Inertial Rotary Drive Device Based on Piezoelectric Fiber
A rotary drive device and piezoelectric fiber technology, applied in the direction of piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motors, generators/motors, electrical components, etc., can solve large retraction motion, mechanism is not easy to control, Signals are not easy to generate and other problems, to achieve the effect of storing kinetic energy, overcoming difficult control, and reducing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
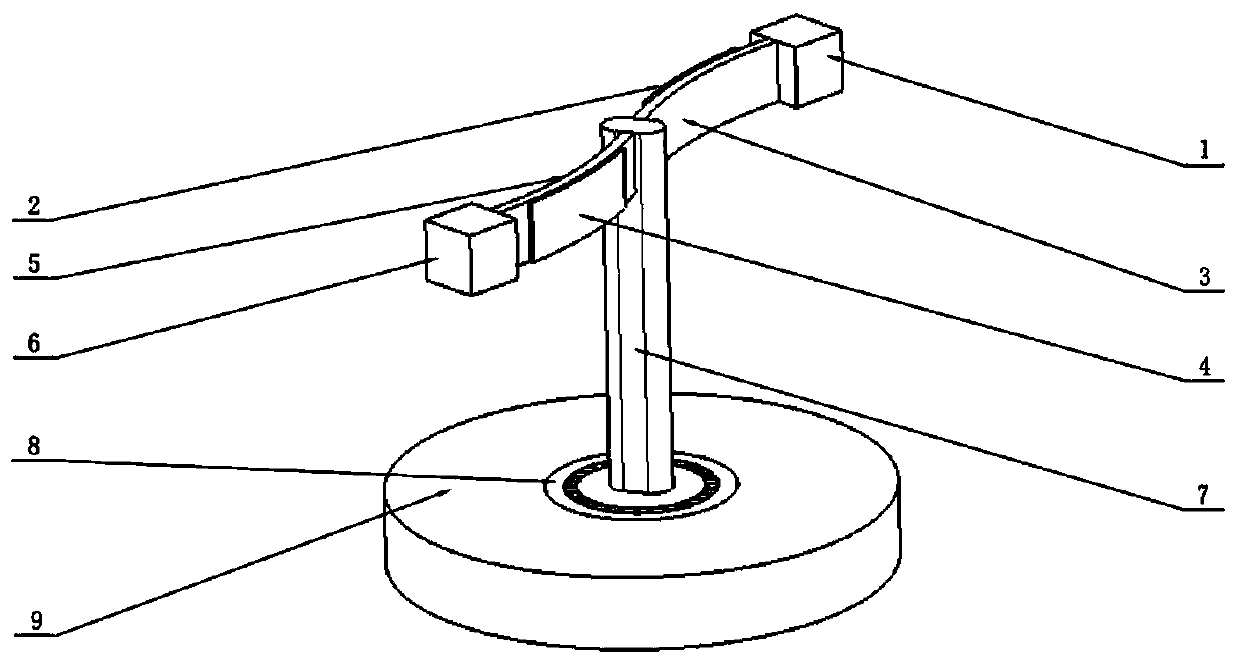
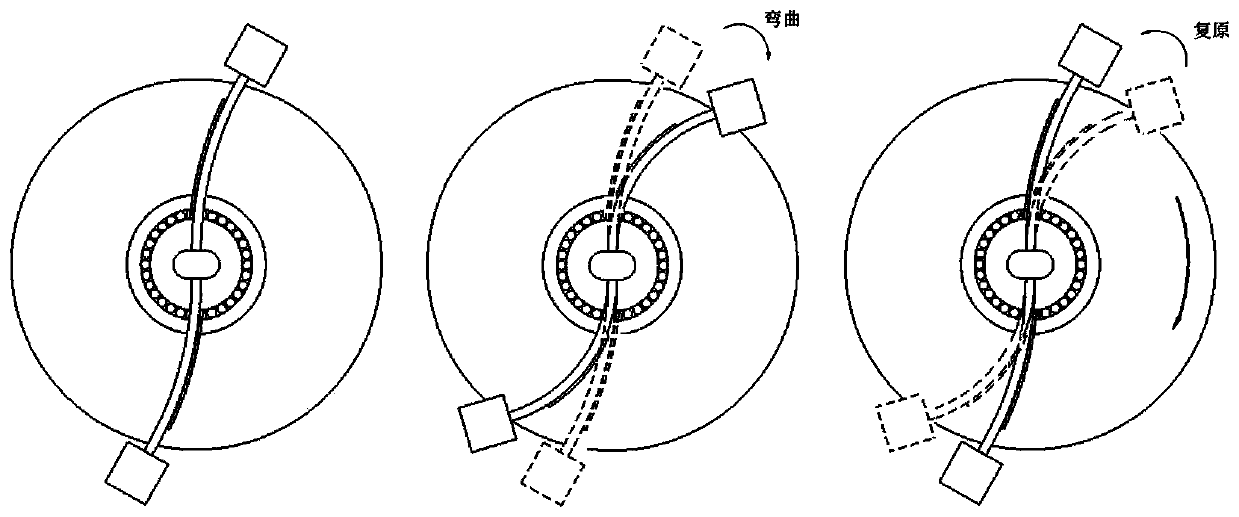
[0015] The invention relates to an inertial rotation drive device based on piezoelectric fibers, which is a new type of drive device that utilizes the inverse piezoelectric effect of piezoelectric fibers and the principle of inertial drive to drive a mechanism to realize rotation. Such as figure 1 As shown, the two ends of the metal plate 1 (3) are respectively connected to the mass block 1 (1) and the support (7), the two ends of the metal plate 2 (5) are respectively connected to the mass block 2 (6) and the support (7), and the mass block 1 (1) and mass block 2 (6) produce inertia force in the process of motion. The power source is two pieces of flexible piezoelectric fibers, a metal plate pre-bent to a certain radian is bonded to the piezoelectric fibers and a mass block is connected at one end to form an actuator as a whole. The piezoelectric fiber and the metal plate are bonded in parallel with conductive glue. Metal plate 1 (3), metal plate 2 (5) are processed into a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com