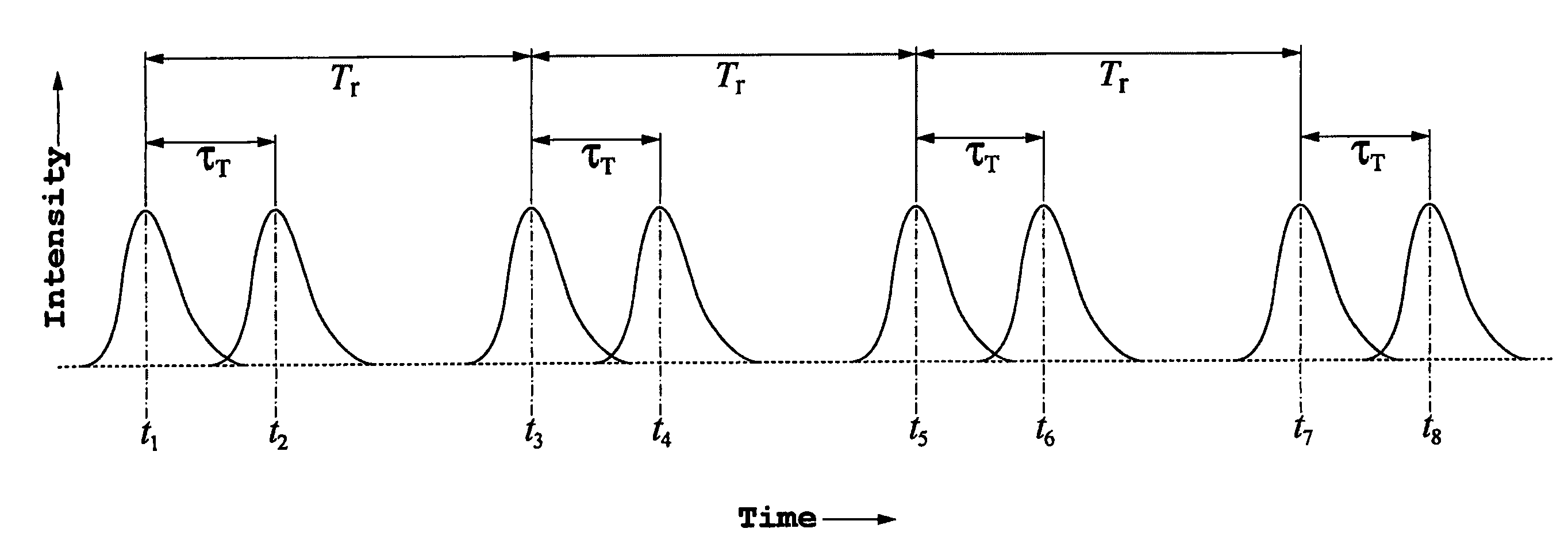
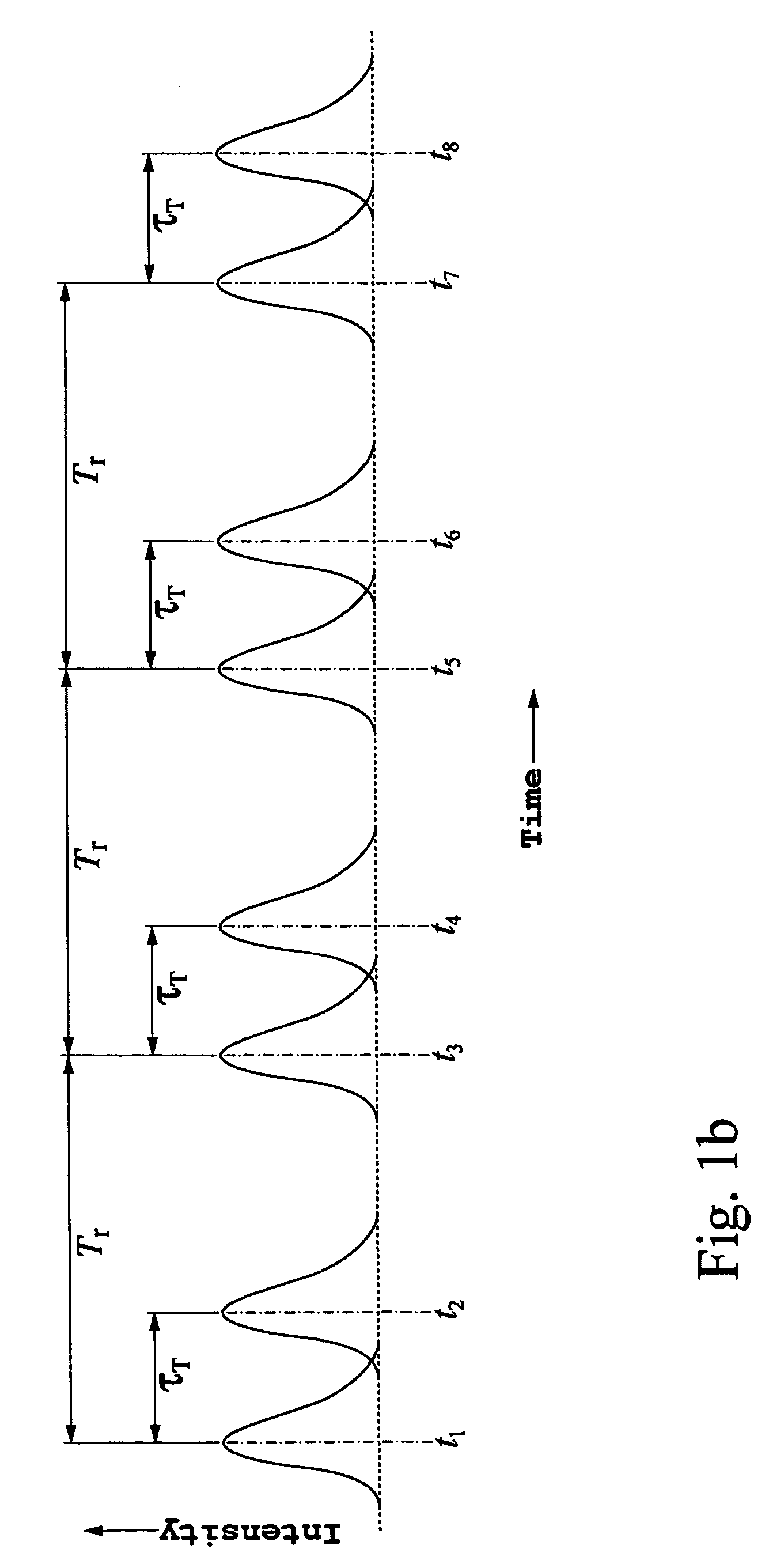
A method of interferometrically obtaining measurements for properties associated with a spot on or in an object, the method involving: receiving a sequence of M optical pulses separated in time; from each pulse in the sequence of M optical pulses, generating an n-tuplet of measurement pulses, and an n-tuplet of reference pulses, wherein each measurement pulse has a corresponding reference pulse aligned with it in time; from each pulse of each n-tuplet of reference pulses for the sequence of M optical pulses, generating a reference beam; from each pulse of each n-tuplet of measurement pulses for the sequence of M optical pulses, (a) generating a measurement beam; (b) directing the measurement beam onto the spot to thereby produce a return measurement beam from the spot; and (c) combining the return measurement beam with the corresponding reference beam that was derived from the reference pulse corresponding to that measurement pulse to generate an interference beam, wherein the sequence of M n-tuplets of measurement pulses forms n interleaved sequences of M measurement pulses, and wherein the method further involves, for each of the n interleaved sequences of M measurement pulses, introducing a combination of phase shifts between the measurement beams and corresponding reference beams.
Owner:ZETETIC INST
Multi-channel flash module with plane-interleaved sequential ECC writes and background recycling to restricted-write flash chips
InactiveUS7966462B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInterleave sequenceBlock number
A RAM mapping table is restored from flash memory using plane, block, and page addresses generated by a physical sequential address counter. The RAM mapping table is restored following a plane-interleaved sequence generated by the physical sequential address counter using interleaved bits extracted from the lowest bits of the logical block index. These plane-interleave bits are split into a LSB and a MSB, with middle physical block bits between the LSB and MSB. The physical sequential address counter generates a physical block number by incrementing the plane-interleave bits before the middle physical block bits, and then relocating the MSB to above the middle physical block bits. This causes blocks to be accessed in a low-high sequence of 0, 1, 4096, 4097, 2, 3, 4098, 4099, etc. in the four planes of flash memory. Background recycling and ECC writes are also performed.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Multi-element error correcting code transmitting and receiving apparatus, data communication system and related method
InactiveCN101425871AImprove error correction performanceImprove the ability to resist sudden errorsNon-binary linear block codesCode conversionError correctingSource data
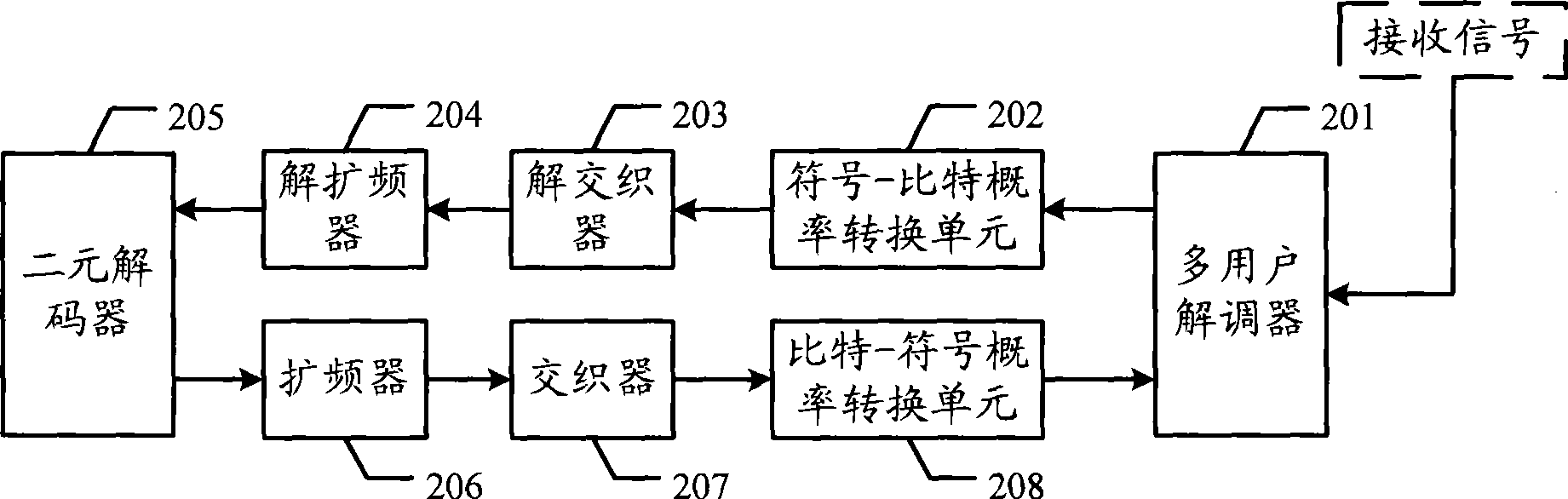
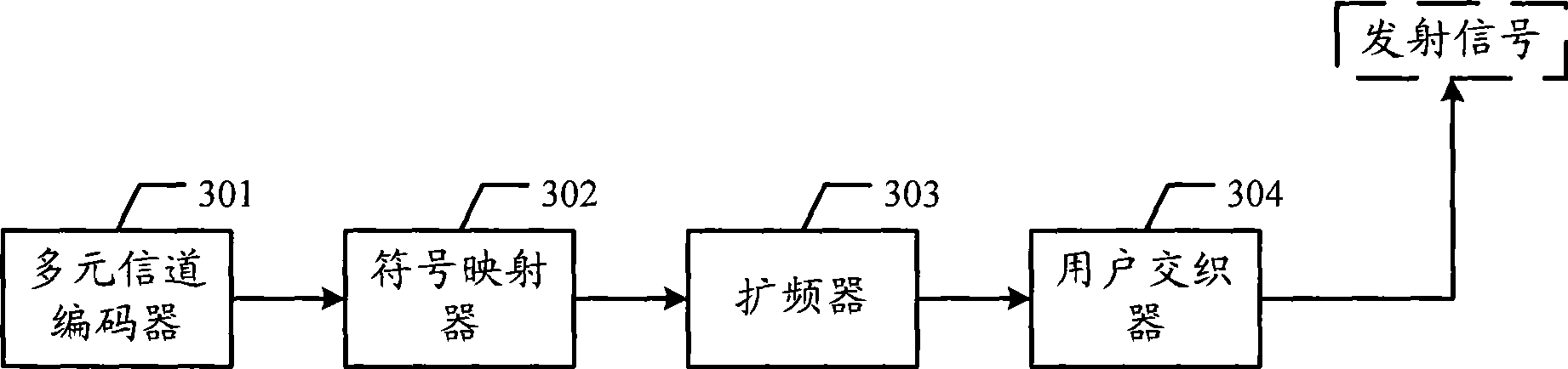
The invention discloses a multiple-unit error correcting code transmitting and receiving device and a data transferring system as well as related methods, which can be used for reducing the complexity of operation. The multiple-unit error correcting code transmitting device comprises a multichannel decoder, a symbol mapper, a user interleaver and a frequency amplifier, wherein the multichannel decoder is used for carrying out the multiple-unit coding on the source data frames of users to obtain a coding sequence; the symbol mapper is used for carrying out the symbol mapping on the coding sequence to obtain a symbol sequence; the user interleaver is used for interleaving the symbol sequence to obtain an interleaved sequence; and the frequency amplifier is used for carrying out the frequency amplifying on the interleaving sequence to obtain a frequency amplifying sequence. The invention also provides a multiple-unit error correcting code receiving device, a data transferring system and the related methods, and can effectively reduce the complexity of operation.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
Control channel formulation in OFDM systems
ActiveCN101911577AGood interference randomizationGood frequency diversity performanceSignal allocationTelecommunicationsResource element
Control channel information is formulated for transmission in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems. In an example embodiment, a method entails formulating control channel information for a transmitting device operating in an OFDM system in which a control channel spans n OFDM symbols, with n being an integer. The method includes acts of allocating, creating, and mapping. Control channel data is allocated to at least one set of resource element groups. At least one order for the set of resource element groups is created in accordance with one or more permutation mechanisms that involve at least one interleaving sequence having a low cross-correlation property. The set of resource element groups is mapped to resource elements of the n OFDM symbols of the control channel responsive to the order that is created using the permutation mechanism(s). The permutation mechanisms may include interleaving sequence(s) and / or cyclic shift(s).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
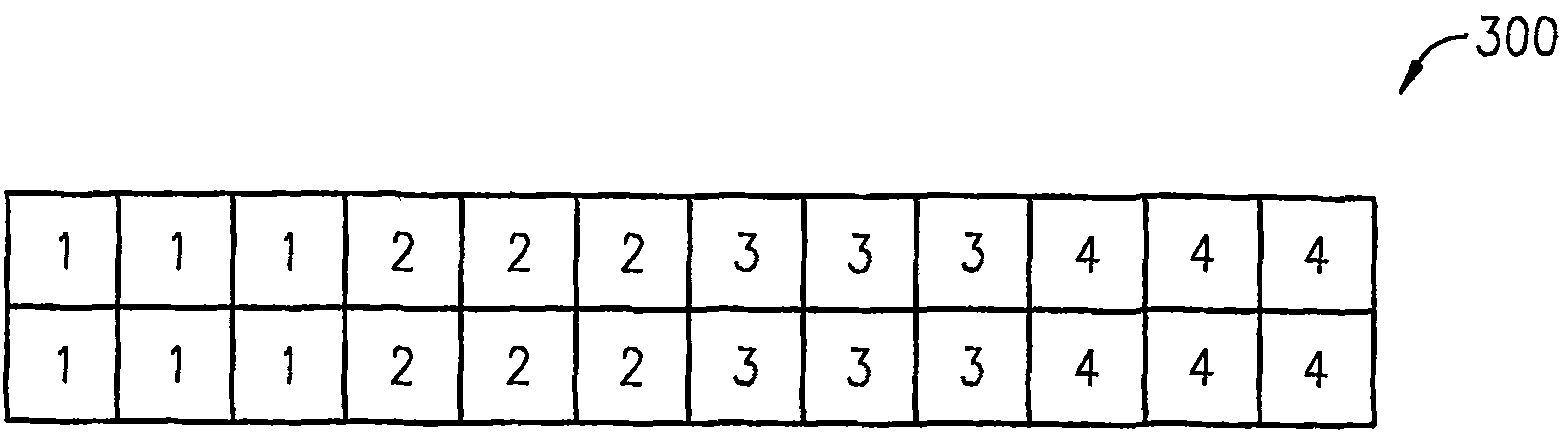
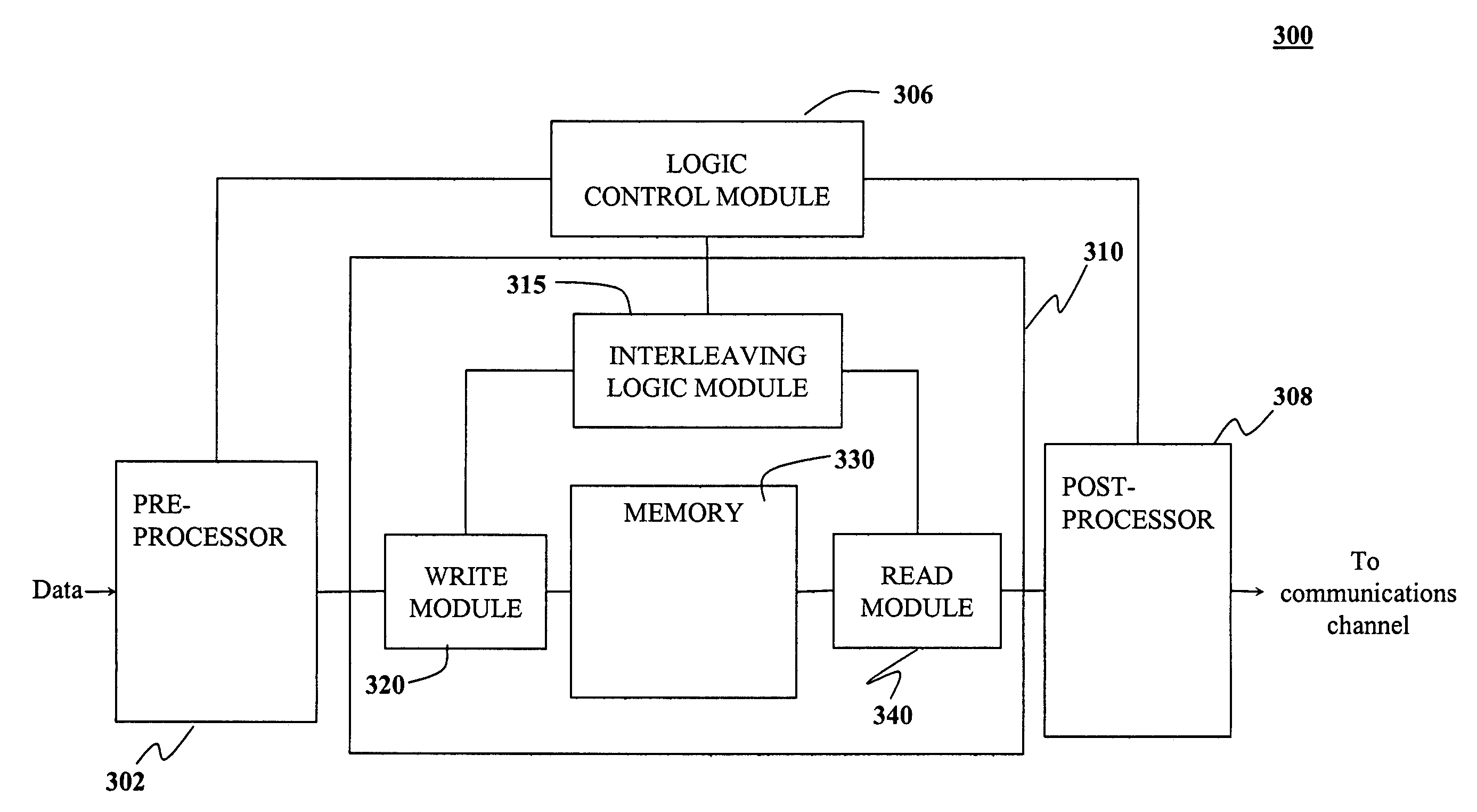
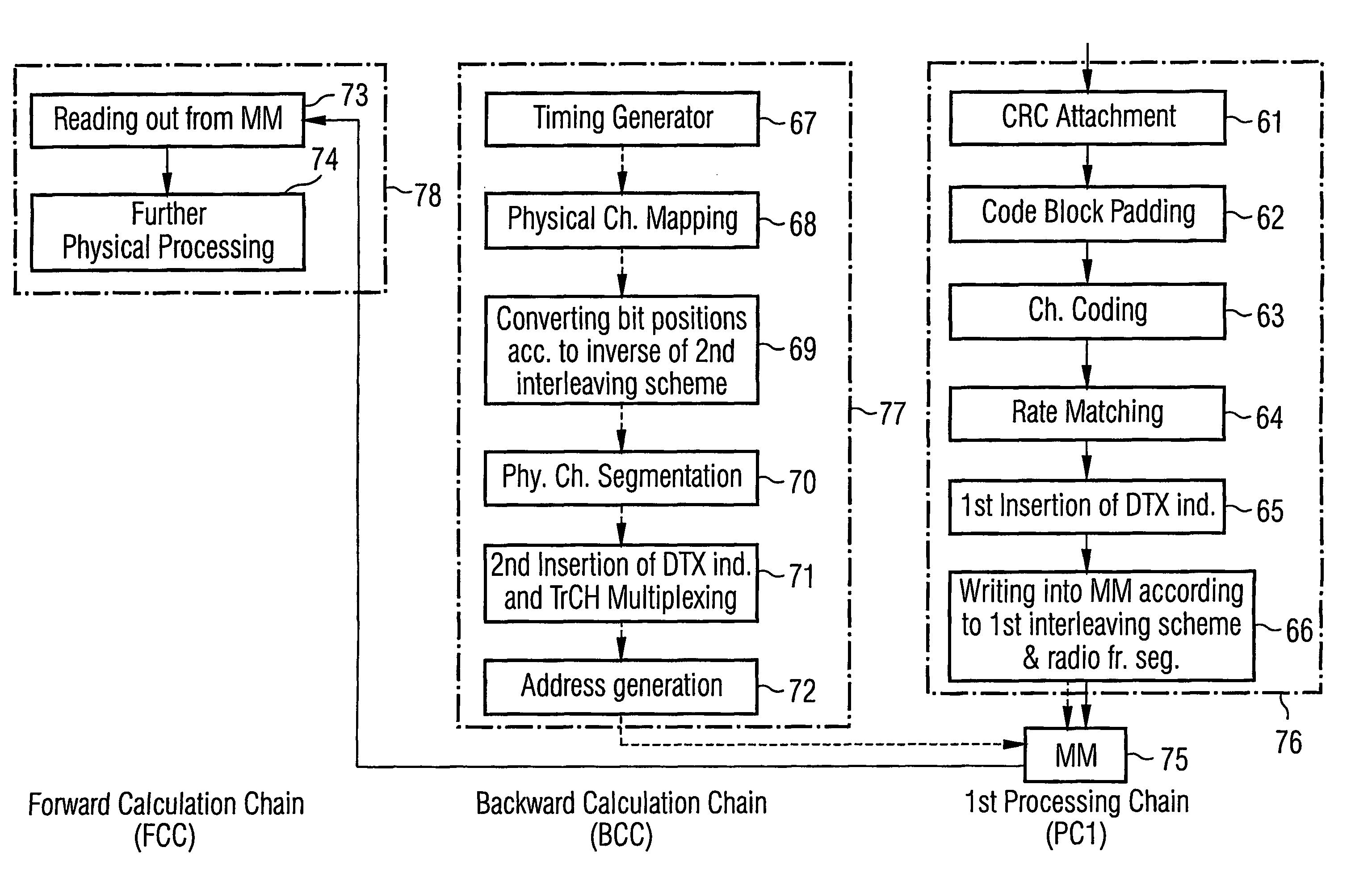
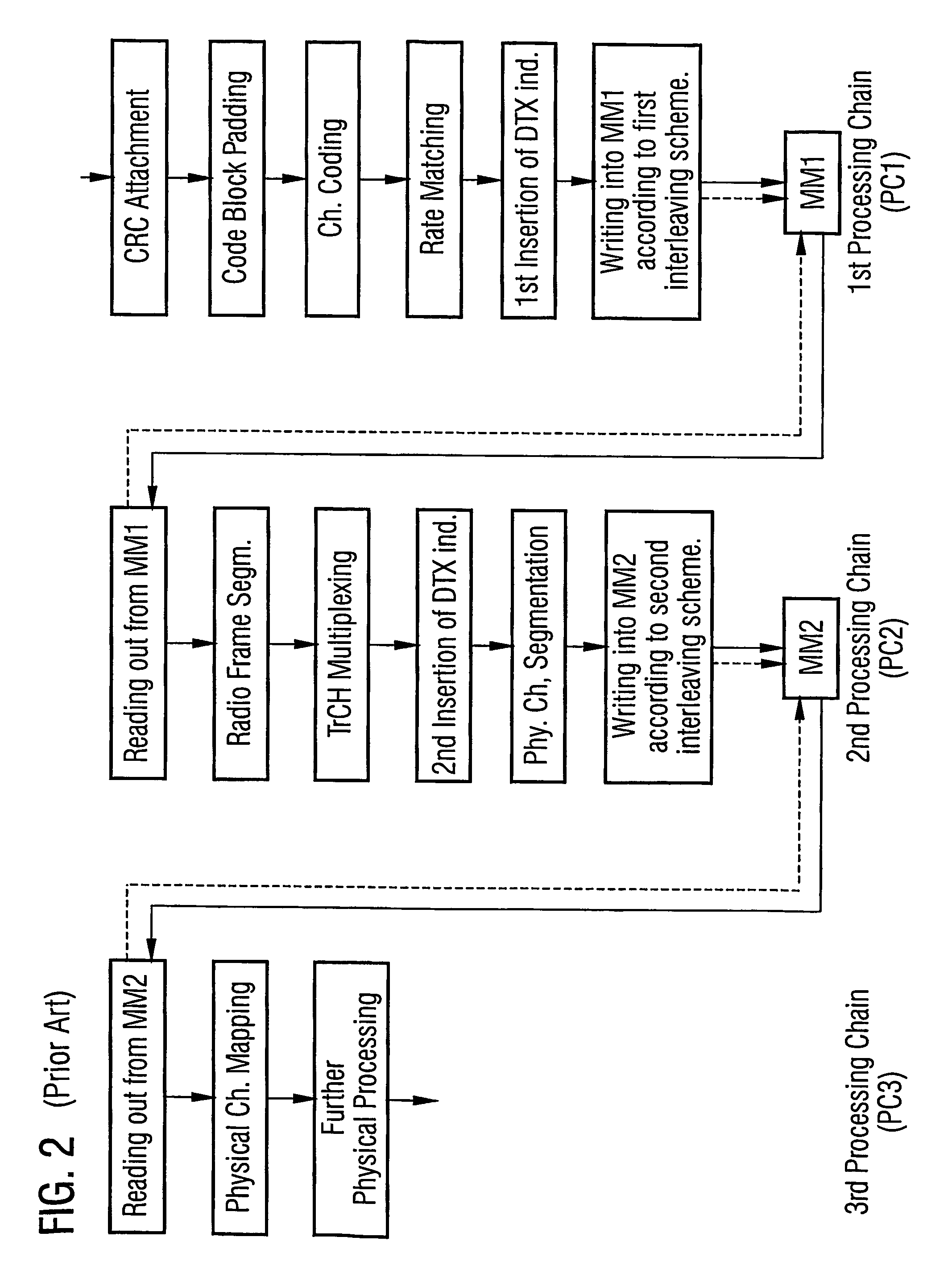
System and method for interleaving data in a communications device
InactiveUS7073012B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationCode conversionMemory addressInterleave sequence
A system and method is provided for interleaving data in a communications device. The system includes a memory for storing symbols of a data block, a read module and a write module, each of which is coupled to the memory. The system also includes a interleaving logic module coupled to the read and write modules. The interleaving logic module determines an interleaving sequence comprising a sequence of memory addresses. Each memory address is then communicated sequentially to the read and write modules. When the read module receives the address, the read module reads the stored data symbol. When the write module receives the address, the write module writes a symbol from a next data block to the vacated address. The interleaving logic module repeats these steps until every symbol of the stored block has been read and every symbol of the next data block has been written to memory.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
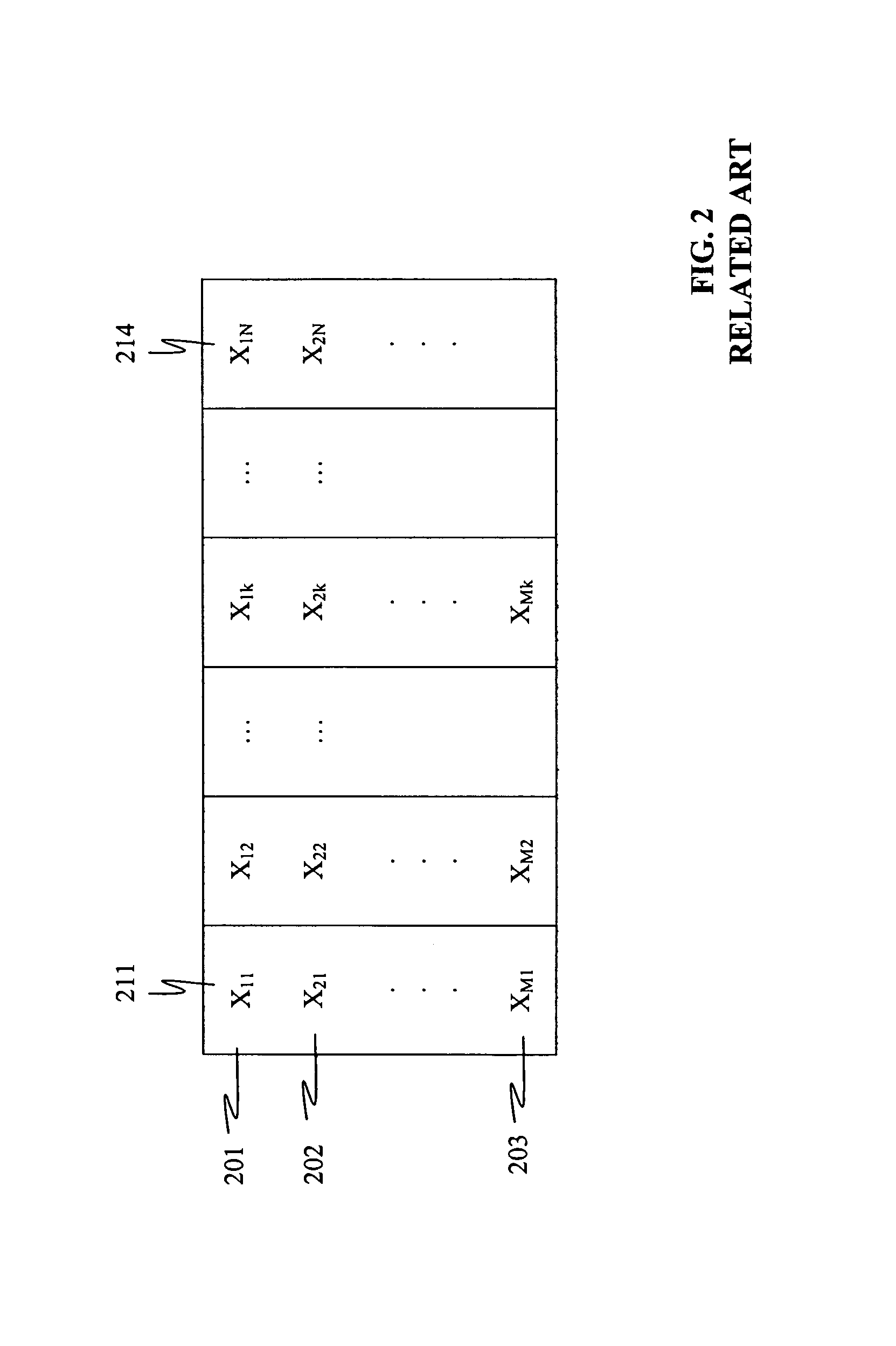
Addresses generation for interleavers in turbo encoders and decoders
InactiveUS7170432B2Adapt quicklyAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsInterleave sequenceTurbo encoder
An arrangement for generating addresses for interleaving / de-interleaving sequences (X1, X2, X3, . . . , XK) including a given number (K) of items, wherein each value for said given number (K) identifies a corresponding set of interleaving parameters (R, C, p, v). The arrangement has at least one memory unit wherein a plurality of records are stored, each record being indicative of a respective set of parameters (R, C, p, v) corresponding to at least one value for said given number (K). Sets of interleaving parameters (R, C, p, v) are thus available in the memory unit to be promptly and directly retrieved for all possible values of said given number of items (K). A preferred use is in turbo encoders / decoders for advanced telecommunications applications such as UMTS.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
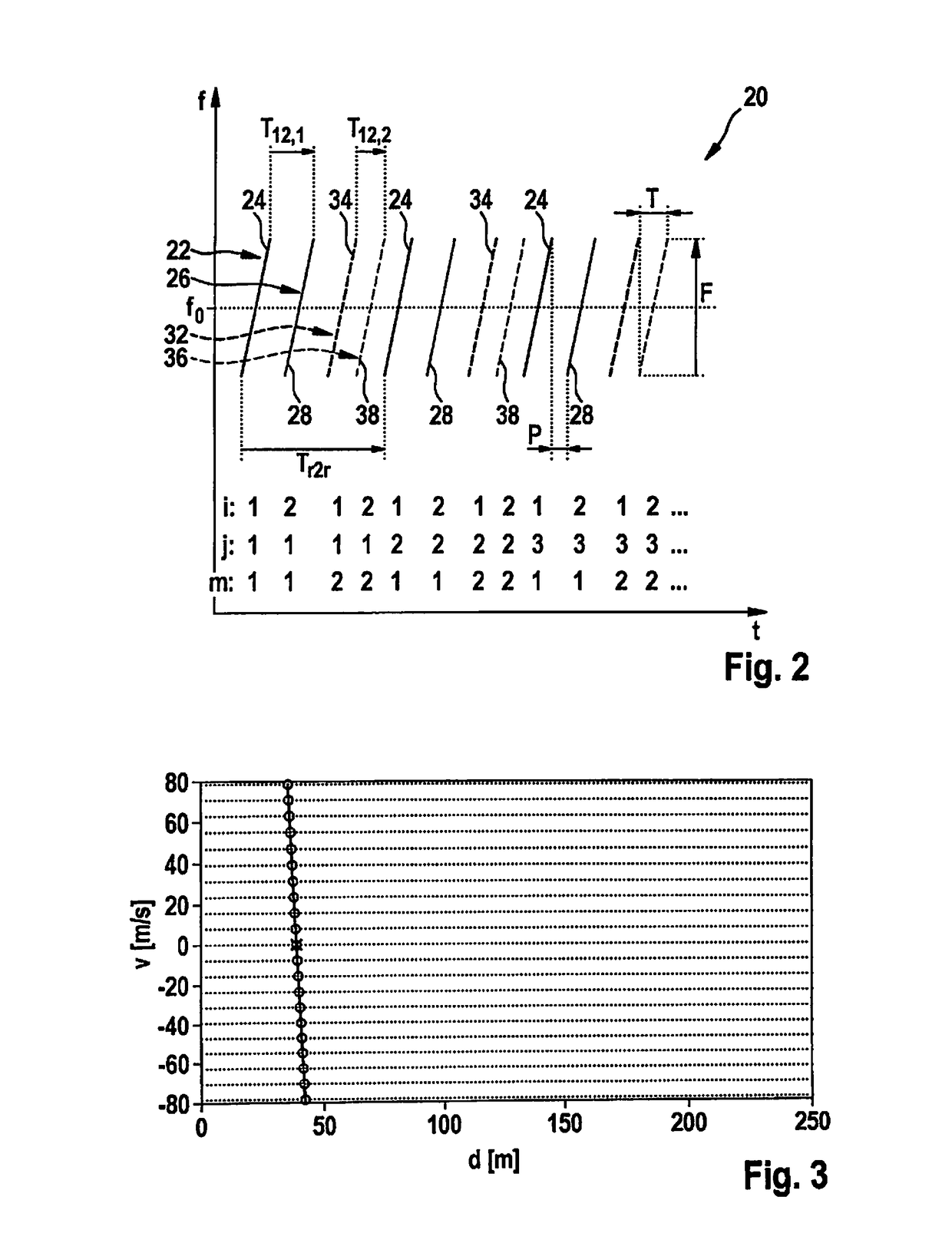
Radar measuring method
ActiveUS20170131396A1Accurate estimateHardware outlay can be reducedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumInterleave sequence
An FMCW radar sensor and method for determining a relative velocity of a radar target, in which an FMCW radar measurement is performed with a transmitted signal whose modulation pattern encompasses mutually temporally interleaved sequences of ramps; from the baseband signals a two-dimensional spectrum is calculated separately for each of the sequences; from a position of a peak in at least one two-dimensional spectrum of the baseband signals, values for the relative velocity of a radar target which are periodic with a predetermined velocity period are determined; a phase relationship between spectral values that are obtained respectively at the same position in the separately calculated two-dimensional spectra is checked for agreement with phase relationships expected for several of the determined periodic values of the relative velocity; and based thereon, an estimated value for the relative velocity of the target is selected from the determined periodic values of the relative velocity.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Addresses generation for interleavers in turbo encoders and decoders
InactiveUS20060109158A1Adapt quicklyAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsEncoder decoderInterleave sequence
An arrangement for generating addresses for interleaving / de-interleaving sequences (X1, X2, X3, . . . , XK) including a given number (K) of items, wherein each value for said given number (K) identifies a corresponding set of interleaving parameters (R, C, p, v). The arrangement has at least one memory unit wherein a plurality of records are stored, each record being indicative of a respective set of parameters (R, C, p, v) corresponding to at least one value for said given number (K). Sets of interleaving parameters (R, C, p, v) are thus available in the memory unit to be promptly and directly retrieved for all possible values of said given number of items (K). A preferred use is in turbo encoders / decoders for advanced telecommunications applications such as UMTS.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
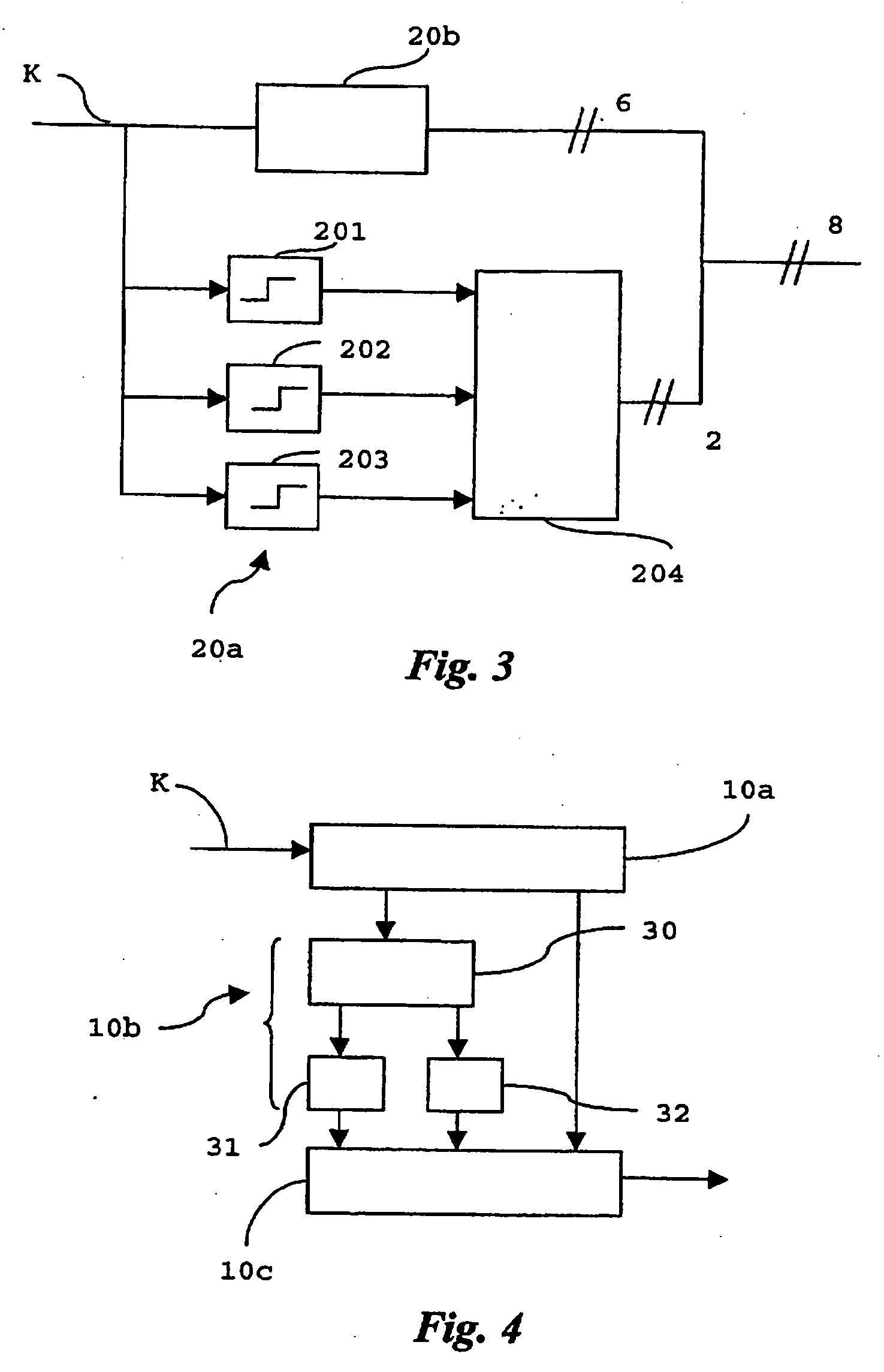
Interleaving for mobile communications
InactiveUS7269149B2Reduce complexityReduce delaysCode conversionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemInterleave sequence
A method for processing a bit sequence in a digital communication system, includes the steps of (a) storing the bits of said bit sequence at locations of a memory means indicated by a first interleaving scheme, (b) converting output bit positions into input bit positions according to an inverse of a second interleaving scheme, (c) reading out bits stored at locations of said memory means corresponding to said input bit positions, thereby generating an interleaved sequence which is interleaved according to said first and said second interleaving schemes, and (d) processing said interleaved sequence according to further physical processing steps. Alternatively, step (a) may include storing the bits of said input bit sequence in a memory means and step (b) may include converting output bit positions into input bit positions according to the inverse of a sequential application of a first interleaving scheme and a second interleaving scheme.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
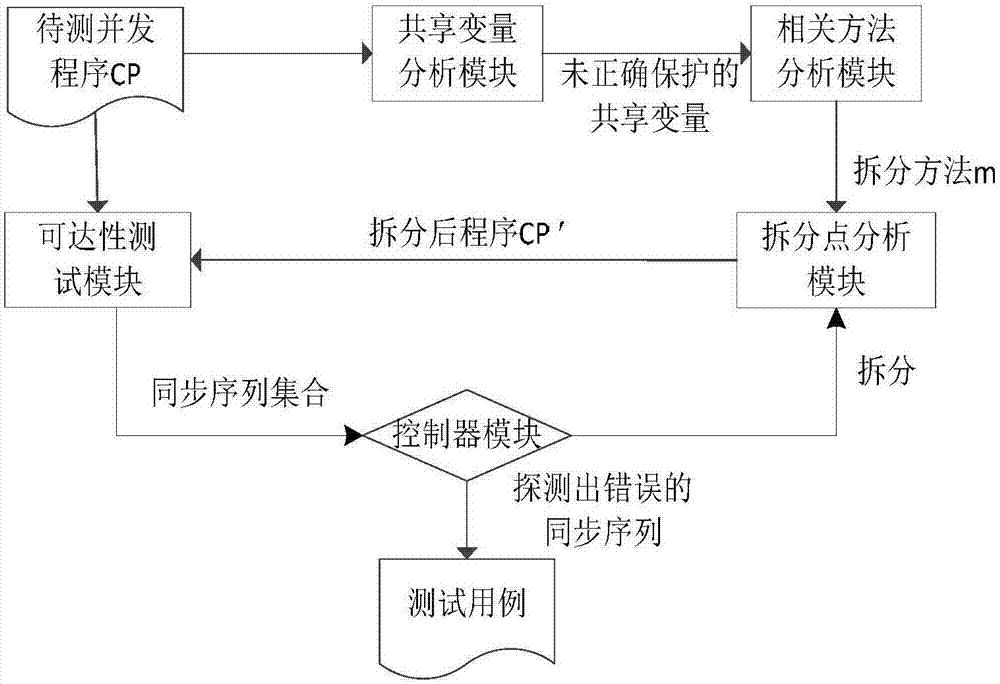
Concurrent-program test method based on lock-object splitting strategy and test system thereof
InactiveCN107391381AEfficient detectionImproved ability to detect such concurrent program errorsSoftware testing/debuggingProgram controlSoftware bugProgram testing
The invention discloses a concurrent-program test method based on the lock-object splitting strategy and a test system thereof. The concurrent-program test method includes the steps that relevant codes are analyzed with the static program analysis technology, and shared variables protected without same lock objects are determined; then abnormal access codes of the shared variables are split, the split codes are protected through the same lock objects, and the fine-grained synchronization method is generated; reachability testing (all feasible synchronization sequences are operated) is carried out, interleaved sequences between fine-grained synchronization events on different monitor objects in a raw to-be-test concurrent program are generated and carried out, and as the shared variables are protected through false lock objects, concurrent program errors such as data hazards, atomic against and deadlocking are shown. By means of the concurrent-program test method based on the lock-object splitting strategy and the test system thereof, the capacity of detecting the concurrent program errors can be effectively improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
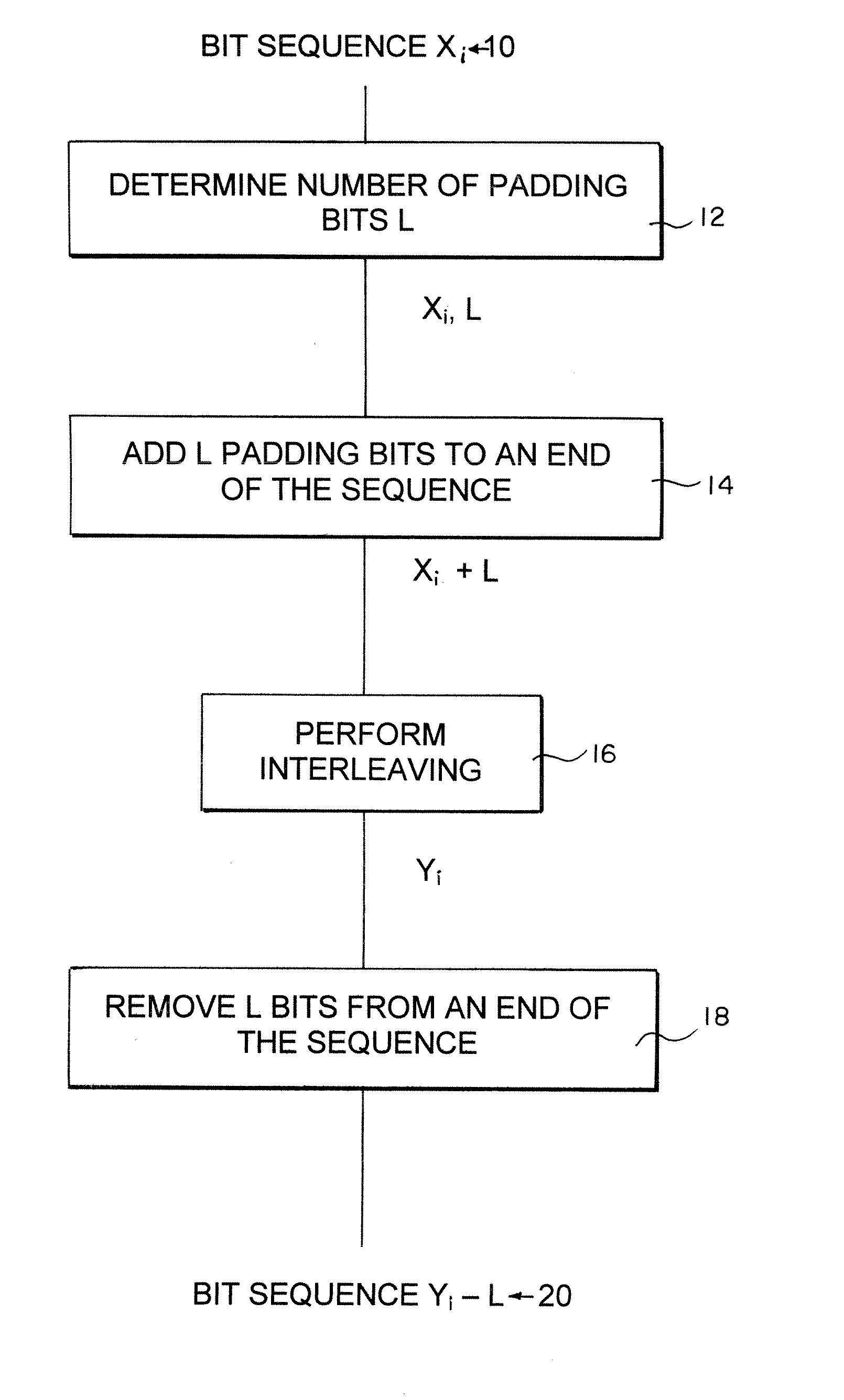
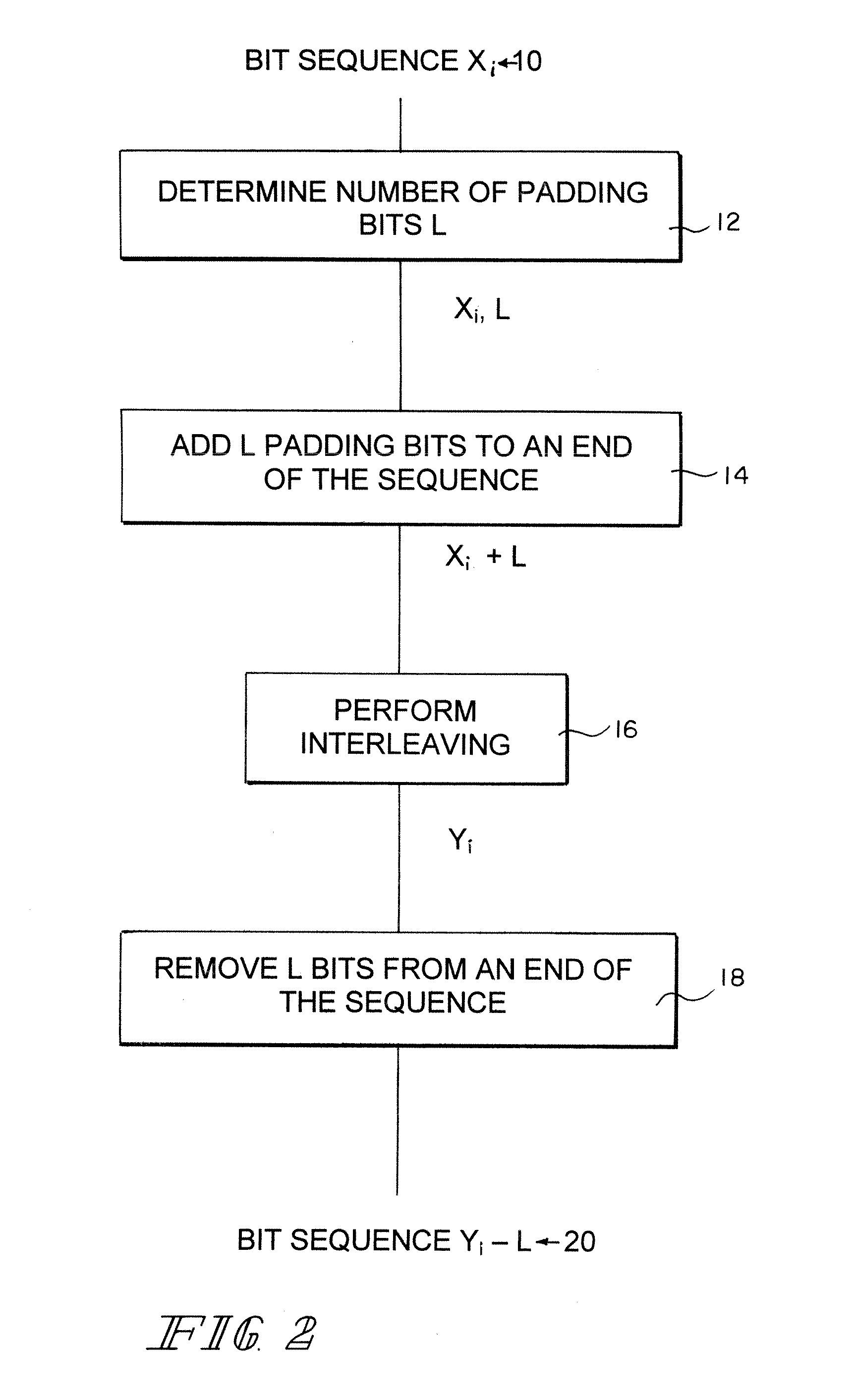
Method of first interleaving of a two interleaver transmitter
ActiveUS7236480B2Noise burstRapid development timeCode conversionRadio transmissionPresent methodInterleave sequence
The present invention involves padding the bit sequence in the first interleaver. The present method adds to an end of the bit sequence a sufficient number of padding bits L to permit modulus 16 operation of the bit sequence. After performing the interleaving, L bits are removed from an end of the interleaved sequence. This allows the interleaving to be performed in 16-bit segments simultaneously.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Radar measurement method with different fields of view
ActiveUS20170131393A1Improve overall utilizationLong rangeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionVisual field lossFrequency spectrum
An FMCW radar sensor and a method for localizing a radar target, in which FMCW radar measurements are performed with transmitting antennas having different fields of view which differ in terms of an aperture angle and / or a range, the measurements each encompassing temporally interleaved sequences of ramps, and measurements with different fields of view being temporally interwoven with one another; ambiguous values for the relative velocity of the radar target being determined from a position of a peak in a two-dimensional spectrum; phase relationships between spectral values of spectra being checked for agreement with phase relationships expected for several of the determined values of the relative velocity; and on the basis thereof an estimated value for the relative velocity of the radar target being selected from the determined periodic values of the relative velocity.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
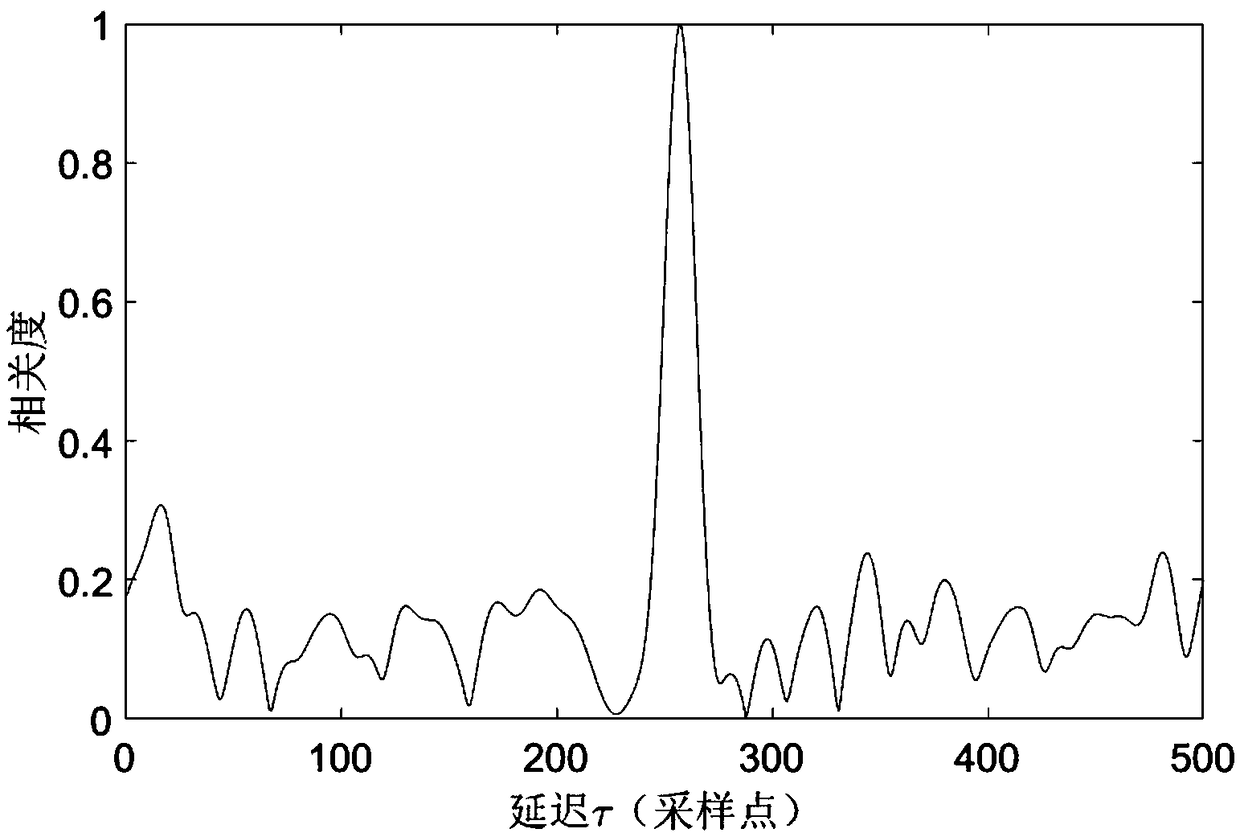
M-sequence pseudo random interleaving identification method in non-cooperated condition
ActiveCN106230556AEffectively complete the identification problemEasy to identifyForward error control useInterleave sequenceCorrelation function
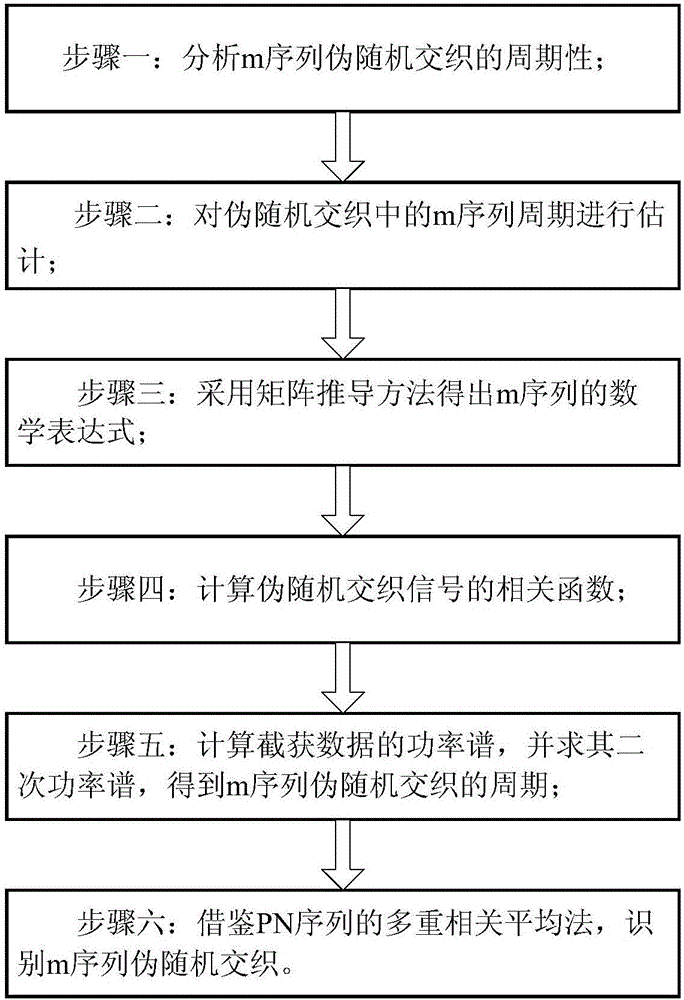
The invention discloses a m-sequence pseudo random interleaving identification method in a non-cooperated condition. The method comprises the steps of analyzing periodicity in m-sequence pseudo random interleaving, estimating a m-sequence period in pseudo random interleaving, obtaining a mathematical expression of a m-sequence e(t) according to a matrix derivation method, calculating a related function of a pseudo random interleaving signal f(t), calculating a related function of the pseudo random interleaving signal f(t), calculating the power spectrum of intercepted data, calculating a secondary power spectrum, deriving the period in m-sequence pseudo random interleaving, identifying m-sequence pseudo random interleaving in reference to a PN-sequence multi-scale correlation averaging method. The m-sequence pseudo random interleaving identification method can effectively settle a problem of identifying a pseudo random interleaving sequence in the non-cooperated condition. The m-sequence pseudo random interleaving identification method has advantages of simple process, high identification accuracy, high convenience in application, etc. Furthermore communication signal identification capability can be greatly improved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS ENG COLLEGE PLA
Apparatus and method for joint and time delayed measurements of components of conjugated quadratures of fields of reflected/scattered and transmitted/scattered beams by an object in interferometry
InactiveUS7161680B2Reduce sensitivityInterferometersUsing optical meansPhase shiftedInterleave sequence
A method of interferometrically obtaining measurements for properties associated with a spot on or in an object, the method involving: receiving a sequence of M optical pulses separated in time; from each pulse in the sequence of M optical pulses, generating an n-tuplet of measurement pulses, and an n-tuplet of reference pulses, wherein each measurement pulse has a corresponding reference pulse aligned with it in time; from each pulse of each n-tuplet of reference pulses for the sequence of M optical pulses, generating a reference beam; from each pulse of each n-tuplet of measurement pulses for the sequence of M optical pulses, (a) generating a measurement beam; (b) directing the measurement beam onto the spot to thereby produce a return measurement beam from the spot; and (c) combining the return measurement beam with the corresponding reference beam that was derived from the reference pulse corresponding to that measurement pulse to generate an interference beam, wherein the sequence of M n-tuplets of measurement pulses forms n interleaved sequences of M measurement pulses, and wherein the method further involves, for each of the n interleaved sequences of M measurement pulses, introducing a combination of phase shifts between the measurement beams and corresponding reference beams.
Owner:ZETETIC INST
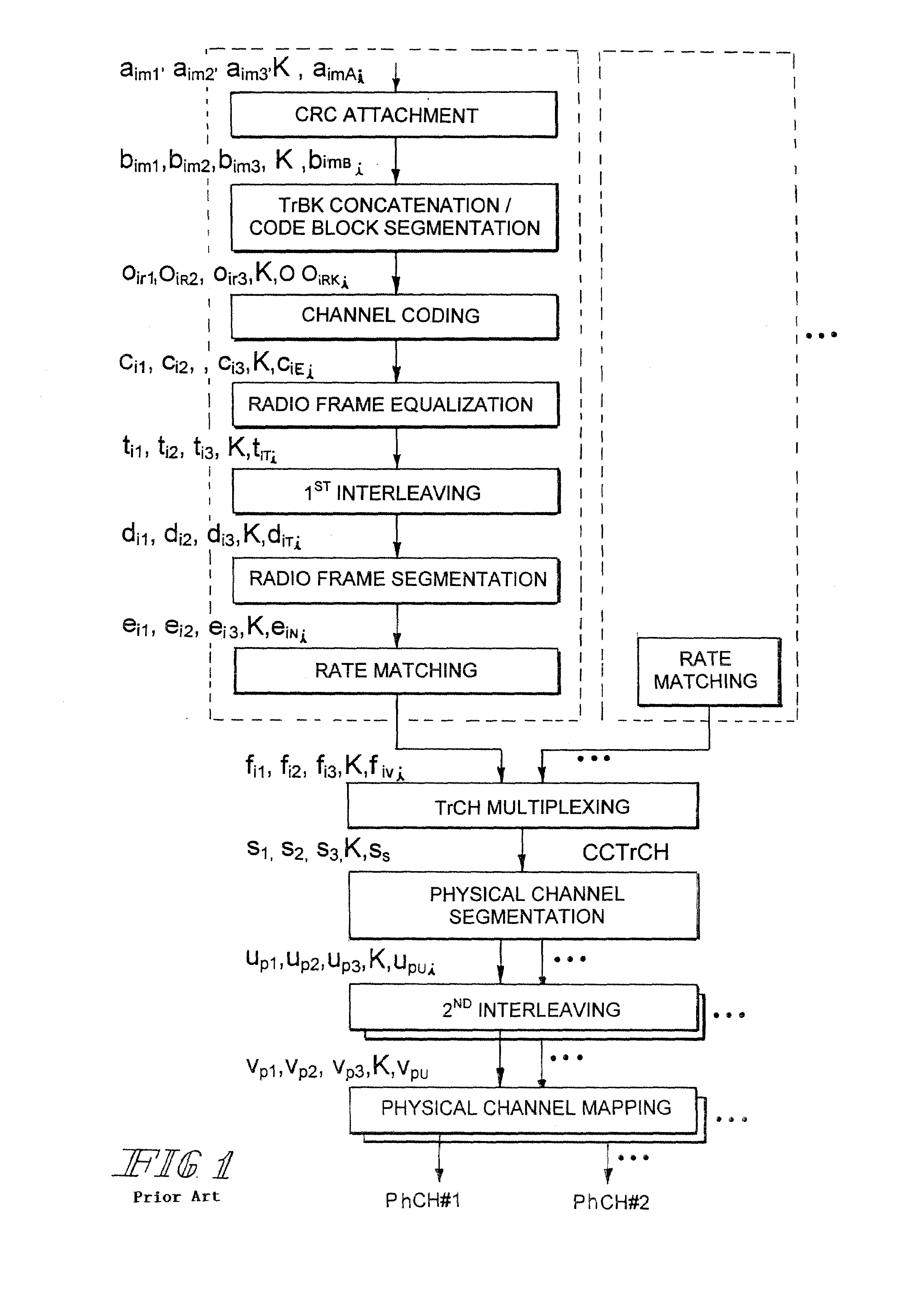
Encoding apparatus, decoding apparatus, encoding method, decoding method, and information recording and playback apparatus
InactiveUS20080001792A1Modulated-carrier systemsRecord information storageDecoding methodsInterleave sequence
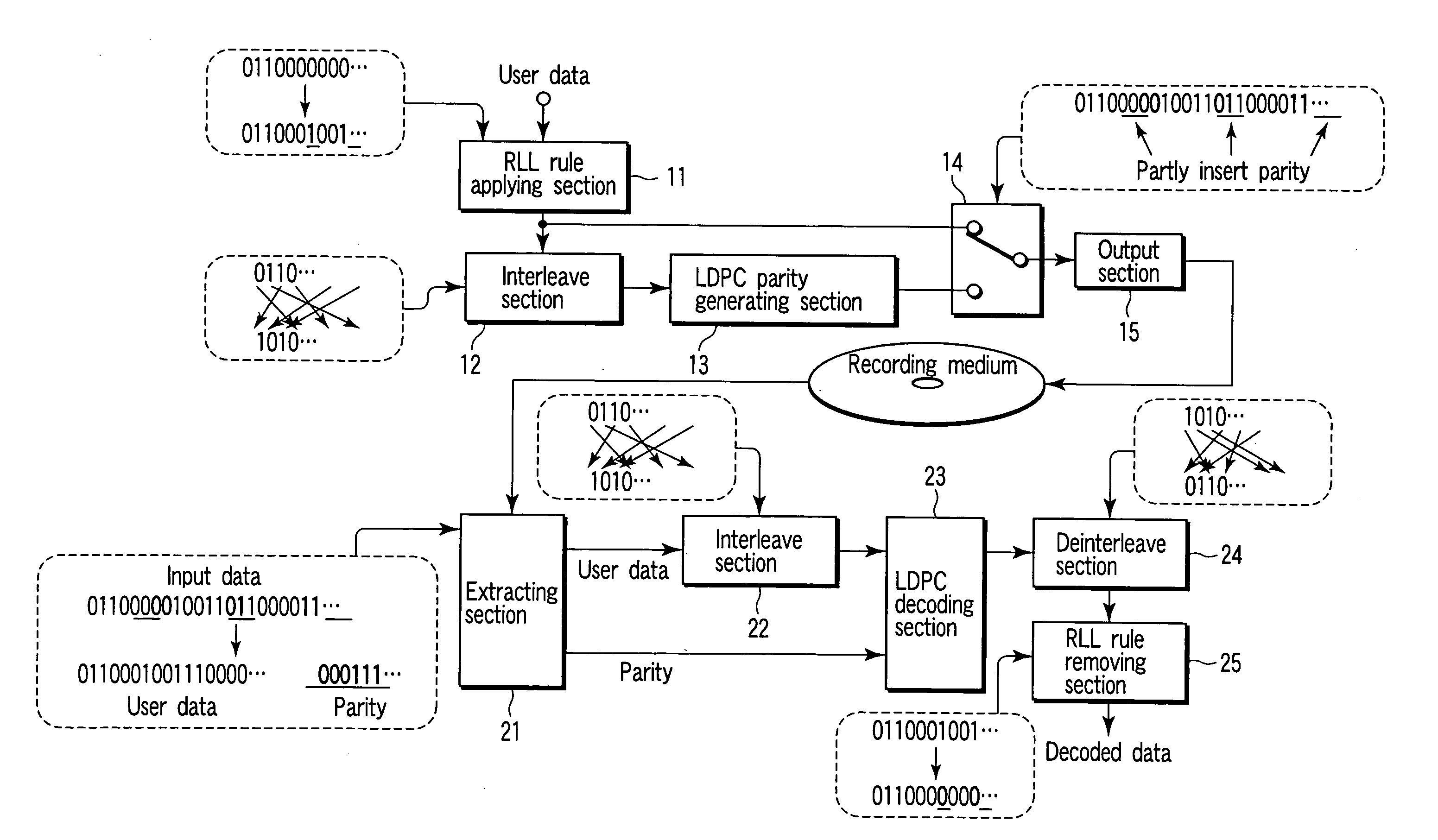
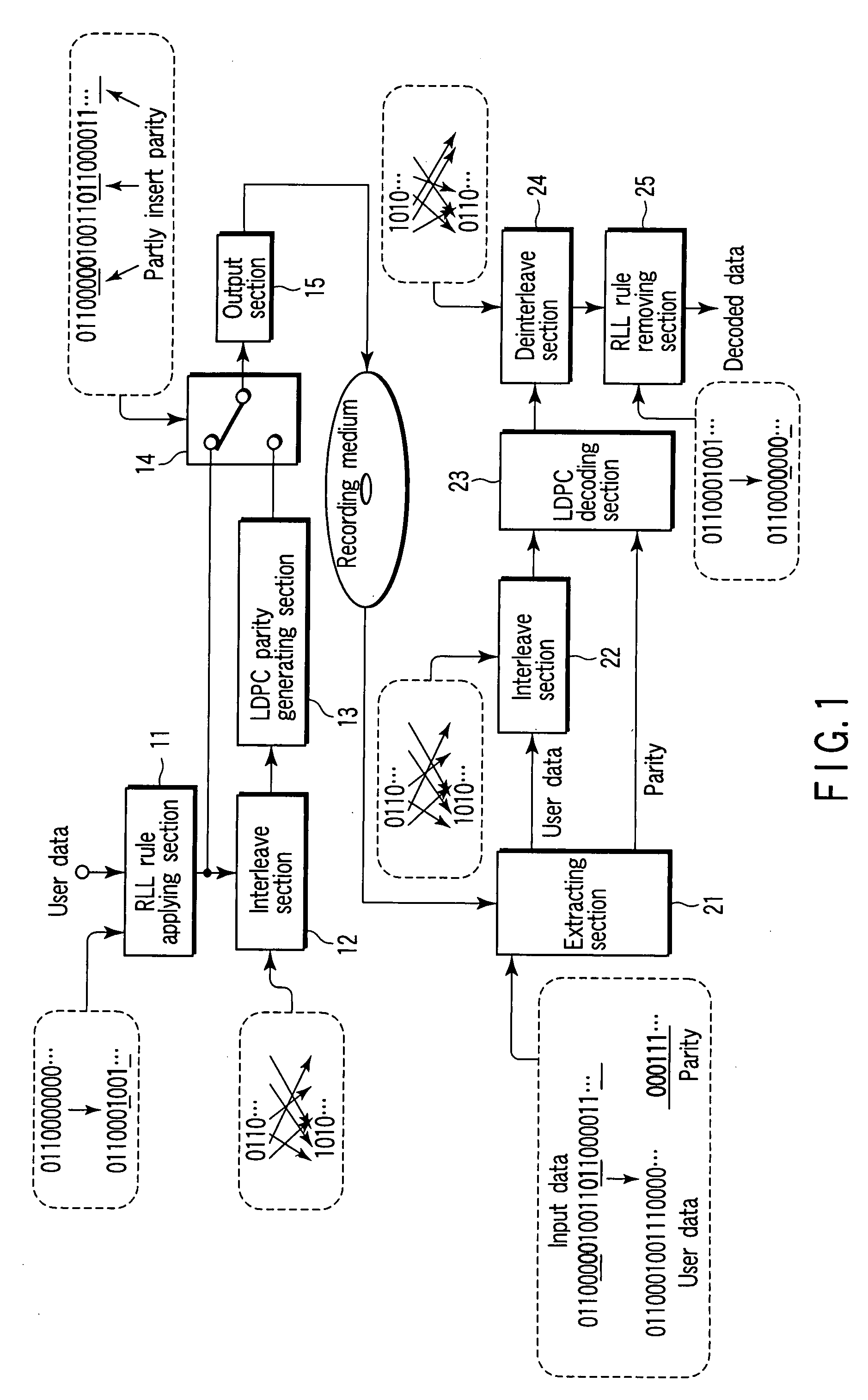
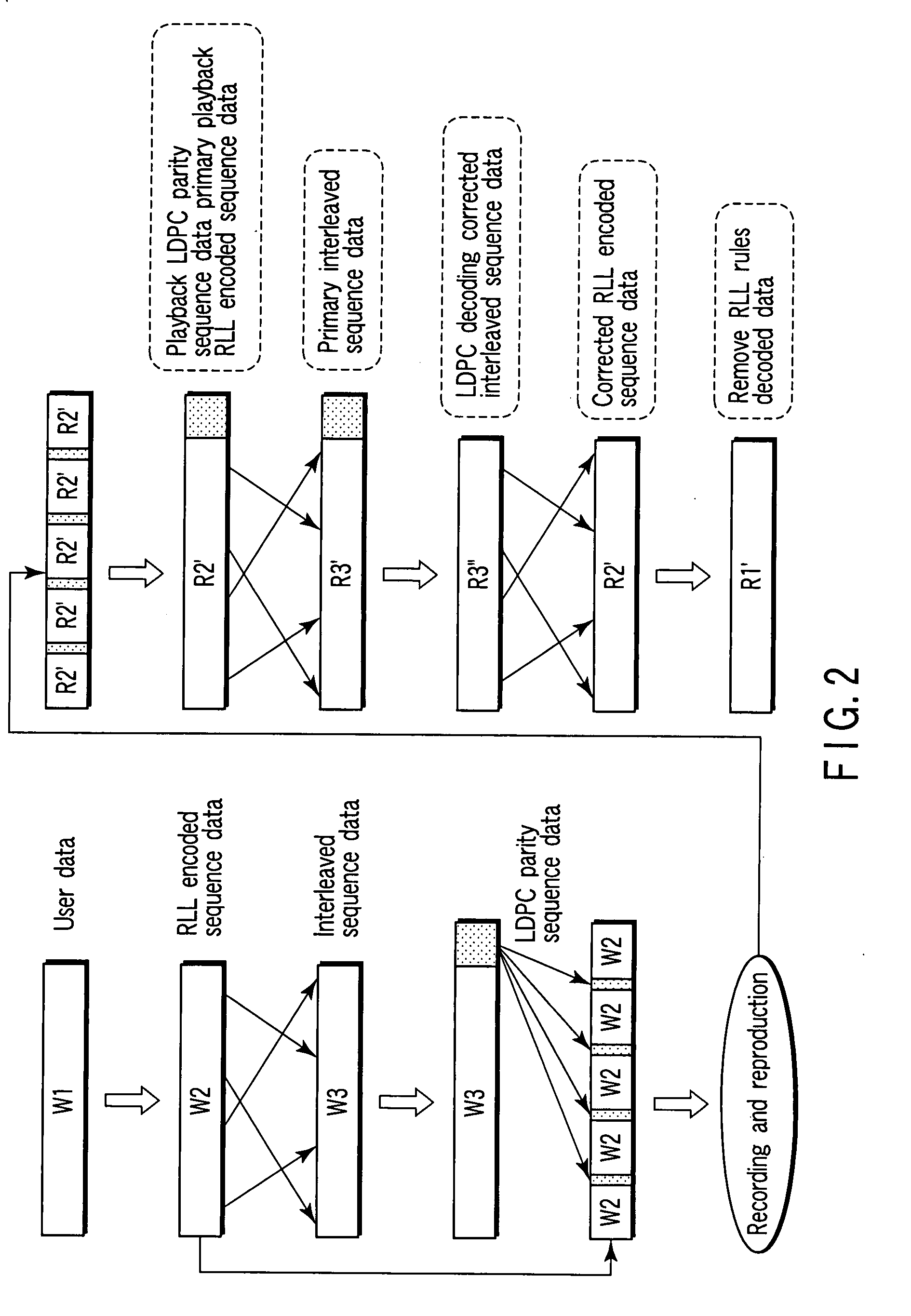
There is provided an apparatus which obtains a circumstance where LDPC codes are interleaved without damaging modulation rules and thereby a correction ability of LDPC encoding and decoding method is fully exhibited. The apparatus includes an RLL rule applying section which modulates user data by applying an RLL rule to the user data and thereby obtains RLL encoded sequence data, an interleave section which interleaves the RLL encoded sequence data and thereby obtains interleaved sequence data, an LDPC parity generating section which subjects the interleaved sequence data to LDPC encoding processing and thereby obtains LDPC parity sequence data, an inserting section which inserts parity of the LDPC parity sequence data in the RLL encoded sequence data in a distribution manner and thereby obtains output data, and an output section which records or transmits the output data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
MIMO radar measurement sensor
ActiveUS10416299B2Hardware outlay is decreasedPrecise positioningRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumTransmission switching
A MIMO FMCW radar sensor and a MIMO time multiplexing method for localizing a radar target, in which an FMCW radar measurement is performed with a transmitted signal whose modulation pattern encompasses, for different transmission switching states that differ in terms of the selection of antenna elements used for transmission, mutually temporally interleaved sequences of ramps; ambiguous values for the relative velocity of the radar target are determined from a position of a peak in a two-dimensional spectrum; phase relationships between spectral values of spectra are checked for agreement with phase relationships expected for several of the determined values of the relative velocity; on the basis thereof, an estimated value for the relative velocity of the radar target is selected from the determined periodic values of the relative velocity; and the angle of the radar target is determined on the basis of amplitudes and / or phase relationships between obtained baseband signals.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Error control device and method using cycle code
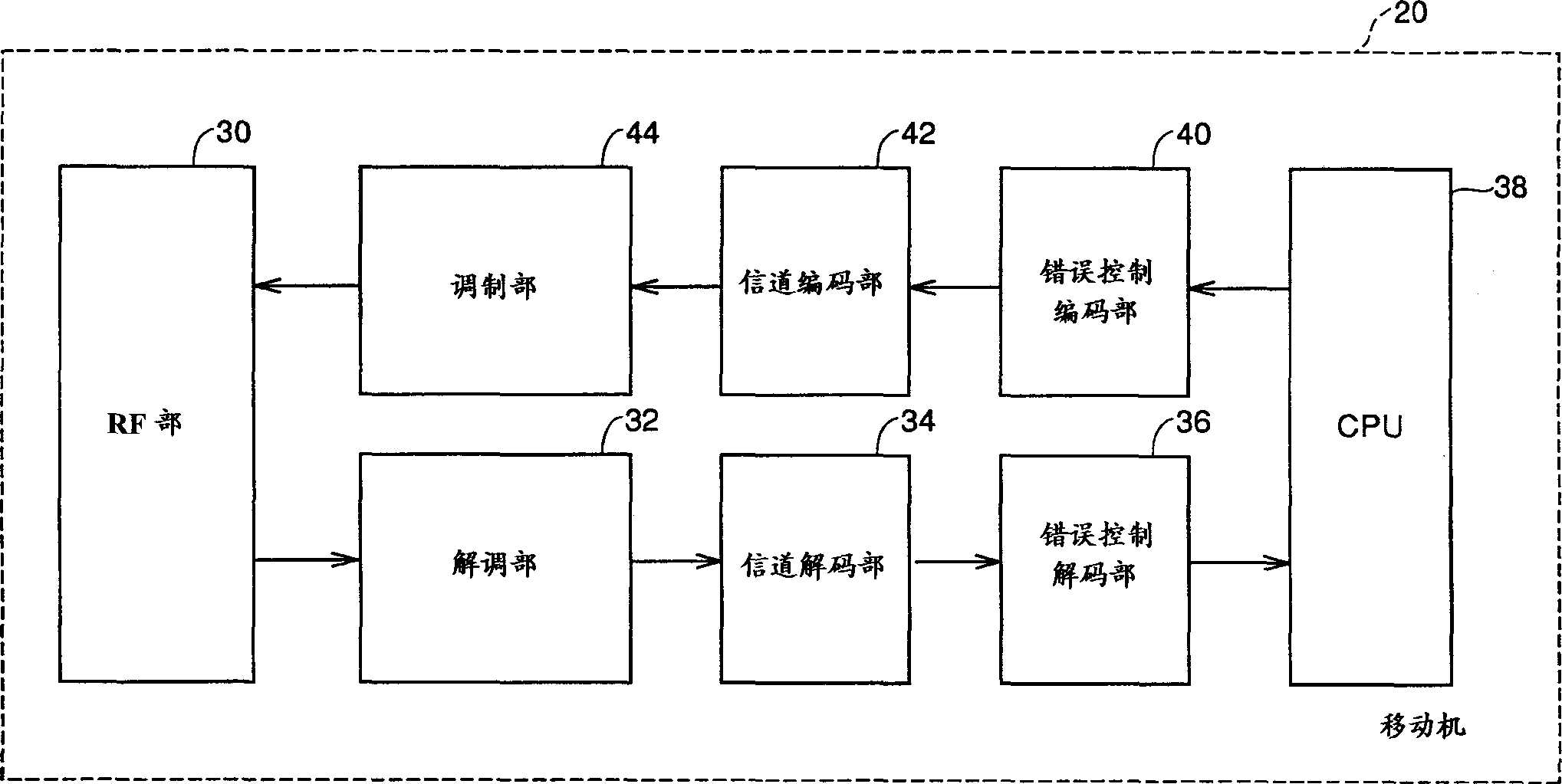
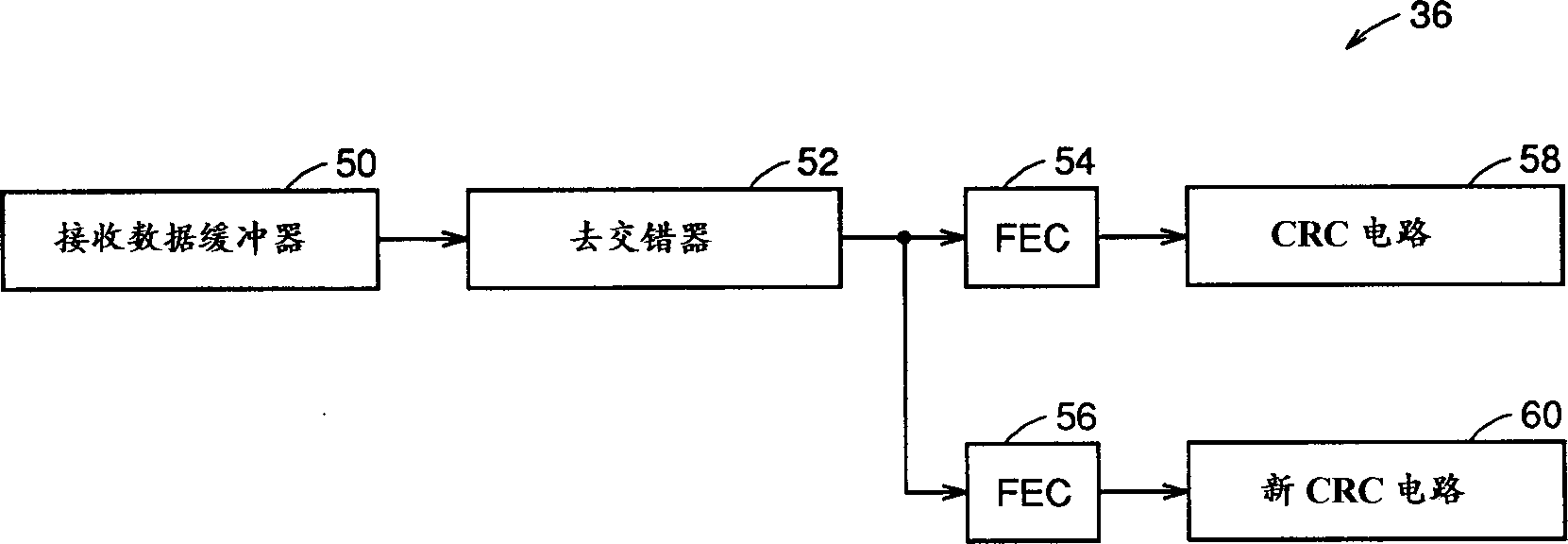
An error control device including a de-interleaver for de-interleaving data with a specfied number of bits which has been coded by a preset cyclic code and is scheduled to be interleaved in a present interleaving sequence, a first cyclic code inspection circuit for performing a cyclic code inspection on the data with the specified number of bits using an inspection method in conformity with a cyclic code coding system on receiving an output from the de-interleaver, and a second cyclic code inspection circuit for performing a cyclic code inspection on the data with the specified number of bits using an inspection method in conformity with a cyclic code coding system while canceling an interleaving effect by the de-interleaver concurrently with the cyclic code inspection by the first cyclic code inspection circuit and within a virtually identical time on receiving the output from the de-interleaver.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
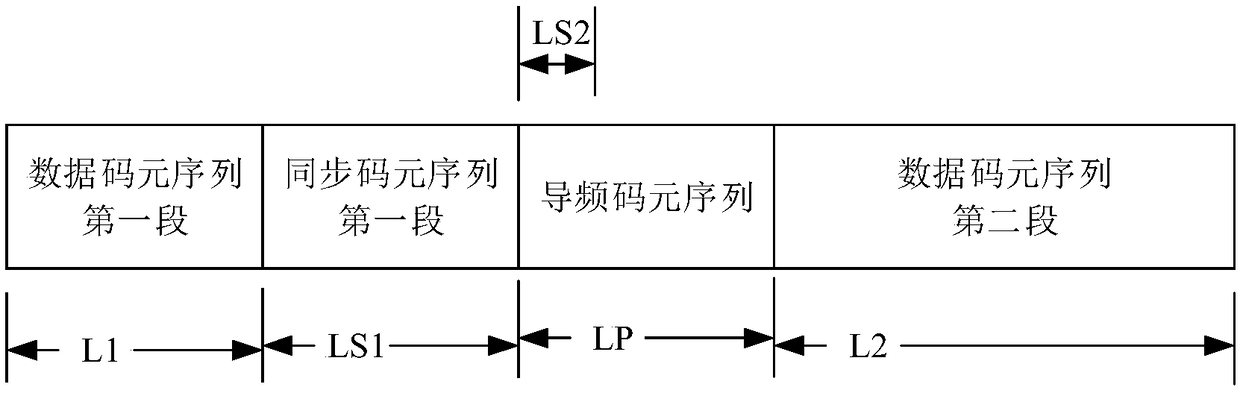
Frame structure for wireless communication and signal processing method thereof
ActiveCN109120378AReduce distanceSimple demodulationMulti-frequency code systemsForward error control useInterleave sequenceCoded element
The invention discloses a frame structure for wireless communication and a signal processing method thereof. The frame structure for wireless communication is composed of a data code element sequence,a pilot frequency code element sequence and a synchronous code element sequence, wherein a pilot frequency code element sequence of a length LP is inserted between two segments of data code element sequence; the first segment of the synchronous code element sequence with a length LS1 is inserted between the first segment of data code element sequence and the pilot frequency code element sequence;and the first LS2 code elements of the pilot frequency code element sequence are also the second segment of the synchronous code element sequence. The signal processing method of the frame structurefor wireless communication includes the steps: performing channel coding on the input data to obtain a coding sequence; performing XOR on the coding sequence and a scrambling code sequence to obtain ascrambling sequence; performing interleaving on the scrambling sequence to obtain an interleaving sequence; mapping the interleaving sequence to a data code element sequence; combining the code element sequences to form an uplink frame according to the above frame structure; and performing code element upsampling on the code element sequences of the uplink frame to obtain an uplink signal to be transmitted. The frame structure for wireless communication and the signal processing method thereof make full use of channel resources and can reduce the cost of transmitting pilot frequency and synchronous signals.
Owner:SHANGHAI TAOLINK TECHNOLOGIES CORPORATION
UDIF cooperation strategy and a JMC-TED detector for underwater acoustic cooperative communication
ActiveCN109818715AImprove performanceLower end-to-end latencyError preventionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMultiuser systemSteady state mean square error
The invention relates to the technical field of underwater acoustic cooperative communication systems, in particular to a UDIF cooperative strategy and JMC-suitable for a multi-user system and capableof saving end-to-end delay and used for underwater acoustic cooperative communication. The TED detector can still extract signals of the source node and the relay node according to different interleaving sequences even if interference exists between data packets, and meanwhile, the scheme can also reduce the end-to-end delay time; JMC-disclosed by the invention The TED detector combines the multiple branches to realize multi-branch combination; Turbo equalization and multi-user detection are carried out; The source node and the relay node use different interleaving sequences; therefore, the received signals cannot be directly combined; the signals are combined after de-interleaving processing; The combination coefficient is obtained on the basis of an output steady-state mean square error(SMSE) of each branch detector and is updated during each time of Turbo iterative processing, the method and the device can adaptively combine a plurality of received signals passing through different paths without knowing the CSI between the nodes, and are more suitable for an actual underwater acoustic cooperative communication system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
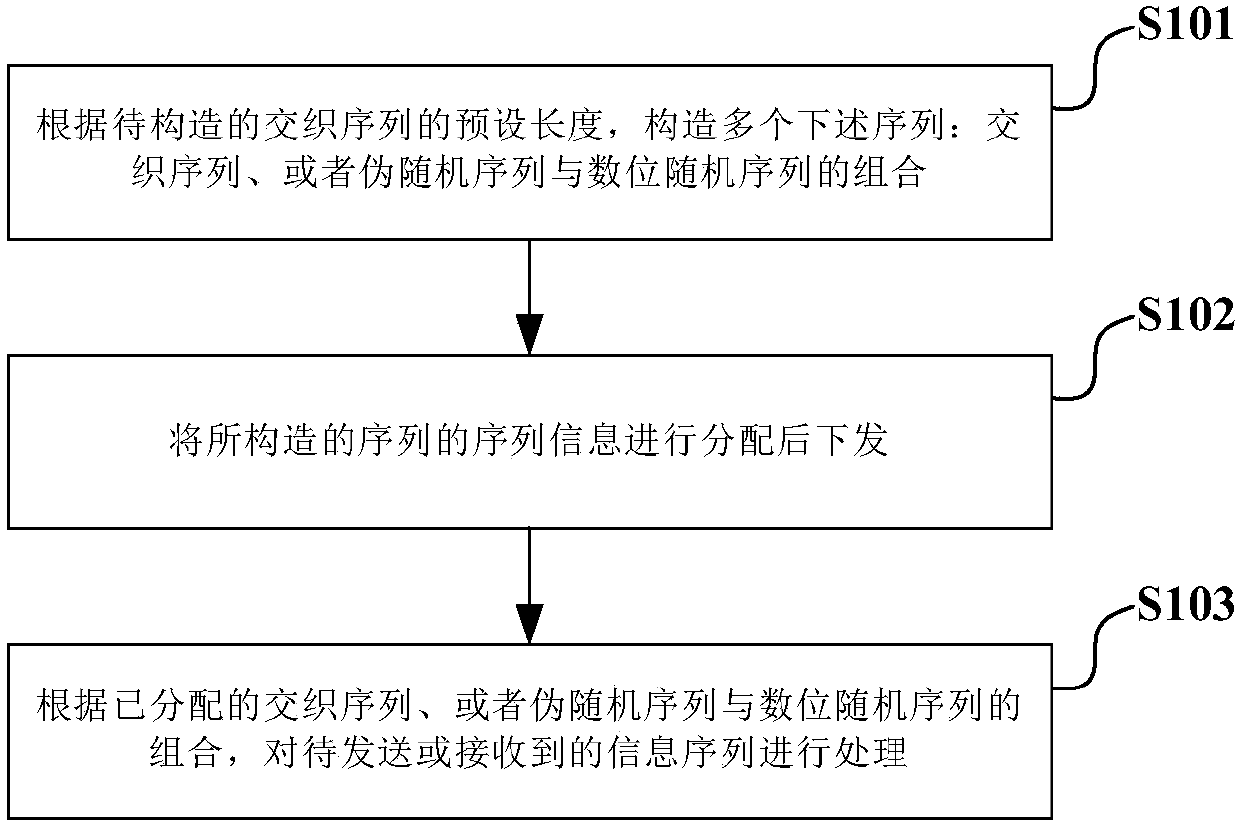
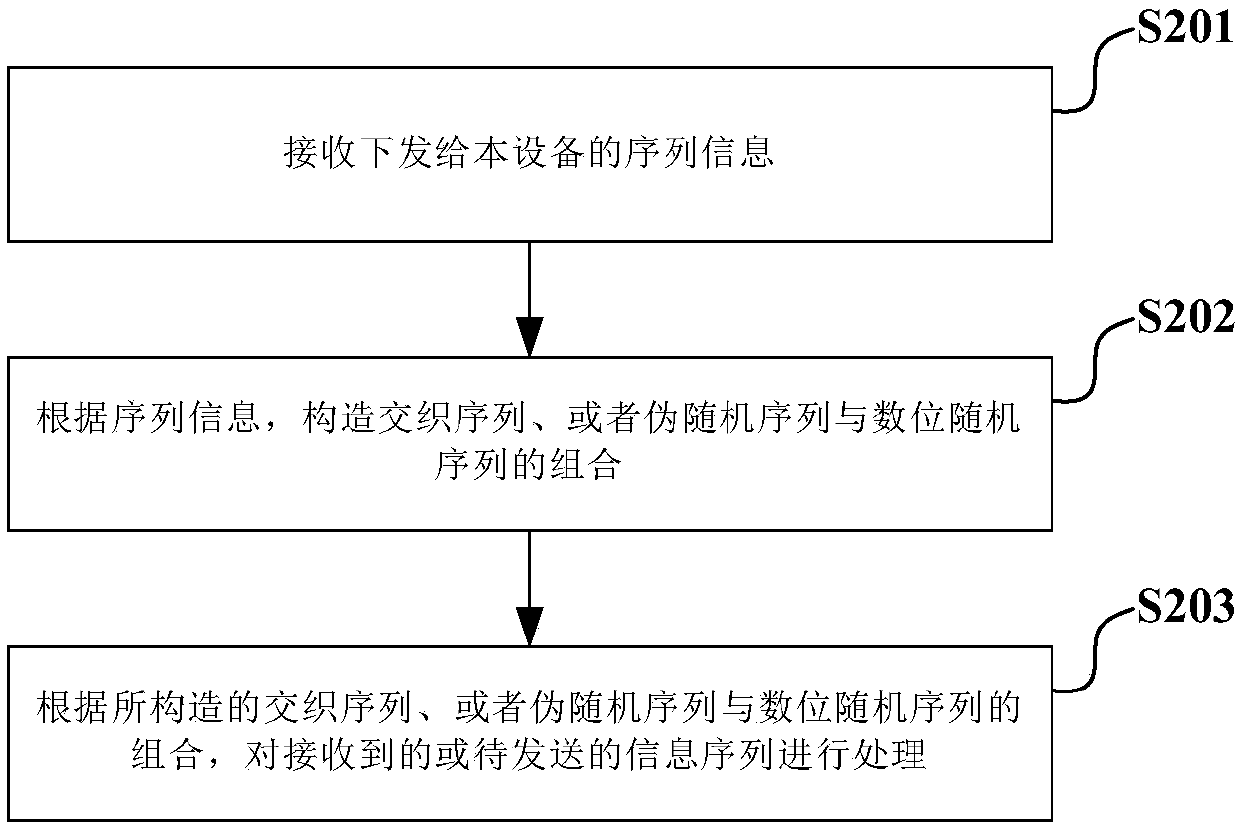
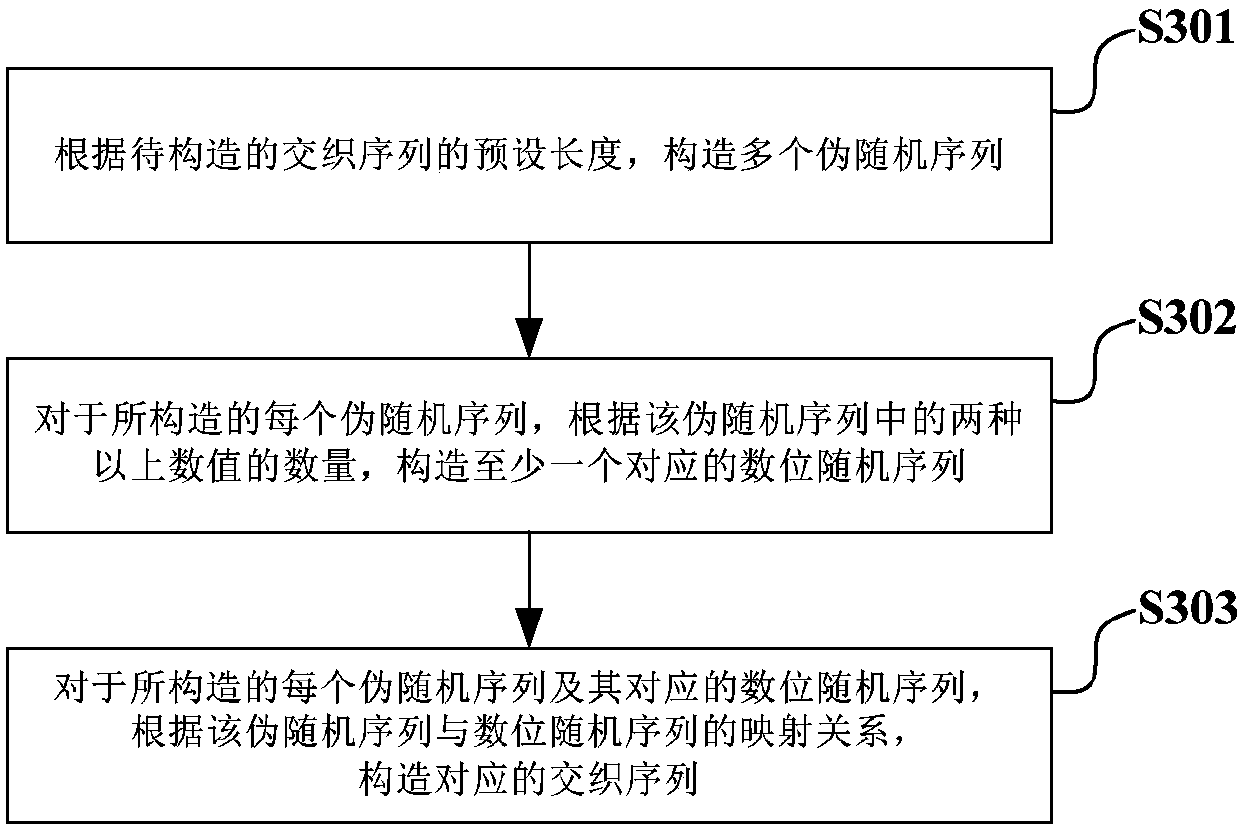
Interleaved sequence constructing method, interleaving-based information processing method and transceiver
ActiveCN107769842AOptimize allocationSmall amount of calculationCode conversionRadio transmission for post communicationInformation processingTransceiver
An embodiment of the invention provides an interleaved sequence constructing method, an interleaving-based information processing method and a transceiver. The interleaved sequence constructing methodcomprises the steps of constructing a plurality of pseudo random sequences according to the preset length of a to-be-constructed interleaved sequence; for each constructed pseudo random sequence, constructing at least one corresponding numerical digit random sequence according to the numbers of more than two kinds of numerical values in the pseudo random sequence; and for each constructed pseudorandom sequence and the corresponding numerical bit random sequence, and constructing a corresponding interleaving sequence according to a mapping relation between the pseudo random sequence and the numerical digit random sequence so that a plurality of interleaving sequences are used as a multiple-access resource for distribution. According to the interleaved sequence constructing method, relatively low computation amount and relatively short time delay are realized in a construction mode of combining the interleaved sequence or pseudo random sequence and the numerical digit random sequence;the combination of the interleaved sequence, or the pseudo random sequence and the numerical digit random sequence is used as a multiple-access user identification, thereby facilitating distribution to the receiver at the user end and facilitating standardization.
Owner:BEIJING SAMSUNG TELECOM R&D CENT +1
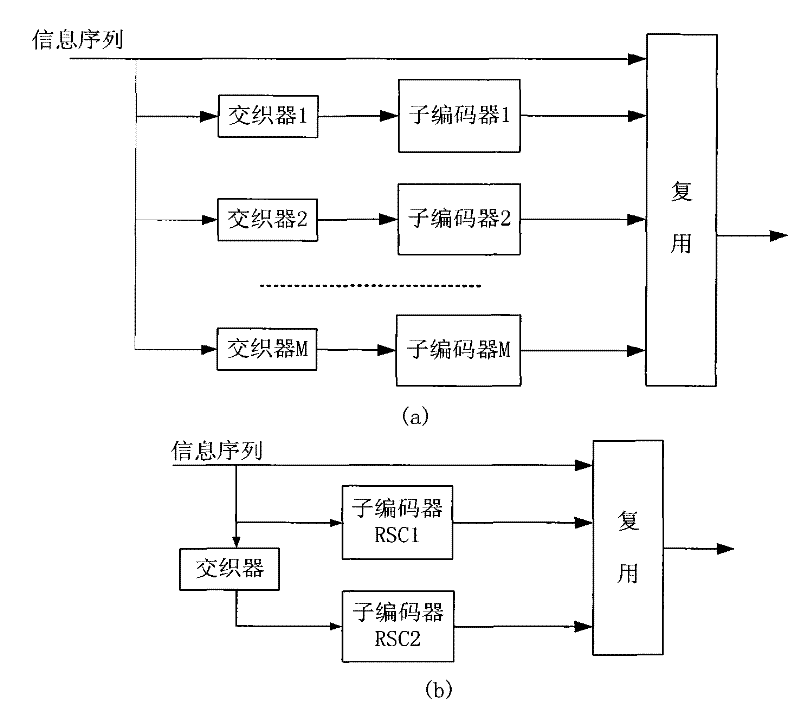
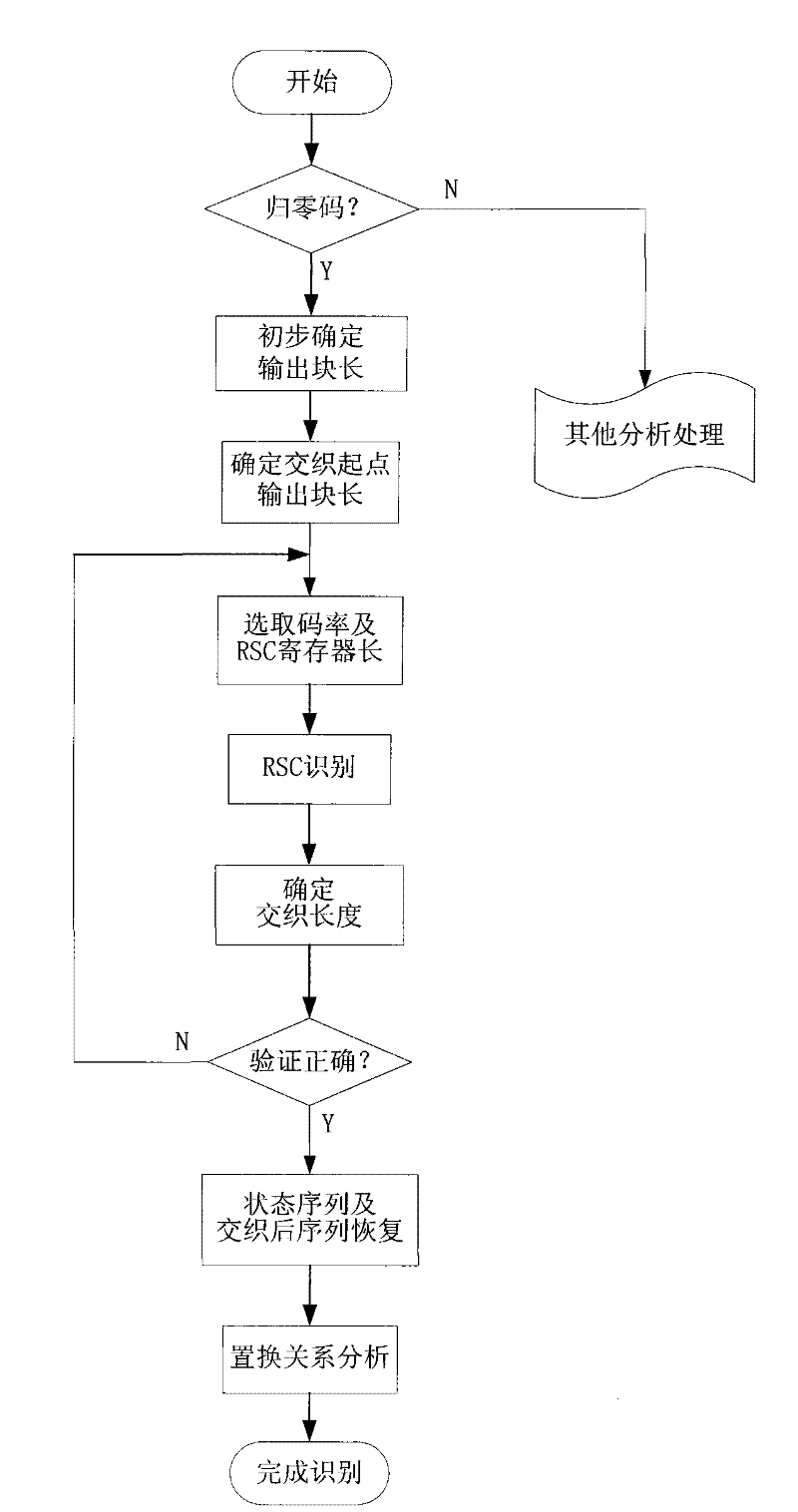
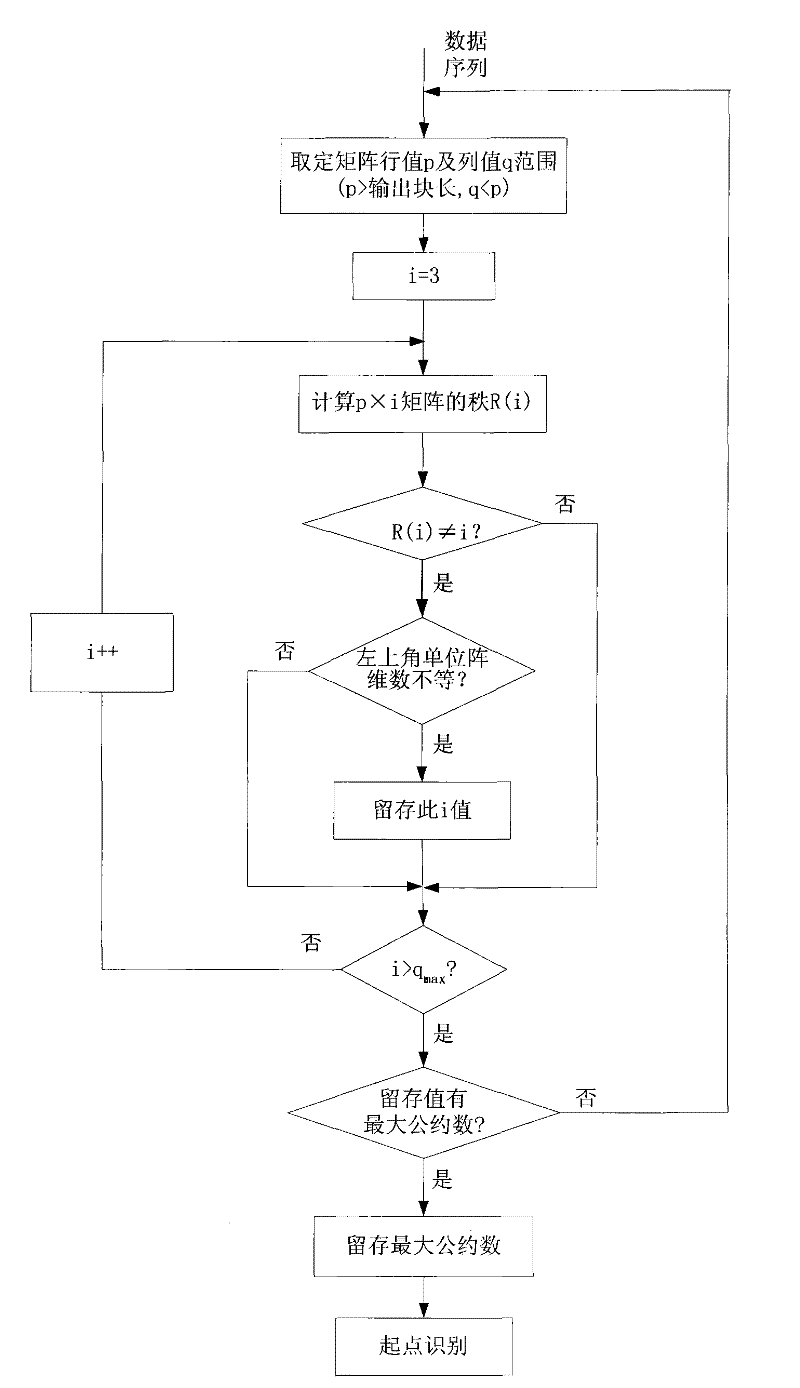
Blind identification method for coding parameter of return-to-zero Turbo code
InactiveCN102244521ARealize blind recognitionClear processError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesInformation processingReturn-to-zero
The invention discloses a blind identification method for a coding parameter of a return-to-zero Turbo code. According to the invention, after a length of an output block and an origin of an interlacing frame of a return-to-zero Turbo code are preliminarily determined by a linear transformation, a code rate of the return-to-zero Turbo code and a length of an RSC register of the return-to-zero Turbo code are estimated; an RSC generator polynominal is determined by constructing an identification sequence of a convolutional code; simultaneously, accuracy of the estimated code rate and the estimated length of the register are determined according to the identified RSC generator polynominal. On the basis of an interlacing length and an interlacing origin, wherein the interlacing length and the interlacing origin are obtained by an analysis, an interlacing sequence is recovered and obtained; and further, an interlacing relation in the return-to-zero Turbo code is finally determined by an exhaustive comparison method. The blind identification method for the coding parameter of the return-to-zero Turbo code provided in the invention is suitable for fields like intelligent communication and information processing and the like.
Owner:36TH RES INST OF CETC
Generation method of variable length S random interleaver
InactiveCN102227097AGuaranteed Bit Error PerformanceReduce computational complexityError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesComputation complexityData set
The invention provides a generation method of a variable length S random interleaver. According to the method, a known S random interleaver having a limited length (assume the length is K) is utilized to be a reference interleaver to carry out a bitwise iteration expansion and an S random interleaver having an arbitrary length which is larger than K is generated based on an expansion characteristic condition of the reference interleaver. The expansion coefficient of the reference interleaver is adopted as the expansion coefficient parameter of the bitwise iteration expansion process to make the generated new S random interleaver can possess a diffusion performance equivalent to that of a reference interleaver, thereby guaranteeing the bit error code performance of the newly generated S random interleaver. Besides, the bitwise iteration expansion process only needs to carry out adding and subtracting operations; hence the calculating complexity is low. It is only necessary to store in the database of the generated interleaver the interlacing sequence [pai] k of the reference interleaver and the corresponding input bit sequence number jN of the interlacing address N of the bitwise expansion in an input data set; hence memory resources are saved, the interlacing time delay is reduced and the interlacing efficiency of the interleaver is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Encoding method and device
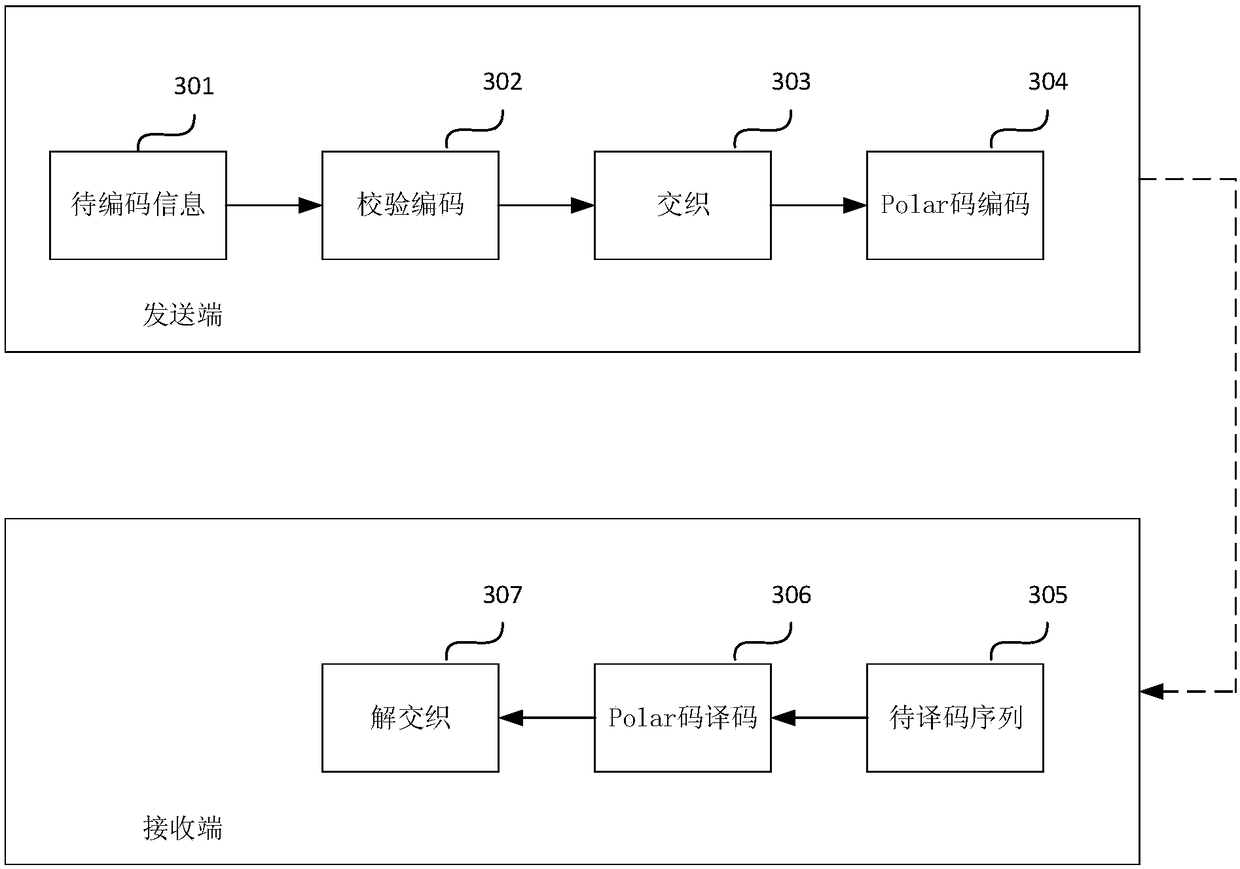
ActiveCN108809506AAvoid wastingImprove decoding efficiencyCode conversionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesInterleave sequenceTheoretical computer science
The application relates to the technical field of communications, and discloses an encoding method and an encoding device, used for providing a new means of checking encoding. The method comprises: atransmitting terminal checks and encodes the information to be encoded to obtain a check encoding codeword, wherein the length of the information bit in the check encoding codeword is K, and the length of the check bit is J; the transmitting terminal performs an interleaving operation on the check encoding codeword, wherein the interleaving sequence S used by the interleaving operation comprises Jsub-sequences, the i-th sub-sequence comprises the position index value and (K+i) value with the element 1 in the intermediate result vector Ti, i is not less than 1 and not greater than J, i is an integer, Ti is equal to (-M)&(Vi), M is equal to m | (Vi), Vi is a column vector of the check part matrix P, P is a sub-matrix of the check encoding system form generator matrix G; - represents a bitwise NOT operation, & represents a bitwise AND operation, and | represents a bitwise OR operation; and the transmitting terminal performs Polar encoding on the check encoding codeword after the interleaving operation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com