Consistent iteration and multi-view transfer learning-based pedestrian re-identification method
A technology of transfer learning and identification method, which is applied in the field of pedestrian re-identification based on consistent iterative multi-view transfer learning, can solve the problems of inconsistent data distribution and small samples of multiple viewing angles, and it is difficult to guarantee, so as to improve accuracy and ensure The effect of reducing complexity and increasing iteration rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
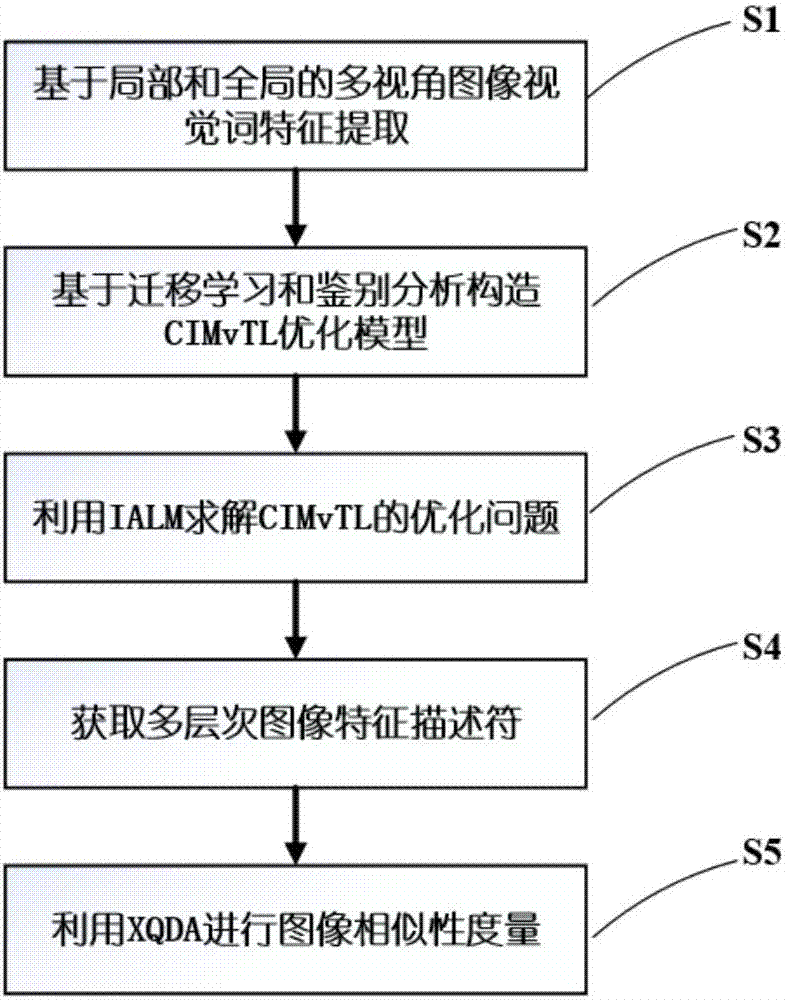
[0047] Such as figure 1 Shown is a flow chart of the present invention, and method among the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0048] Step S1, based on the local and global multi-view image visual word feature extraction, the specific description is as follows: the pedestrian image is divided into 6 horizontal stripes on average in the vertical direction, and 6 groups of local visual words are extracted from different stripes, and at the same time from Extract a group of global visual words from the overall pedestrian image; use an unsupervised clustering method (K-means) to fuse multi-view information to obtain 7 groups of multi-view visual words, defined as: MvVW={D i}, i=1,2,3,4,5,6,7. Among them, D represents the multi-view visual words under different pedestrian structure regions (where {D i}, i=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 represent local multi-view visual words, {D i}, i=7 means the global multi-view visual word).
[0049] Step S2, based on transfer learning an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com