Method for detecting six functional genes of Cr(VI) reducing complex microorganisms through multiple real-time fluorescent PCR
A real-time fluorescent, functional gene technology, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, time-consuming and labor-intensive, and inapplicable expression quantification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
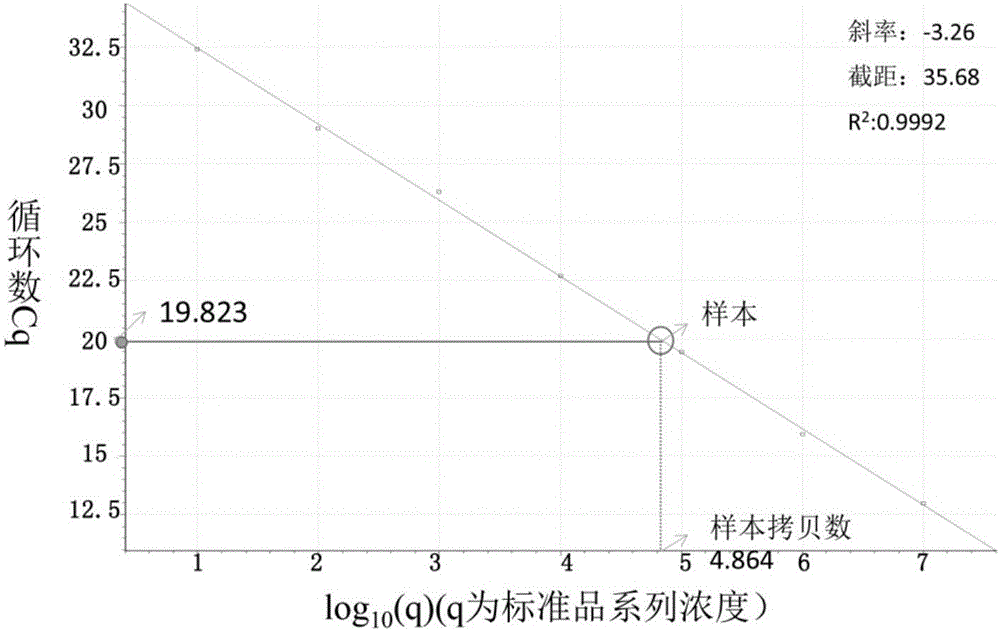
[0057] The preparation of embodiment 1 plasmid standard
[0058] Step 1: Primer Design and Synthesis
[0059] Corresponding primers were designed according to the DNA sequence of the gene. The designed common PCR primers (Table 1) for six genes of HcrR, OmcA, ChrR, 16s rDNA (BB), 16s rDNA (MR-1) and 16s rDNA (F1) were provided by Shanghai Synthesized by Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd., the synthetic amount is 2OD.
[0060] Common PCR primers involved in the present invention in table 1
[0061]
[0062] Step 2: Bacterial Total RNA Extraction
[0063] Take 1 mL of the culture fluid of the three strains containing specific genes and place them in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, and use the RNAprep PureCell / Bacteria Kit (Tiangen (Beijing)) to extract the bacterial total RNA.
[0064] Step 3: Synthesize cDNA by reverse transcription
[0065]Reverse transcription reaction: Add 1 μL of the total RNA template prepared in the previous step to the RNase-Free 0.2mL PCR tube in turn, per...
Embodiment 2
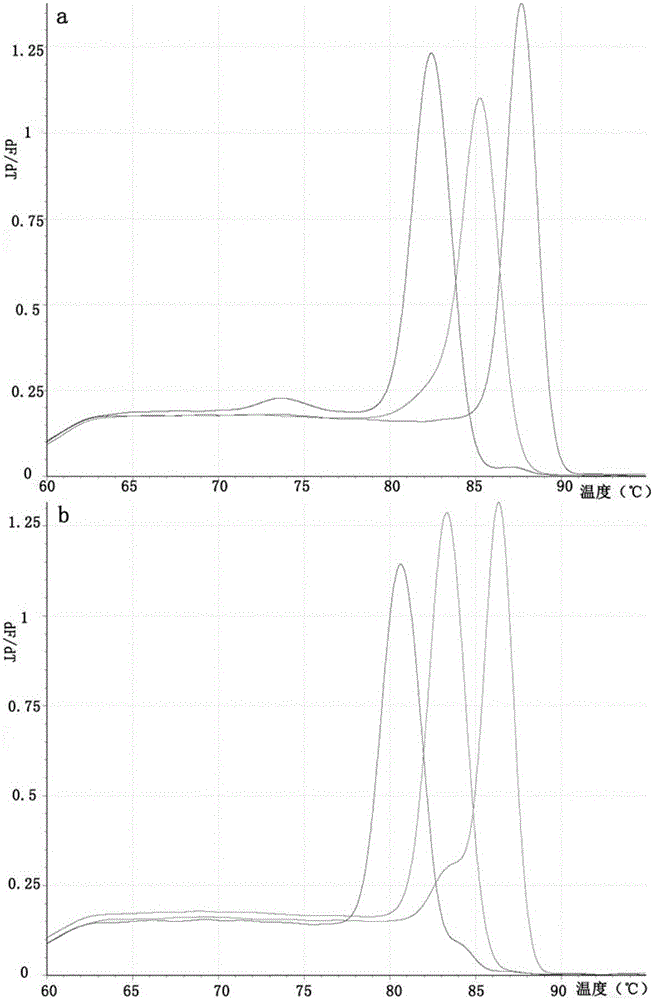
[0070] Embodiment 2 Multiplex real-time fluorescent PCR detects the specificity experiment of six kinds of specific genes
[0071] Specific detection of a single gene in a multiplex system:
[0072] According to the reaction system of Roche LightCycler Nano 32-well fluorescent detection polymerase chain reaction (PCR) instrument, 4 identical multiplex PCR reaction solutions were prepared for the Cr(VI) reduced gene, and 1 μL of known amounts of HcrR and OmcA were added separately. , ChrR standard plasmids, and set up a negative control; for 16s rDNA, prepare 4 identical multiplex PCR reaction solutions, respectively add 1 μL of known amounts of 16s rDNA (BB), 16s rDNA (MR-1), 16s rDNA Set up a negative control for the standard plasmid of rDNA (F1).
[0073] The Cr(VI) reducing gene reaction system is 2×FastStart Essential DNA Green Master 25 μL, the final concentrations of the upstream and downstream primers of HcrR, OmcA, and ChrR genes are 0.05 μM, 0.2 μM, and 0.2 μM, respe...
Embodiment 3
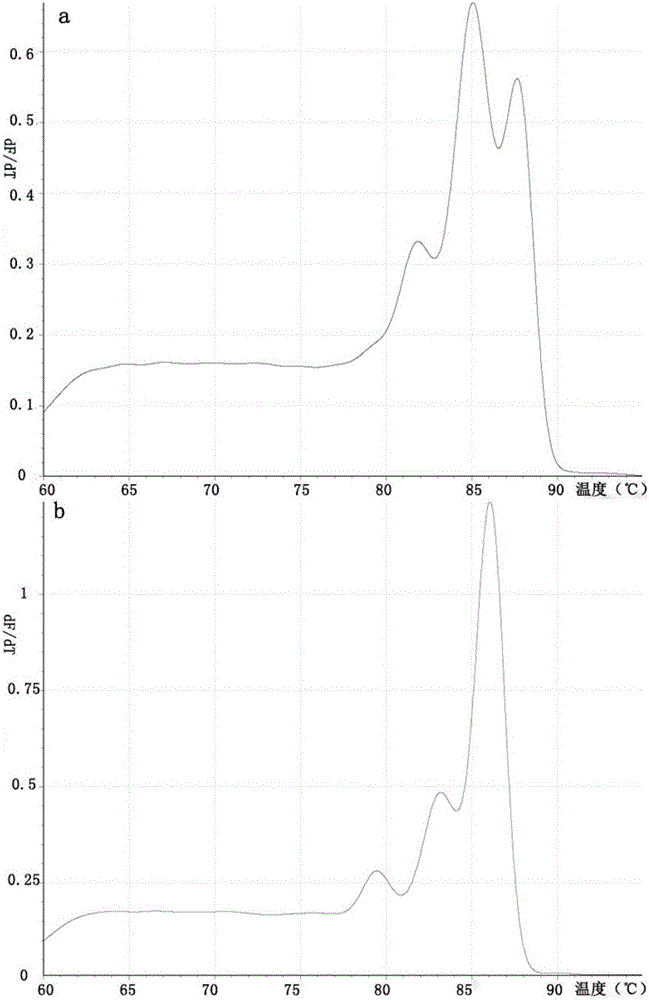
[0076] Embodiment 3 Multiplex real-time fluorescent PCR detects the stability experiment of six kinds of specific genes
[0077] The six genes were operated as follows:
[0078] Take 3 known plasmid standards and a negative control (water without RNase enzyme), and perform repeated tests within and between batches, respectively. The intra-batch repeat test is to carry out the real-time fluorescence detection PCR experiment on 3 samples at the same time; the inter-batch repeat test is to carry out the real-time fluorescence detection PCR experiment at 3 different times (interval 3 days). The average coefficient of variation (CV) of repeated experiments within and between batches of several genes was less than 1%.
[0079] Experimental results show that the detection method of the present invention has good stability.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap