A Compensation Method for End Position of Industrial Robot
An industrial robot, end position technology, applied in manipulators, manufacturing tools, program-controlled manipulators, etc., can solve problems such as difficult program management, complicated robot operation procedures, and increased weight of welding tongs or grinding wheels.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
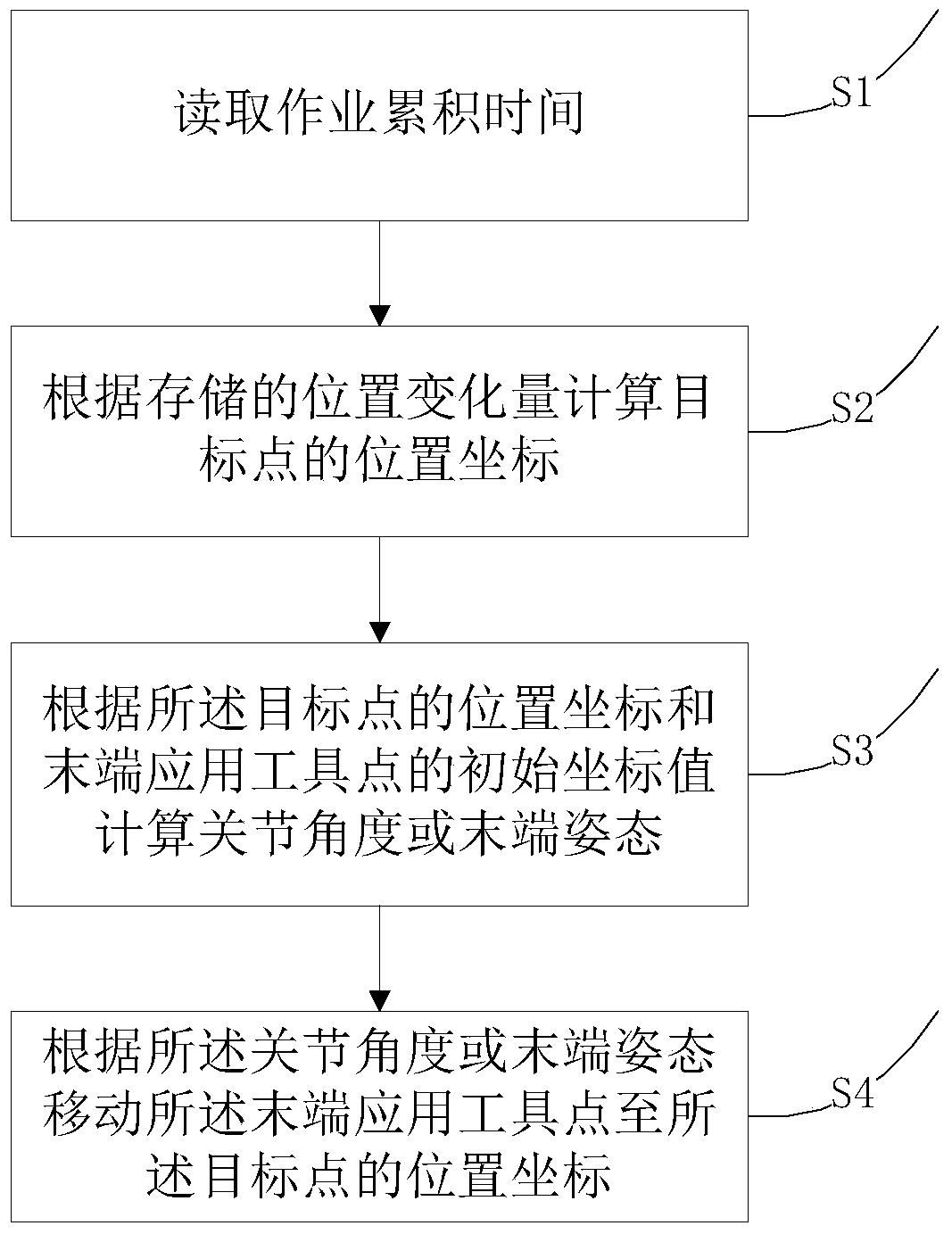
[0029] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides an industrial robot end position compensation method, including the following steps,
[0030] S1. Accumulated time of reading jobs;
[0031] S2. Calculate the position coordinates of the target point according to the stored position change amount;
[0032] Wherein, the position coordinate formula of described calculation target point is:
[0033] X=xi+x(t);
[0034] Y=yi+y(t);
[0035] Z=zi+z(t);
[0036] Among them, t is the cumulative time of the job; xi, yi, zi are the initial coordinate values of the terminal application tool point; x(t), y(t), z(t) are the terminal application tool point in the x, y, z direction change in wear.
[0037] S3. Calculate joint angles or terminal postures according to the position coordinates of the target point and the initial coordinate values of the terminal application tool point;
[0038] S4. Moving the end application tool point to the position coordinates of the target poin...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides an industrial robot end position compensation method, including the following steps,
[0042] S0, call the position point from the saved program data;
[0043] And, after calling the location point from the saved program data, it also includes judging whether the calling location point is a compensation point;
[0044] S1. Accumulated time of reading jobs;
[0045] S2. Calculate the position coordinates of the target point according to the stored position change amount;
[0046] S3. Calculate joint angles or terminal postures according to the position coordinates of the target point and the initial coordinate values of the terminal application tool point;
[0047] S4. Moving the end application tool point to the position coordinates of the target point according to the joint angle or the end posture.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides an industrial robot end position compensation method, including the following steps,
[0050] S1. Accumulated time of reading jobs;
[0051] S2. Calculate the position coordinates of the target point according to the stored position change amount;
[0052] S3. Calculate joint angles or terminal postures according to the position coordinates of the target point and the initial coordinate values of the terminal application tool point;
[0053] Wherein, the joint angle is obtained by calculating the inverse transformation of the coordinate values (Xib, Yib, Zib) in the robot base coordinates and the tool coordinate values (X, Y, Z).
[0054] S4. Moving the end application tool point to the position coordinates of the target point according to the joint angle or the end posture.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com