Method for global optimization and distribution of agile satellite imaging tasks
A global optimization and allocation method technology, applied in satellite radio beacon positioning systems, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of orbit observation cycle allocation, large energy consumption, and time-consuming problems, and achieve imaging task planning Reasonable, optimize the observation results, and ensure the effect of imaging quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0078] The orbit simulation parameters of an agile satellite are shown in Table 1:
[0079] Table 1 Orbit simulation parameters
[0080]
[0081]
[0082] The imaging target position and range are as Figure 4 , where T represents point targets, LA represents off-track targets, LP represents along-track targets, A represents area targets, and LS represents irregular long strip targets.
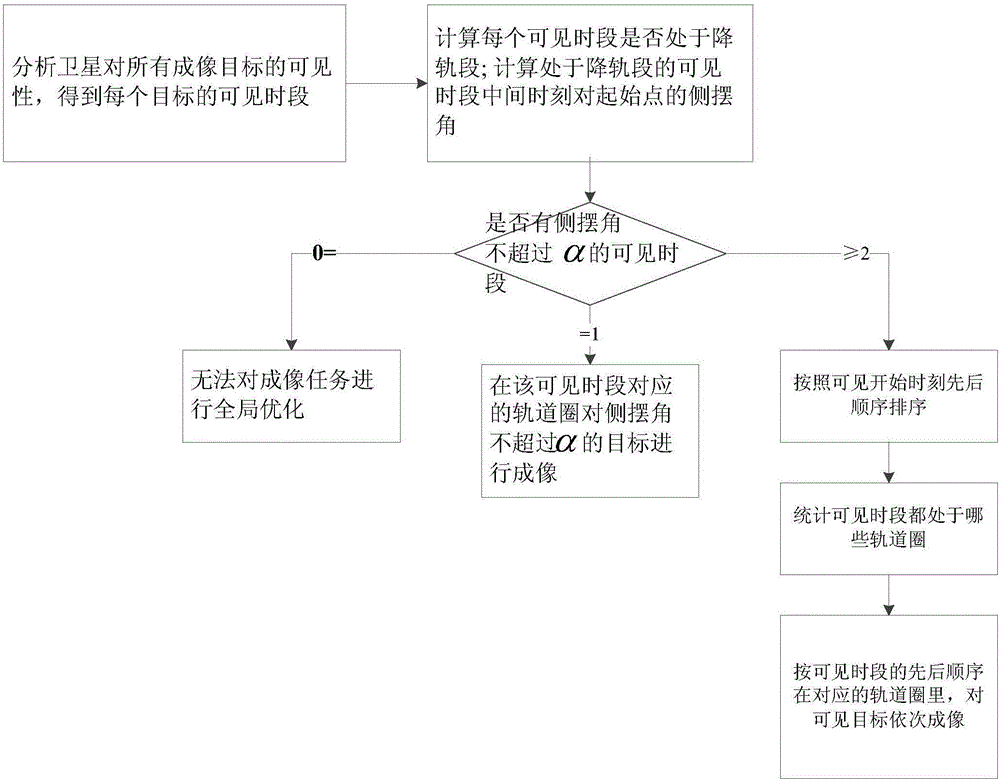
[0083] Utilize the method of the present invention to optimize the global distribution of satellite imaging tasks. According to constraints such as satellite energy, imaging efficiency, and imaging quality, select a visible time period with a roll angle of no more than 60 degrees, a total of 21, in the order of the start time of the visible time period Sort the visible periods that meet the conditions, and count the orbital circles where these visible periods are located. The global allocation results are shown in Table 2.
[0084] Table 2 Global optimal allocation results of an agile ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com