Two-step error compensation method for robot
An error compensation and robot technology, applied in the field of robot calibration, can solve the problem of inability to directly compensate geometric parameter errors, and achieve the effect of improving absolute positioning accuracy and reducing position errors.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
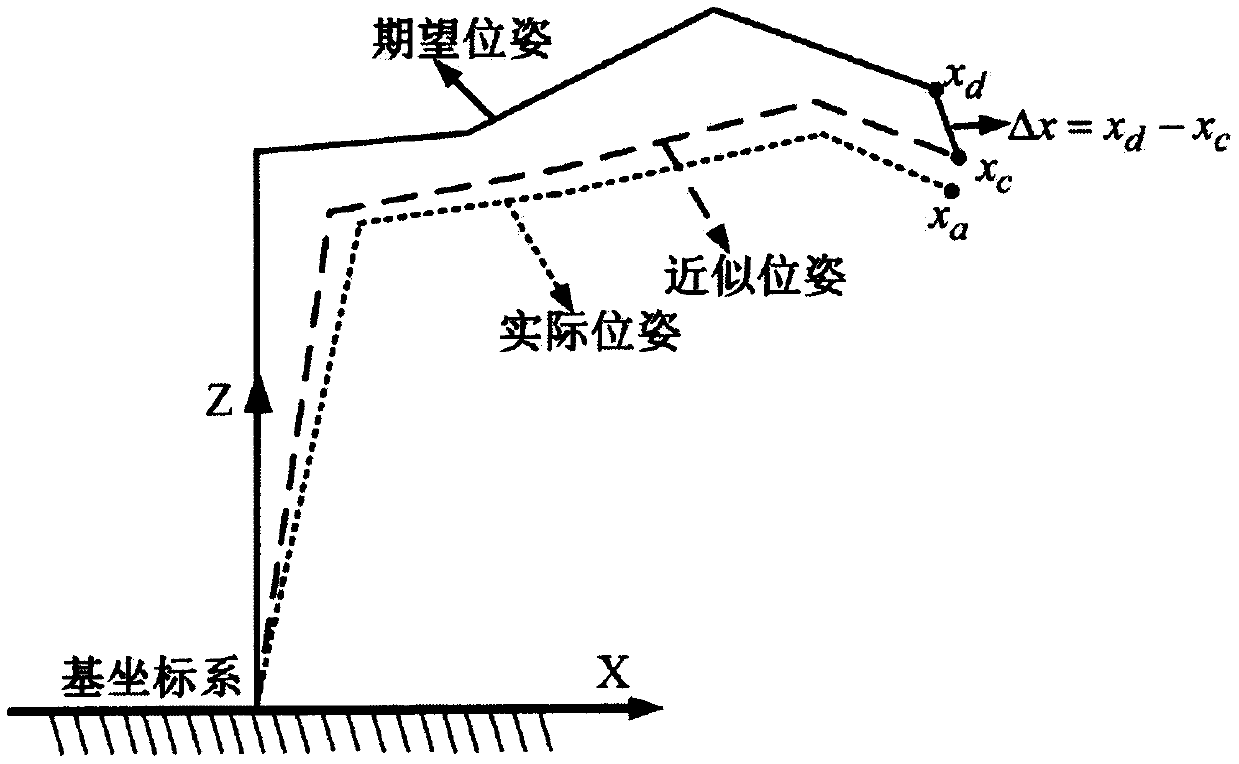
[0032] Further illustrate the present invention below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, a kind of two-step error compensation method for robot that the present invention proposes, comprises the following steps:
[0033] First, establish a robot positioning error model and perform parameter identification:
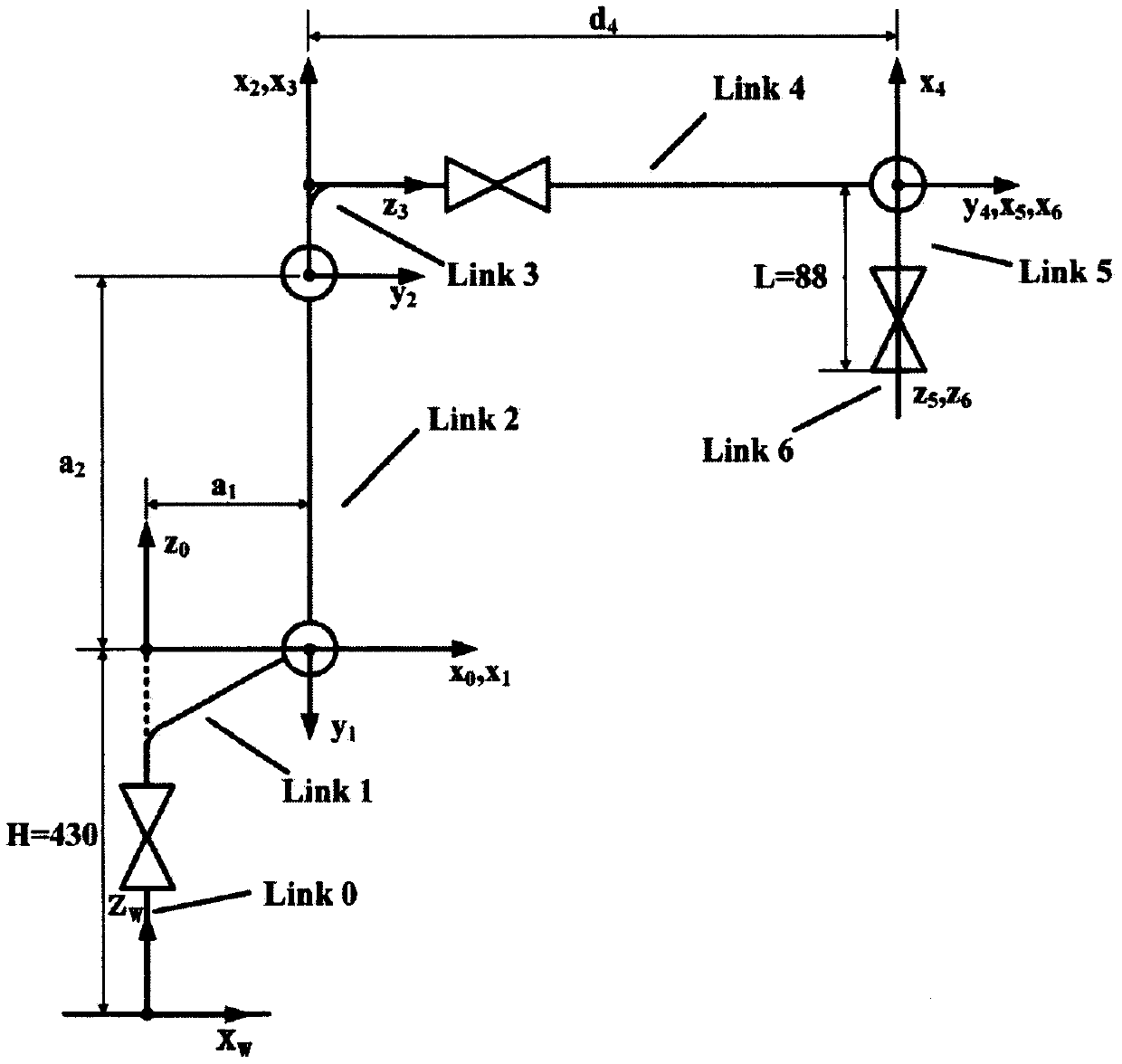
[0034] In this embodiment, the kinematics model of the Kawasaki RS010NA six-degree-of-freedom industrial robot is established according to the D-H method, and the coordinate system of each joint of the robot is shown in the appendix figure 1 , the D-H modeling method uses four parameters to describe the transformation between adjacent joint coordinate systems. However, when the axes of two adjacent joints are parallel or close to parallel, using four parameters cannot describe the angle of rotation around the y-axis in coordinate system transformation. Therefore, the angle β of rotation around the y-axis is added on the basis of the D-H model to obtain The modified...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com