Cell reselection method and device applied to multi-carrier condition, method and device for reducing access load of cells
A cell reselection, multi-carrier technology, applied in the direction of network traffic/resource management, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problem of increasing cell signaling load, heavy data transmission load and access load, and increased user access delay And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
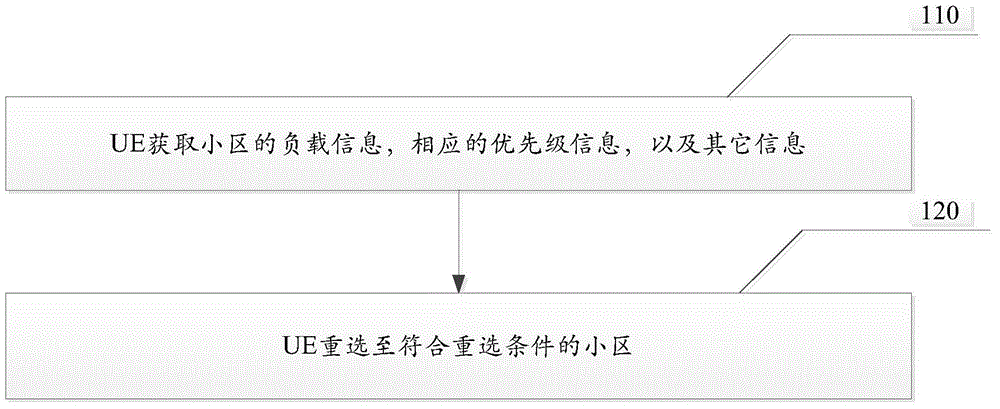
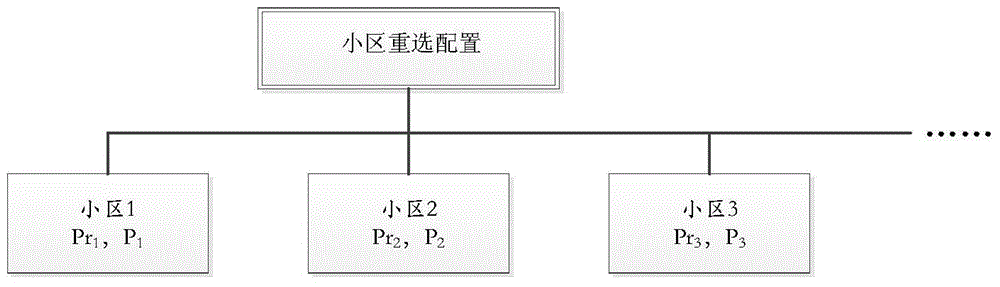
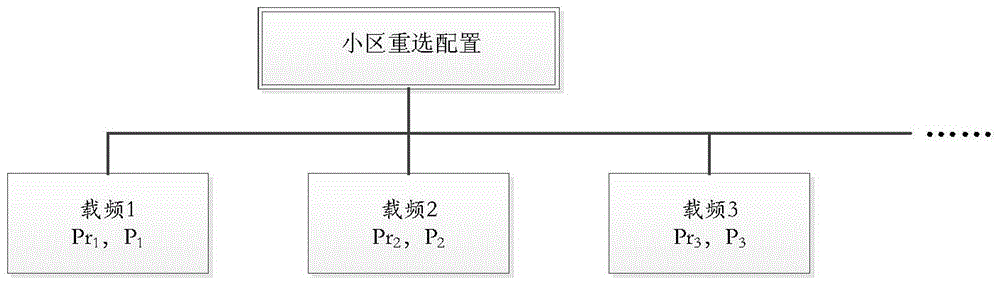
[0118] In this embodiment, the cell load is calculated by the eNB, and the eNB notifies the UE of the load information of the currently camped cell and neighboring cells through signaling. At the same time, the eNB configures corresponding cell priority lists for UEs with different capabilities, such as Figure 5 shown. The UE obtains the neighbor cell list by receiving the signaling of the cell where it is currently camping, and the corresponding neighbor cell load, neighbor cell priority, and neighbor cell reselection probability. The UE reselects to a cell that meets the reselection conditions based on the above information. In this implementation Cells that meet the conditions of H4, E4 or L6 are cells that meet the reselection conditions. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0119] Step 1: The UE receives cell signaling, and obtains a list of neighbor cells, the priority corresponding to each neighbor cell, the reselection probability corresponding to eac...
Embodiment 2
[0129] In this embodiment, the cell load is calculated by the eNB, and the eNB notifies the UE of the load information of the currently camped cell and neighboring cells through signaling. The UE obtains the neighbor cell list by receiving the signaling of the cell where it is currently camping, and the corresponding neighbor cell load, neighbor cell priority, and neighbor cell reselection probability. The UE reselects to a cell that meets the reselection conditions based on the above information. In this implementation Cells that meet the conditions of H1, E1 or L1 are cells that meet the reselection conditions. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0130] Step 1: The UE receives cell signaling, and obtains parameters such as a list of neighboring cells, the corresponding priority of each neighboring cell, and the corresponding reselection probability of each neighboring cell.
[0131] In this embodiment, the reselection probability is a cell-specific parameter...
Embodiment 3
[0139] In this embodiment, when the cell is in an overloaded state, the eNB alleviates the access load of the cell by prohibiting services with high delay tolerance and rejecting paging requests with low priority. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0140] Step 1: The eNB updates the broadcast message, and includes at least delay tolerant access (delayTolerantAccess) in the cell access barring list (ac-BarringInfo).
[0141] Step 2: The eNB feeds back a paging request rejection message to the MME.
[0142] The paging request rejection message includes the index information of the paging request with low priority, and further includes the waiting time suggested by the eNB.
[0143] It should be noted that the sequence of step 1 and step 2 can be interchanged, and can be executed separately.
[0144] So far, this embodiment ends. Through the method of this embodiment, the access load of the cell can be further alleviated without affecting user experience.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com