Light guide plate, design method and dot distribution method thereof, and illumination device
A technology of light guide plate network point and design method, which is applied in the light guide, light guide, optics and other directions of the lighting system, can solve the problems of low practicability, high complexity, long cycle period of dynamic molecular method, etc., and achieve the effect of strong practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
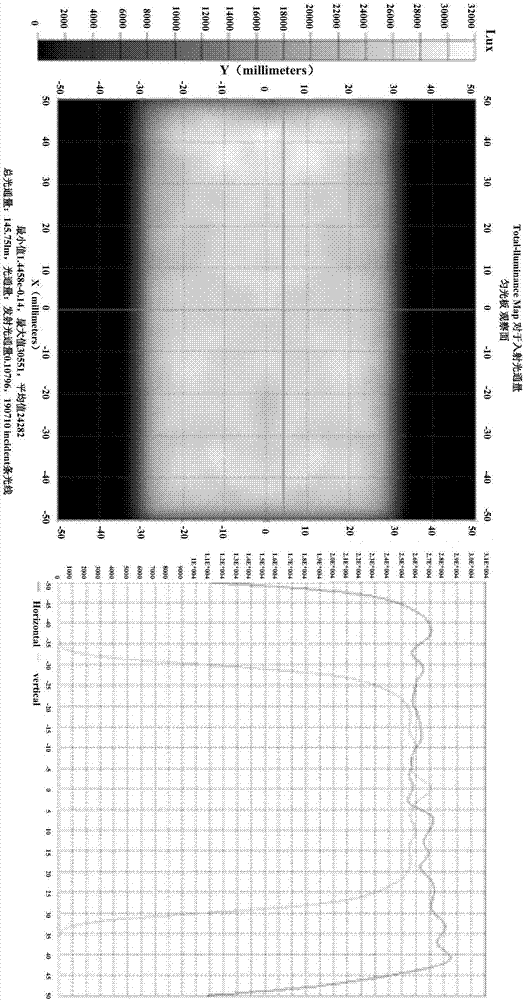
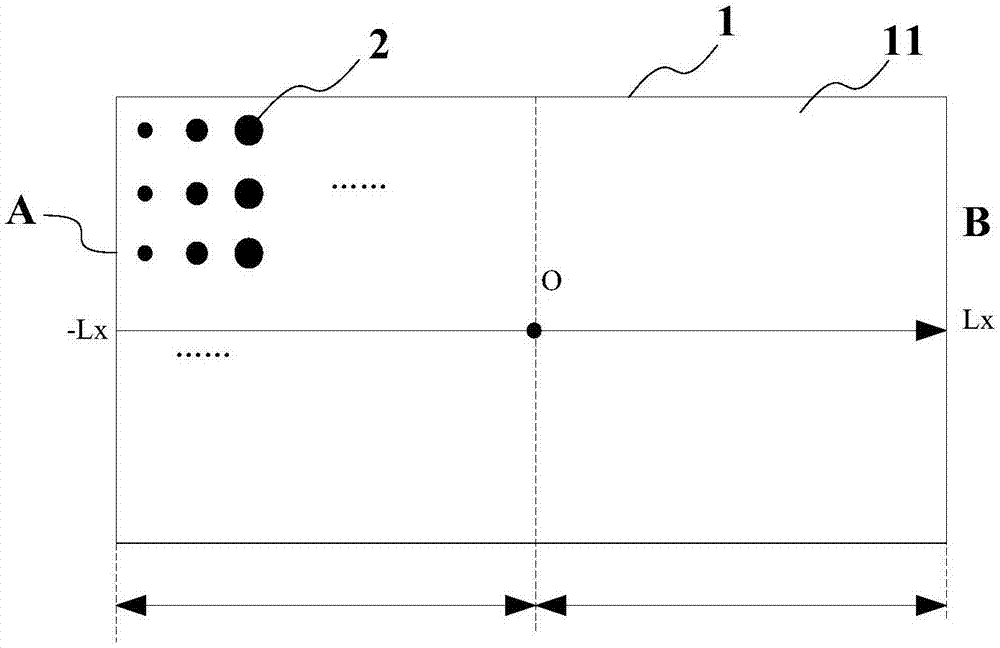
[0046] In this embodiment, the derivation and description are made for the case of a rectangular light guide plate, circular dots, the same dot spacing, and one-sided light entering with varying dot sizes:
[0047] First, step 1 is performed: obtaining the relational formula between the variable parameter of the screen size and the position of the screen. For circular dots, the size variable parameter is the radius (of course, it can also be represented by diameter). In other shapes of dot design, we only need to express the relationship between the dot size variable and the dot area in the design, for example, in square In the dot, it can be characterized by the side length. It should be noted that the size variable of the dot is preferred to only set one size variable. The next parameter is used as a variable, which can greatly reduce the amount of calculation. For the case of unilateral light input in this embodiment, we directly deduce the relationship between the dot rad...
Embodiment 2
[0082] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in that the dot size of the light guide plate remains unchanged and the dot pitch changes. It is used to teach those skilled in the art to understand how the method of the present application can be deformed in the case of different variable types of the light guide plate.
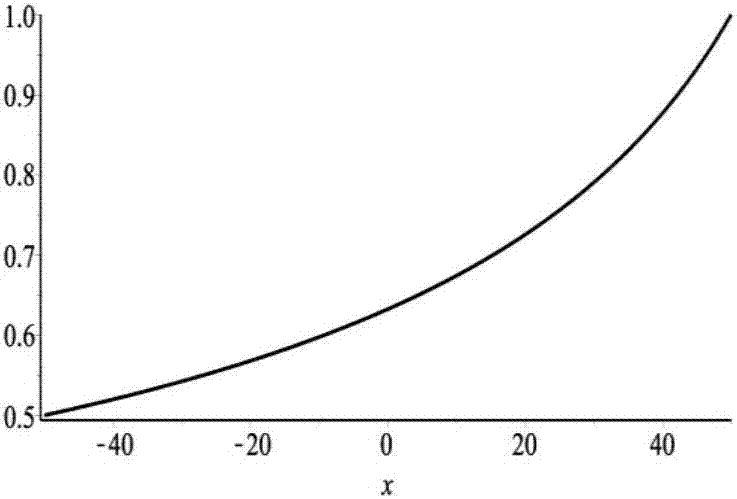
[0083] Similarly, Step 1: obtain the relational formula between the variable parameter of the dot spacing and the position of the dot. Based on the same optical principle and basic formula, the equations (1)~(4) and (6) remain unchanged, and the filling rate formula (5) needs to be deformed due to the change of variables, and the interval between adjacent columns of dots changes. The interval variable is ΔL(x), the distance between each row is a constant b (if it is a square, it is also ΔL(x)), and the dots are circular, then the filling rate η(x) should be the area of the circle divided by the area of the rectangle :
[0084]
[...
Embodiment 3
[0091] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is that the light sources are arranged on both sides or the periphery of the light guide plate. It is used to teach those skilled in the art to understand deformation under the condition of multi-sided light entering.
[0092] Similarly, proceed to step 1: obtain the relational formula between the variable parameter of the dot size and the position of the dot. The method of deriving by the basic principle of optics is introduced in embodiment 1, which is also applicable. Based on the superposition principle of incoherent light, the luminous flux scattered by the dots can be divided into the sum of two parts. At this time, (1) and Equation (2) should be established for the two parts, so that two functions can be obtained. Mathematical calculation process is no longer repeated, those skilled in the art can carry out corresponding deformation according to the teaching of the method in embodiment 1 and embodiment 2, fina...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com