Sparse coding-based human face identification method
A face recognition and sparse coding technology, which is applied in the field of face recognition based on sparse coding, can solve problems such as difficulty in determining the true distribution of residuals, occlusion or noise interference, and poor quality of face images, so as to reduce computational complexity , reduce the vector dimension, improve the recognition rate and the effect of robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
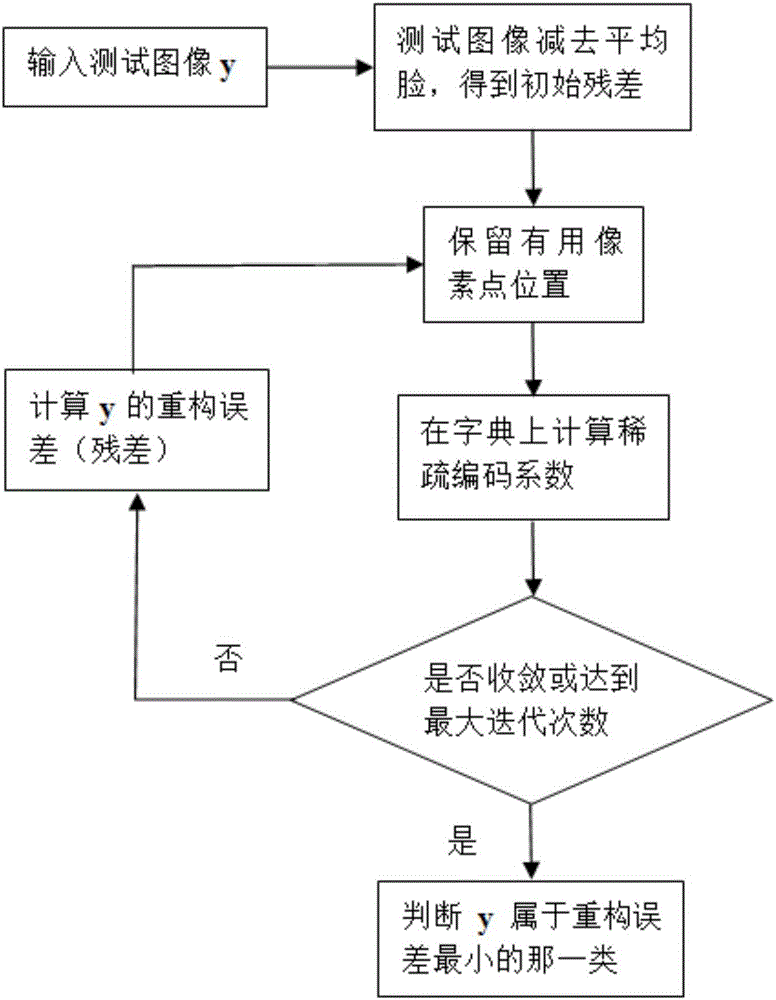
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method provided by the invention specifically includes the following steps:
[0044] The first step, assuming that there are k known objects in the training sample set, among which n objects contained in the i-th object i training samples are expressed as a matrix where i=1,2,...,k,v ij ∈R m ,j=1,2,...,n i , v ij Represents the column vector corresponding to the j-th training sample of the i-th object, m represents v ij dimension, the training sample set A can be expressed as:
[0045]
[0046] in Indicates the total number of training samples;
[0047] In the second step, let the test sample be expressed as y, and let the reconstructed sample y rec Initialized to the mean of all training samples;
[0048] The third step, calculate y and y rec The residual between e=y-y rec ;
[0049] The fourth step is to define the diagonal matrix P=diag(p 1 ,p 2 ,...,p m );
[0050] in s.t.e=y-y rec , e d Represents the dth compo...
Embodiment 2
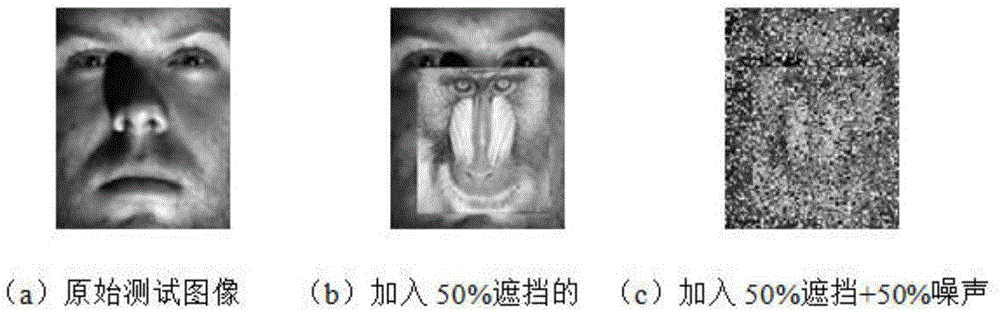
[0063] In order to prove the effectiveness and robustness of the method provided by the present invention, two groups of comparative experiments were carried out in this implementation. In this embodiment, the first set of comparative experiments is done on the Extended Yale-B face database. In the first set of experiments, Subset1 and Subset2 in the EYB face database were used as training sets, and there were a total of 717 training sample images, which were collected under suitable lighting conditions. Using Subset3 as the test set, there are a total of 453 test samples, and these images are all subject to strong lighting. The size of each image is 96×84.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com