Enhanced quad-tree anti-collision algorithm suitable for RFID system
An anti-collision algorithm and quadtree technology, applied in computing, computer parts, electromagnetic radiation induction, etc., can solve the problems of readers' judgment errors, inability to read information correctly, and inability to correctly identify electronic tags, etc., and achieve less Transmission of useless bits, saving query process time, and reducing the effect of the number of idle time slots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
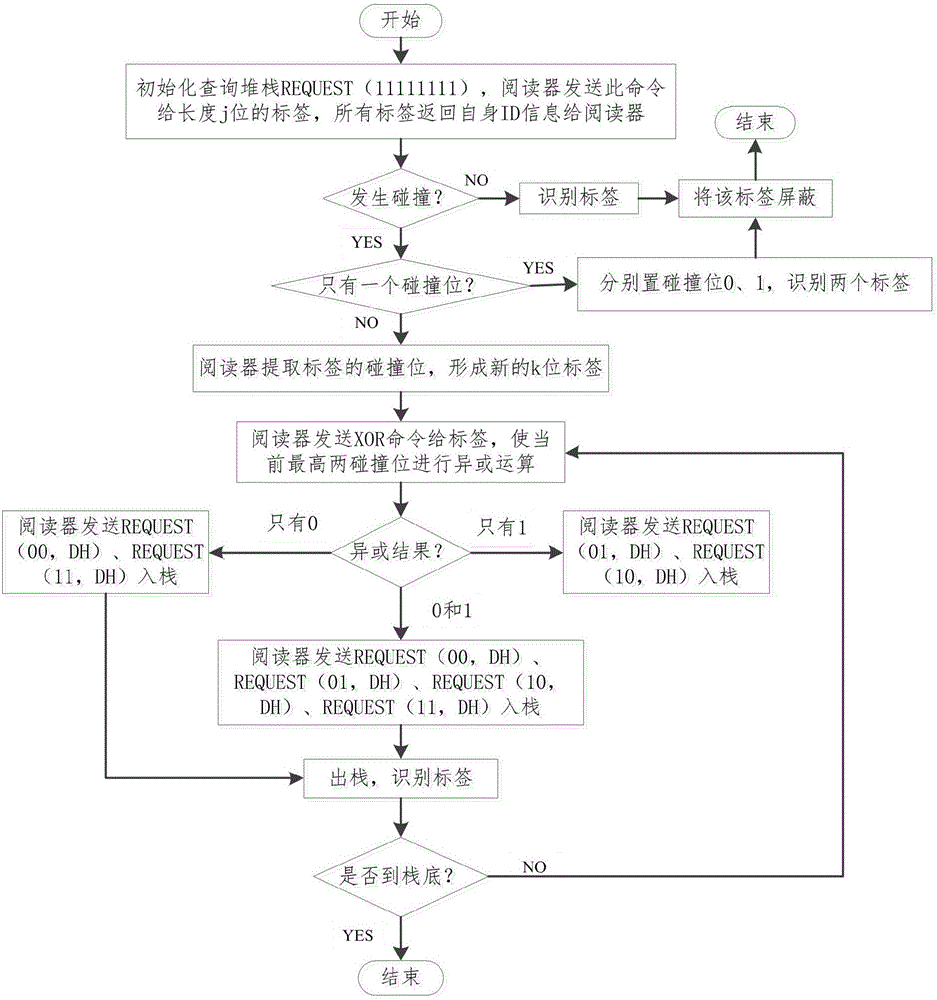
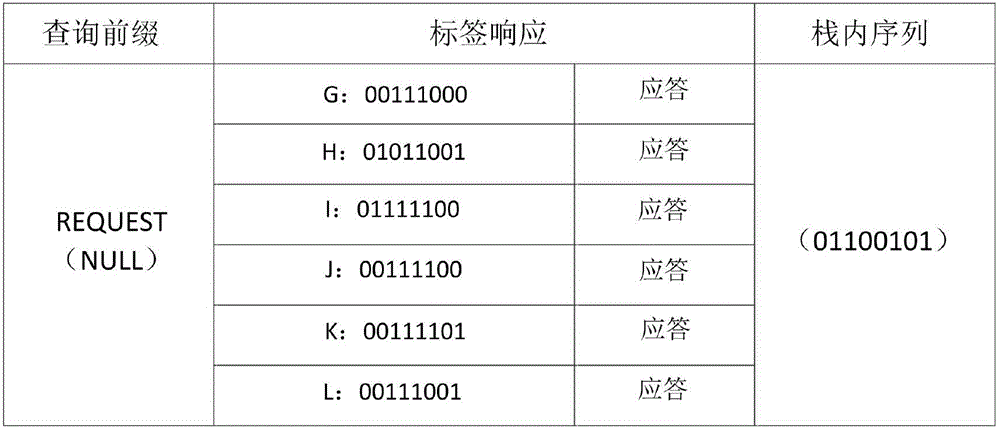
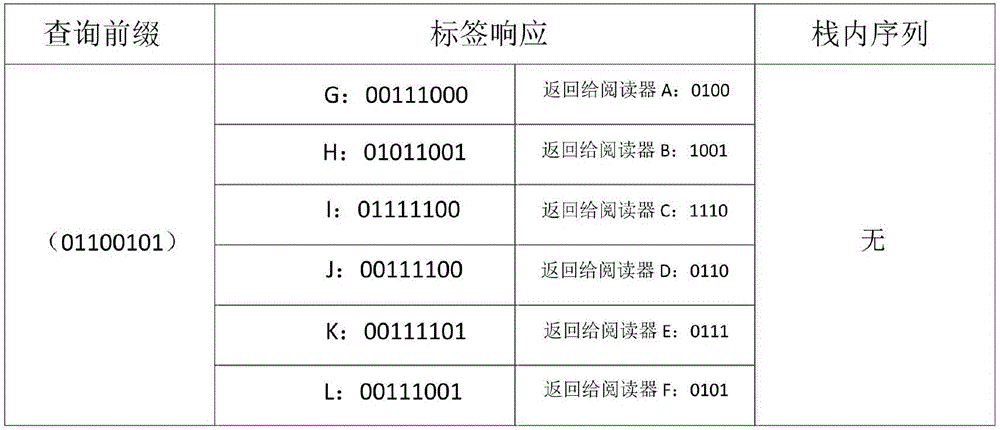
[0034] Below with the accompanying drawings Figure 1-12 And specific examples further illustrate the present invention.
[0035] First make an agreement: the tag ID is unique, and DH is the highest bit among the two adjacent collision bits. Next, introduce the following commands:
[0036] (1) REQUEST (request) command: Contains REQUEST (NULL), REQUEST (prefix, DH). When the reader sends REQUEST (11111111) to the tag, the tag will compare its own ID with it, and if it is less than REQUEST (11111111), it will return its own ID to the reader; otherwise, the tag will not respond. prefix indicates the query prefix sent by the reader to the tag, which is 0 and 1 when using a binary tree, and 00, 01, 10, 11 when using a quadtree. DH represents the highest bit of the current two collision bits.
[0037] (2) SELECT command: When the reader sends a command to the tag, the tag compares its own ID with the query command. If it is less than or equal to the query command, it returns it...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com