A Streaming Balancing Graph Partitioning Method Oriented to Memory Computing
A technology of memory computing and balanced graph, applied in computing, resource allocation, program control design, etc., can solve the problems of low quality of division, ignoring characteristics, difficulty in meeting the requirements of division efficiency and division quality at the same time, and achieves obvious effects. Effects of reduced traffic and reduced edge cutting rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
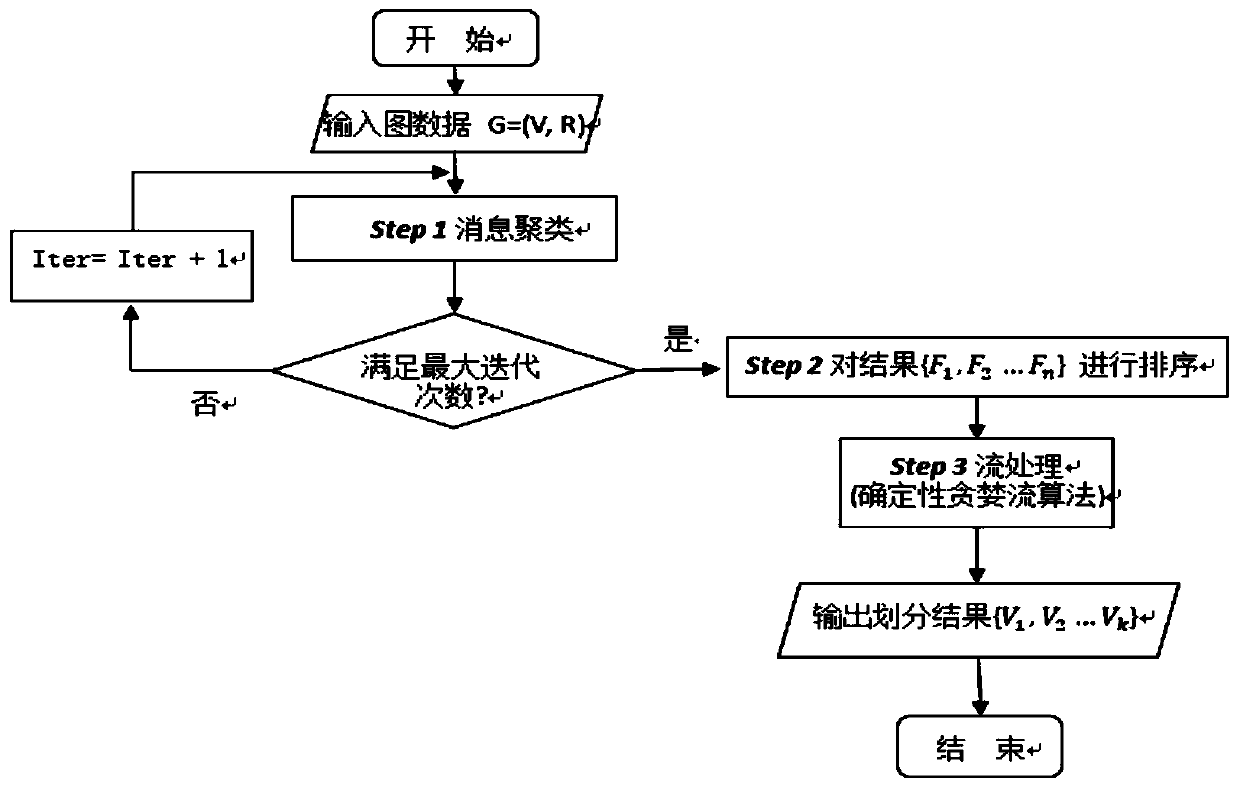
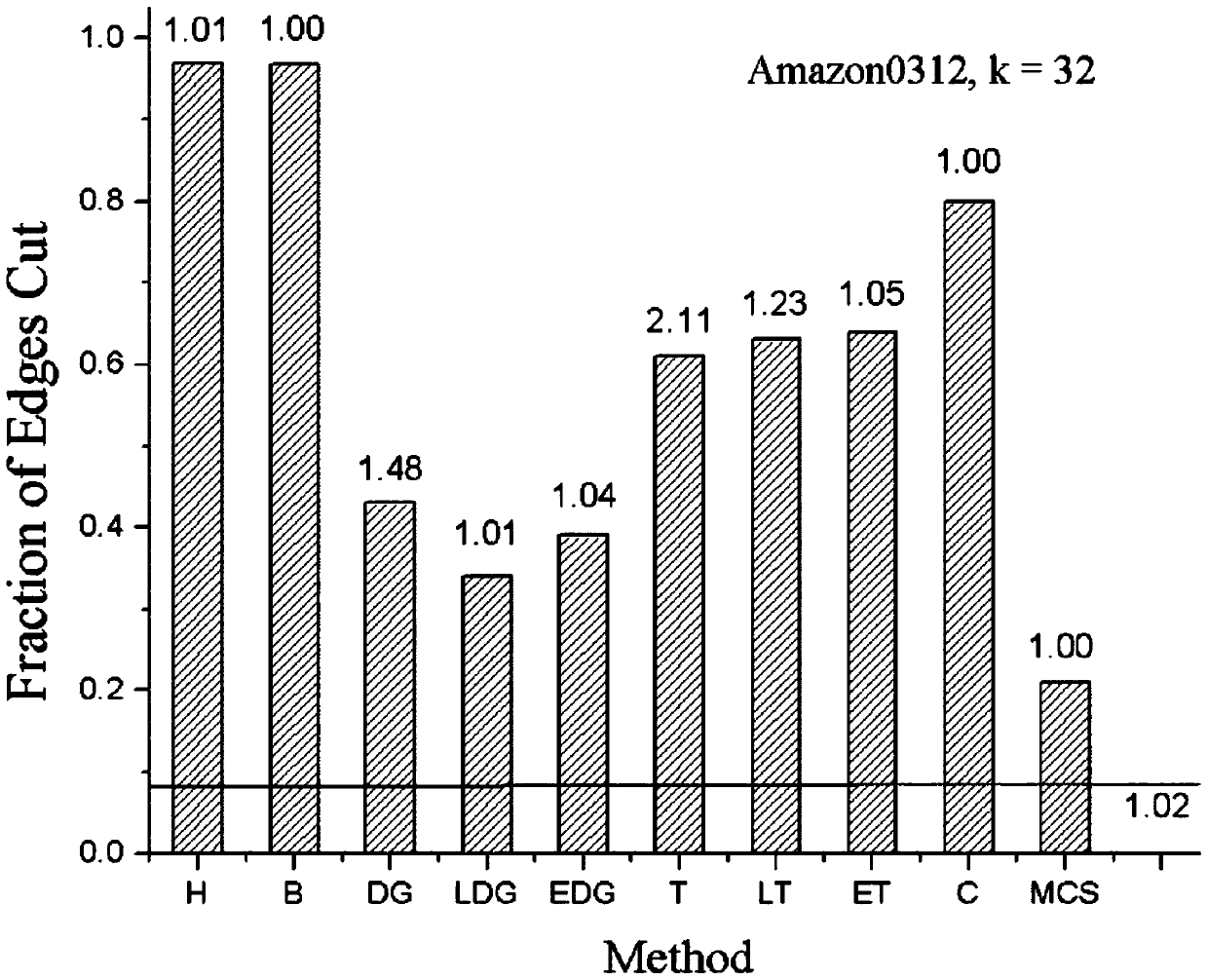
[0043] refer to figure 2 The division results of different division algorithms in Figure Amazon0312, the ordinate indicates the edge cutting rate Ecuti,j Indicates the number of cutting edges between different processing units, and E indicates the total number of edges in the graph. The abscissa indicates different division methods, hash algorithm (H), balance algorithm (B), exponential weight deterministic greedy algorithm (EDG), exponential weight triangular algorithm (ET), linear weight deterministic greedy algorithm (LDG), linear Weighted Triangulation Algorithm (LT), Triangulation Algorithm (T), Blocking Algorithm (C). K=32, the division result 0.08% that red line represents Metis, the numerical value that marks on the figure represents the balance coefficient of corresponding algorithm, and the balance coefficient of triangle algorithm (T) is maximum 2.11, and the balance coefficient of the present invention is 1.00, and the edge cutting rate is 21% , the closest to ...
Embodiment 2
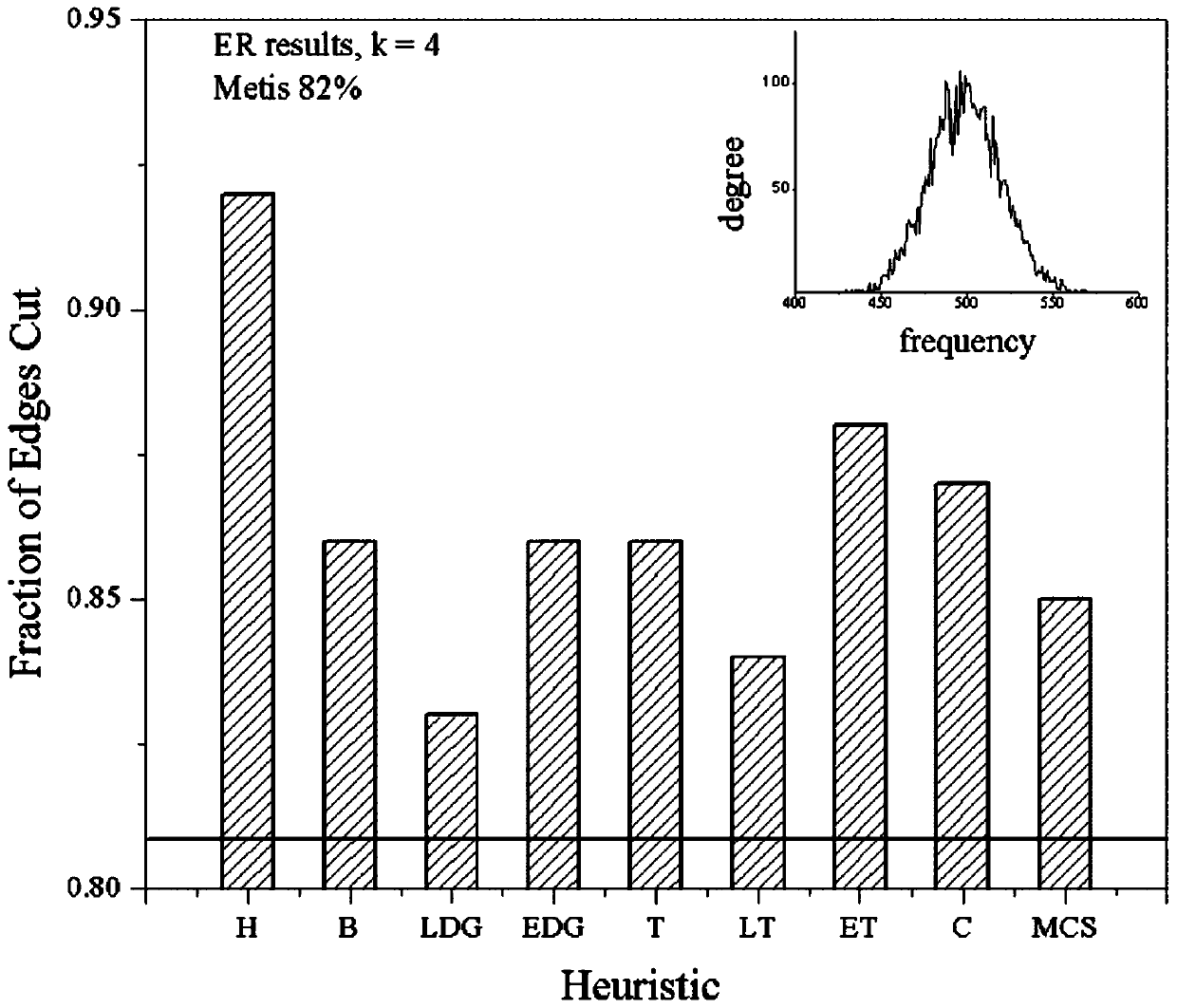
[0045] refer to Figure 3A with Figure 3B , the results of the theoretical power-law graph (PL) and non-power-law graph (ER), the ordinate represents the edge cutting rate The horizontal black line represents the metis division result (ideal value). The closer the value is to Metis, the better the quality of the division. The frequency diagram of the corresponding degree is shown in the upper right corner. The linear weight deterministic greedy algorithm (LDG) division quality in the division result of the ER diagram The best result is 83%, the hash algorithm (hash) result is the worst 92%, the present invention is 85%, and Metis is 81%. In the division results of PL, the edge cutting rate of the present invention is 49%, and that of Metis is 50%. Because the "small world" characteristic of the power-law network graph is particularly suitable for initial community detection, the present invention is particularly suitable for the division of power-law graphs.
Embodiment 3
[0047] refer to Figure 4 In the first step of the present invention, for the label selection problem of points, if there are more than one type of labels in the surrounding neighbors, one is randomly selected at this time, which contains randomness. Result has influence. Come verification stability of the present invention with 3 real figures (amazon0505, amazon0312, amazon0601), ordinate is standard deviation value Diferenc=λ t -λ t+1 Represents the difference between the edge cutting rate of the previous experiment and the edge cutting rate of the next time, and the abscissa indicates the number of experiments, by Figure 4 It can be seen that each time the difference fluctuates at a*10 2 , near (a∈[1,9]), the volatility is very small, which is negligible for large graphs, which shows the stability of this algorithm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com