Method and device for managing meta information
An information management device and a technology for meta-information, applied in the field of managing meta-information, can solve problems such as data loss, file damage, and consumption for a long time, and achieve the effects of improving security, avoiding loss, and improving startup speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
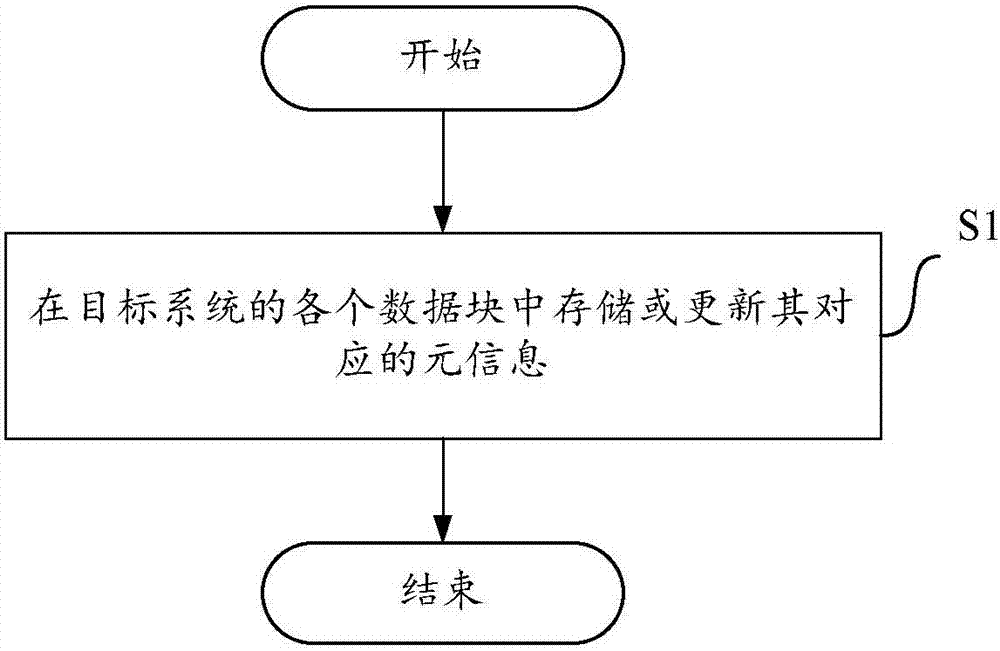
[0014] figure 1 A flow chart of a method for managing meta-information according to the present invention is schematically shown. The method according to the invention comprises a step S1.
[0015] Wherein, the method according to the present invention is implemented by an information management device included in the computer equipment. The computer equipment includes an electronic equipment that can automatically perform numerical calculation and / or information processing according to pre-set or stored instructions, and its hardware includes but not limited to microprocessors, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), programmable gates Arrays (FPGA), digital processors (DSP), embedded devices, etc. The computer equipment includes network equipment and / or user equipment. Wherein, the network device includes but is not limited to a single network...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com