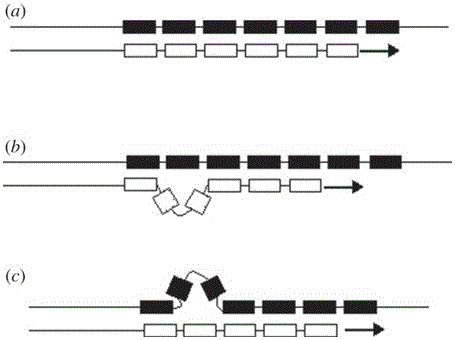
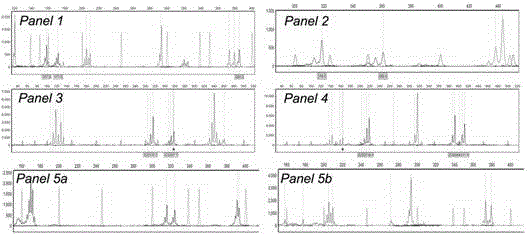
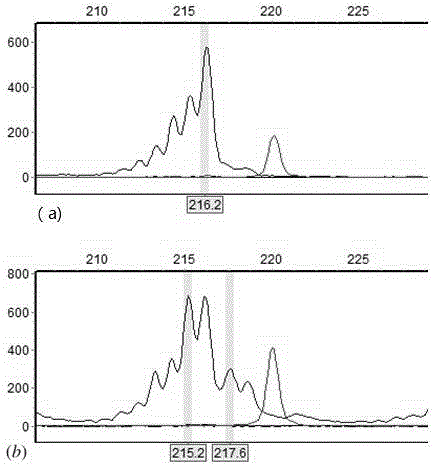
Method for identifying human-derived genetic relationship through two-nucleotide repeated microsatellite
A kinship, two nucleotide technology, applied in the field of DNA fingerprinting, can solve the problems of the complexity of allele classification and high mutation rate, and achieve the effect of improving identification accuracy, low mutation rate, and avoiding the interference of slip peaks.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0029] Example: See Table 2 for the STR, primers, primer modification, primer final concentration, annealing temperature, final dilution factor, PCR grouping and capillary electrophoresis grouping.
[0030] The DNA extracted from the biological sample required by the method of the present invention is less, about 50ng is enough. After commercially synthesizing the primers in Table 2, these 30 pairs of primers were diluted and paired with the forward and reverse primers according to the PCR primers, and the concentration was 20 times the final concentration of the primers in Table 2, so that multiple STRs could be detected simultaneously. PCR amplification reduces workload; for example, for D1S2757, add its forward (F direction) and reverse (R direction) primers to TE solution, so that the concentration of both primers is 6.4 μM (pmol / ul). According to the experimental determination, the primers that will not interfere with each other are put together as a group, and the primer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com