Finite element boundary integral method for rapidly analyzing electromagnetic scattering properties of non-uniform targets
A target electromagnetic scattering and boundary integration technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as limiting solution efficiency, large unknowns in boundary surfaces, etc., reducing algorithm complexity and easy program implementation. , the effect of reducing far-field memory requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
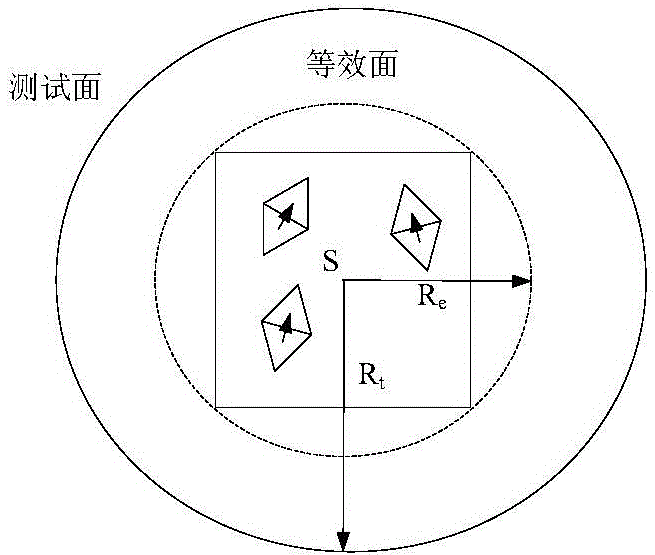
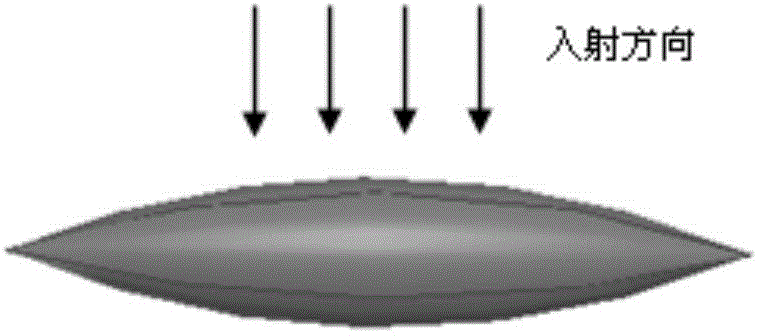
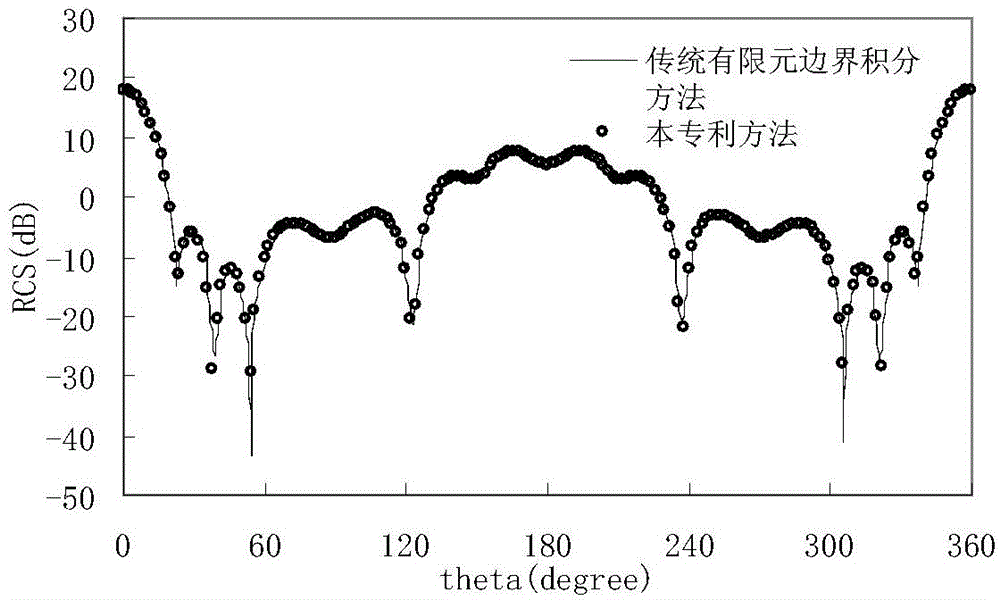
[0057] In this embodiment, a typical simulation of electromagnetic scattering is carried out. The simulation is implemented on a server with a main frequency of 2.0GHz and a memory of 512GB. The pointed arch model with dimensions of 3.49m, 0.698m, and 0.698m in x, y, and z directions is E.g figure 2 As shown, the surface has a coating with a thickness of 0.03m and a relative permittivity of (4.0, 0.5). The model was subdivided with a subdivision size of 0.03λ, and 41570 tetrahedrons and 13138 triangular elements were obtained. A three-layer structure is obtained by using 0.2λ wavelength grouping in the thinnest layer. The frequency of the incident wave is 300MHz, the direction of the incident wave is θ=0°, The viewing angle is The method of the invention and the traditional finite element boundary integral method are respectively used to analyze the electromagnetic scattering of the target. image 3 The RCS curves simulated for the two electromagnetic scattering character...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com