Engine assisted brake control on wheel slip
An engine and wheel technology, applied in the direction of brakes, control devices, etc., can solve problems such as mechanical wear, weight increase, damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0011] It should be noted that the methods and systems described herein can be adapted to a variety of machines. The machine may be an off-highway vehicle, such as a truck, used in operations in connection with industries such as mining, construction, agriculture, transportation or any other industry known in the art. For example, the machine may be an off-highway truck or an earth moving machine such as a bulldozer, wheel loader, excavator, dump truck, backhoe, motor grader, material handler, and the like.
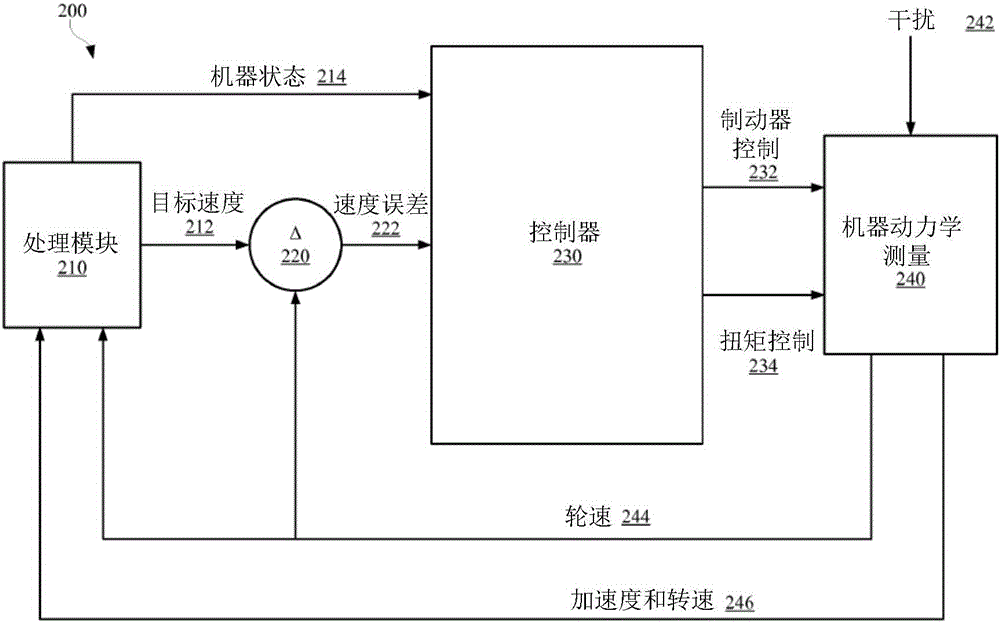
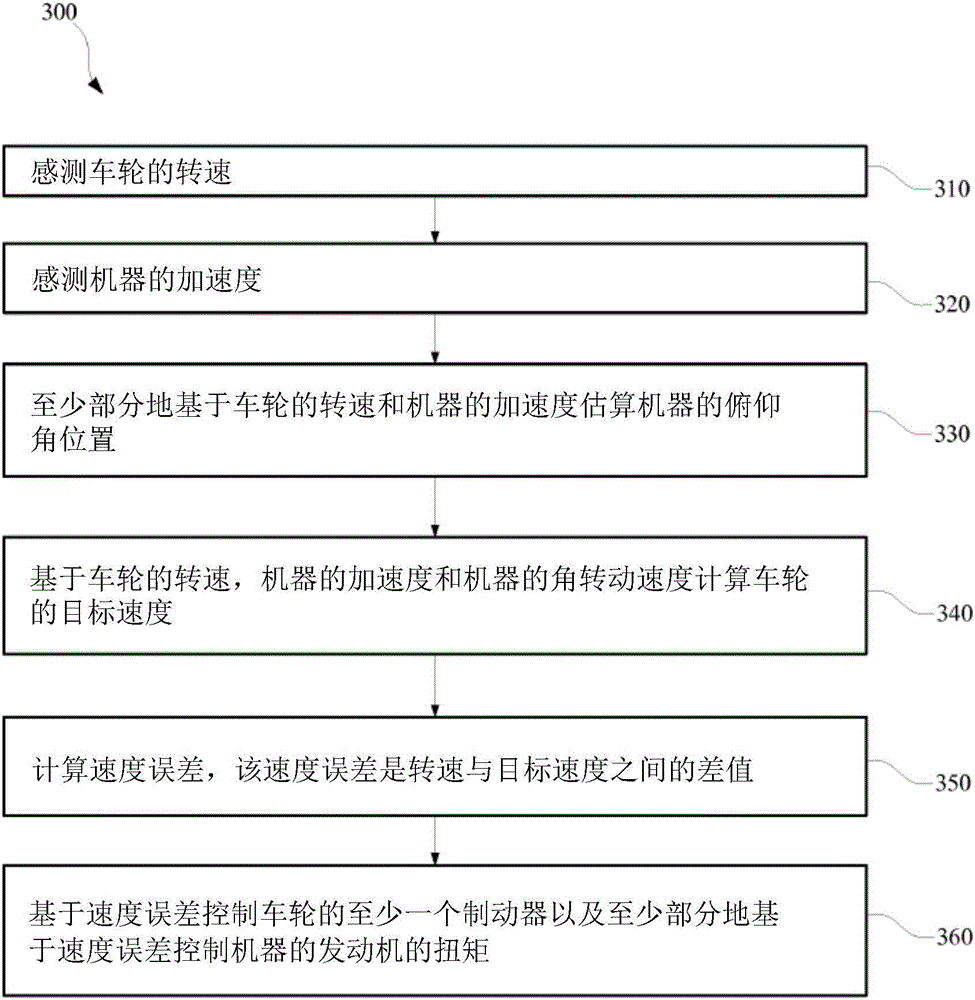
[0012] Furthermore, it should be noted that the drawings are merely illustrative and not drawn to scale.
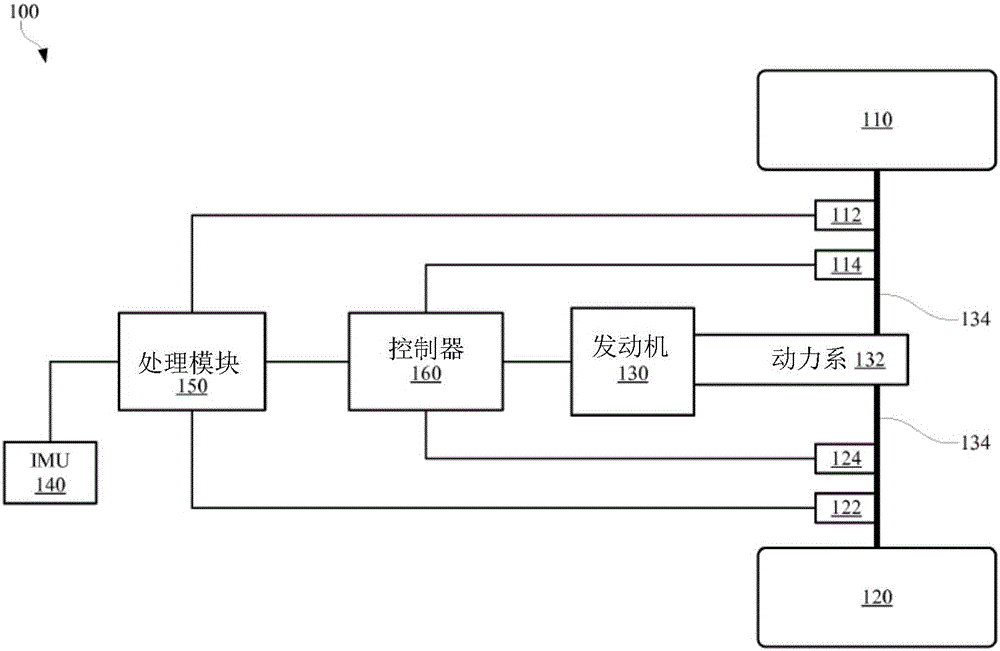
[0013] figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a portion of an exemplary machine 100 in accordance with at least one embodiment of the invention. Some example machines 100 may include a chassis and wheels 110, 120 (or tracks). In some examples, machine 100 may have multiple wheels, such as four or six wheels. For exemplary purposes, figure 1 Only two wheels 110, 120 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com