Continuous elimination list decoding method of software polarization code
A polar code and decoding technology, applied in data representation error detection/correction, using linear codes for error correction/detection, using block codes for error correction/detection, etc., can solve the problem of reducing path update complexity and affecting translation Code speed, complexity increase, etc., to achieve obvious acceleration effect, reduce path update delay, and reduce the number of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] Below in conjunction with specific examples and accompanying drawings, the continuous elimination list decoding method of the software polar code in the present invention is specifically explained and illustrated. code, the code length is N, and the information bit length is K.
[0018] 1. Initialization of the reference matrix
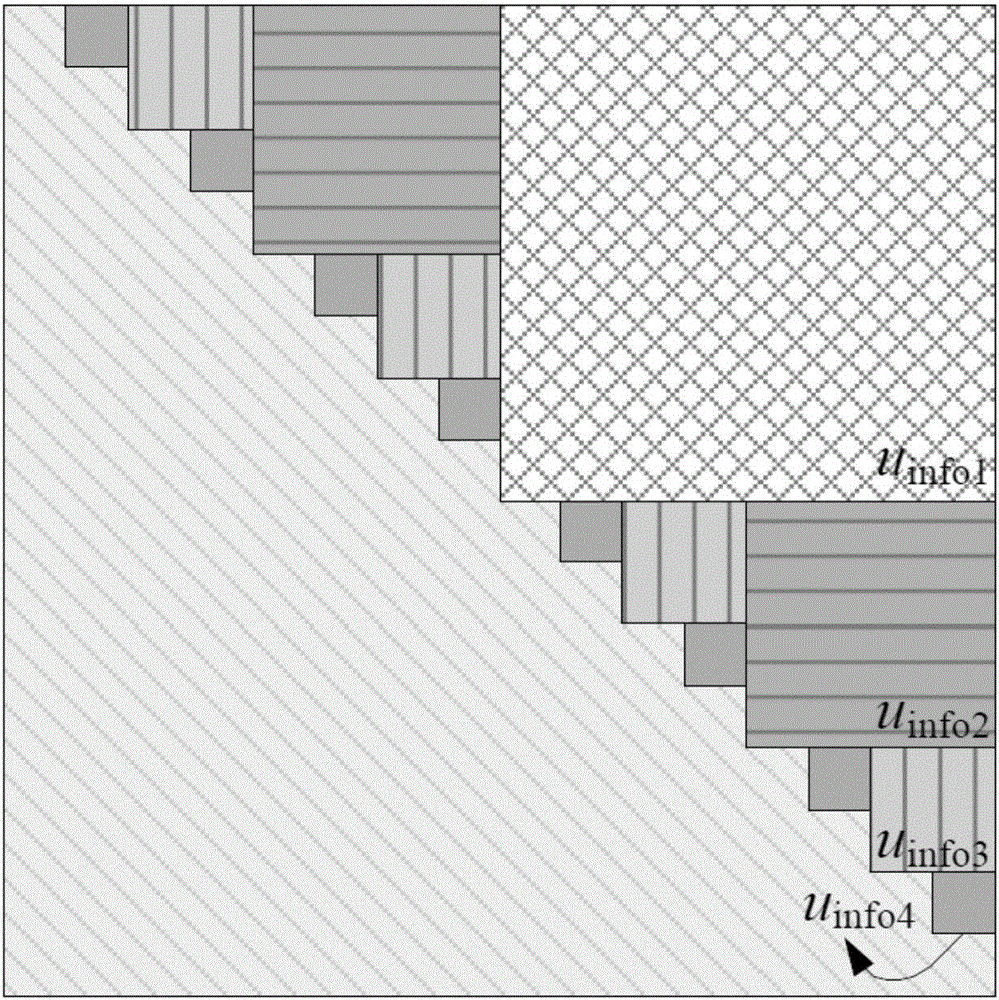
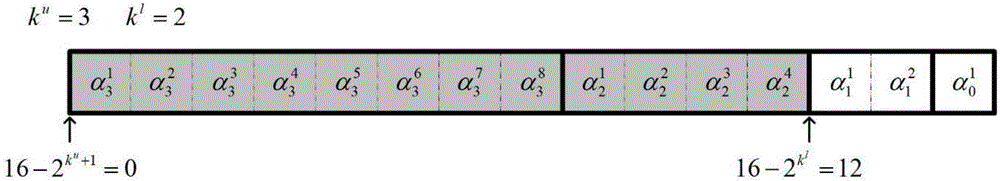
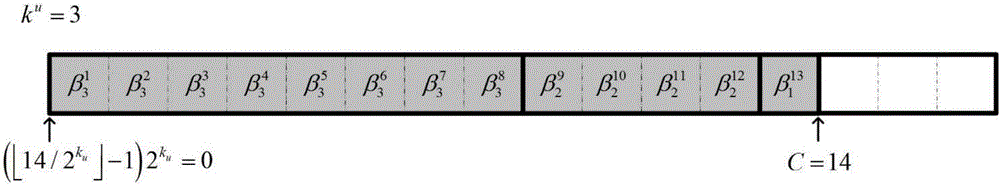
[0019] It is not enough to determine the bounds of replication by the position of the current bit, we need to know the distribution of different bits in the estimates of the new path and the old path. Since it is impossible to predict which path will replace this path when translating the current bit, it is necessary to record all possible situations. A reference matrix A is established to record the position of the first different bit between each pair of paths. There are on the path. Therefore, A is a strictly upper triangular matrix of L×L, containing elements, each of which is labeled a ij , i<j.
[0020] in the initial log 2 Matr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com