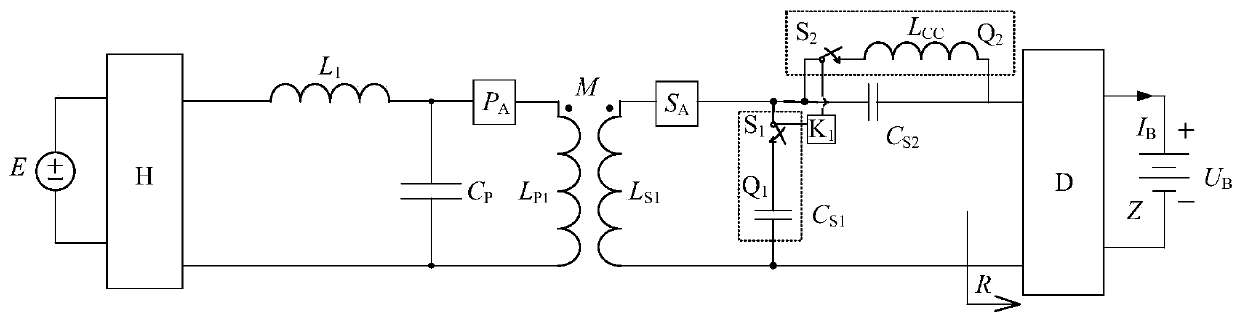
An inductive wireless charging system with variable secondary structure
A secondary structure, wireless charging technology, applied in charging/discharging current/voltage regulation, current collectors, electric vehicles, etc., can solve problems such as reducing system stability, unstable system operation, and increasing inverter capacity requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
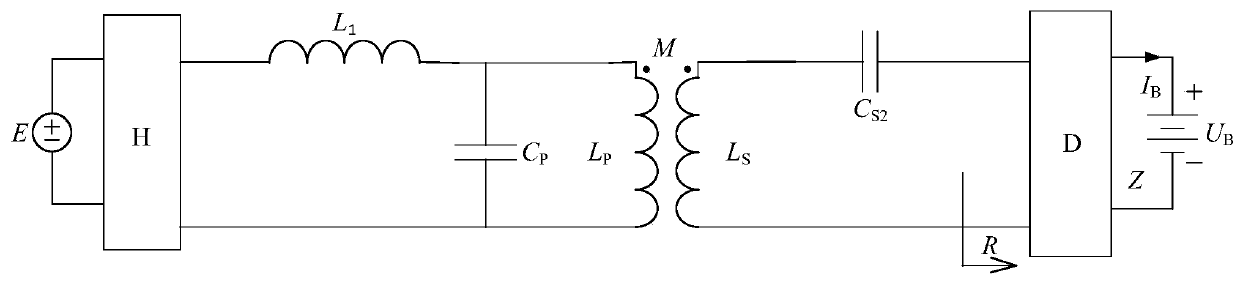
[0131] image 3 As shown, the first specific implementation of the present invention is an inductive wireless charging system with a variable secondary structure, which is composed of a transmitting part and a receiving part. The transmitting part includes a DC power supply E and a high-frequency inverter connected in sequence. H. Primary compensation inductance L 1 , Primary coil compensator P A , Primary coil L P1 ; And in the primary compensation inductance L 1 With primary coil compensator P A The connection point and the high frequency inverter H and the primary coil L P1 A primary compensation capacitor C is connected between the connection points P ; The receiving part includes the secondary coil L connected in sequence S1 , Secondary coil compensator S A , Secondary compensation capacitor C S2 And rectifier filter circuit D, battery load Z.
[0132] The secondary winding compensator S A With secondary compensation capacitor C S2 Connection point and secondary coil L S1 A co...
specific Embodiment approach
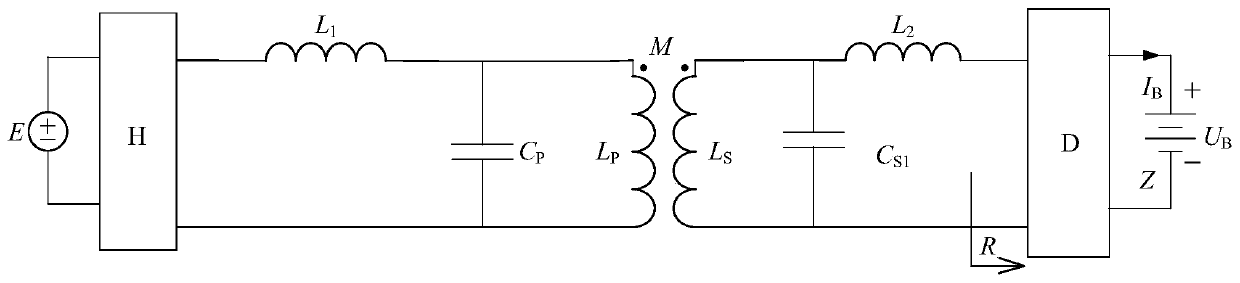
[0152] Figure 4 Shown is the second specific embodiment of the present invention, an inductive wireless charging system with a variable secondary structure, which is composed of a transmitting part and a receiving part. The transmitting part includes a DC power supply E and a high-frequency inverter H connected in sequence. , Primary compensation inductor L 1 , Primary coil compensator P A , Primary coil L P1 ; And in the primary compensation inductance L 1 With primary coil compensator P A The connection point of the high frequency inverter H and the primary coil L P1 A primary compensation capacitor C is connected between the connection points P . The receiving part includes the secondary coil L connected in sequence S1 , Secondary coil compensator S A , Secondary compensation inductance L 2 And rectifier filter circuit D, battery load Z.
[0153] The secondary winding compensator S A With secondary compensation capacitor C S2 Connection point and secondary coil L S1 A constan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com