A theoretical zero-error dynamometer
A dynamometer and zero-error technology, which is applied in the field of theoretical zero-error dynamometers, can solve problems such as complex structure, failure to meet energy-saving requirements, and large floor space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
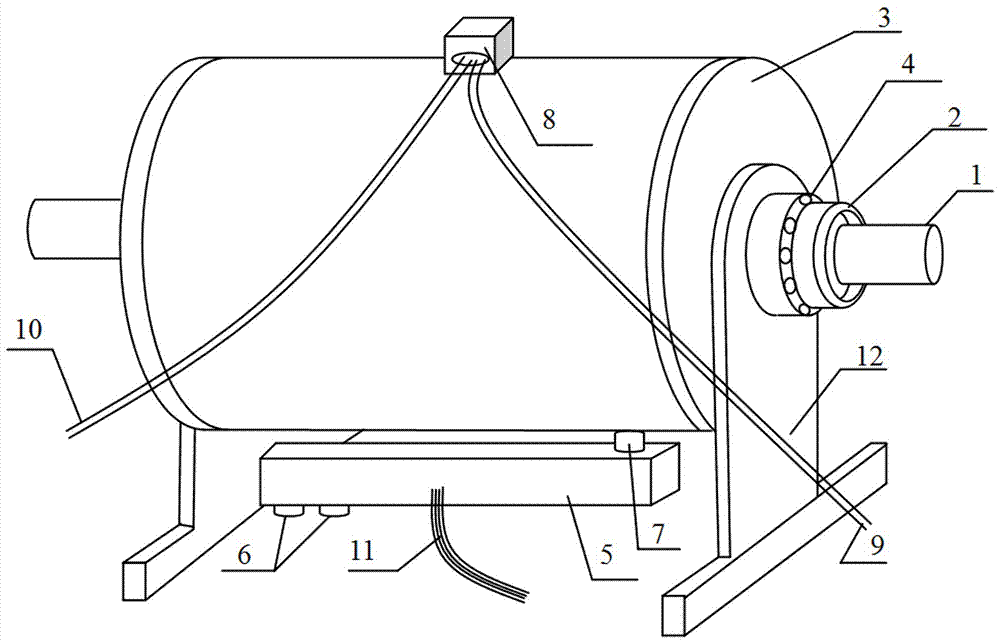
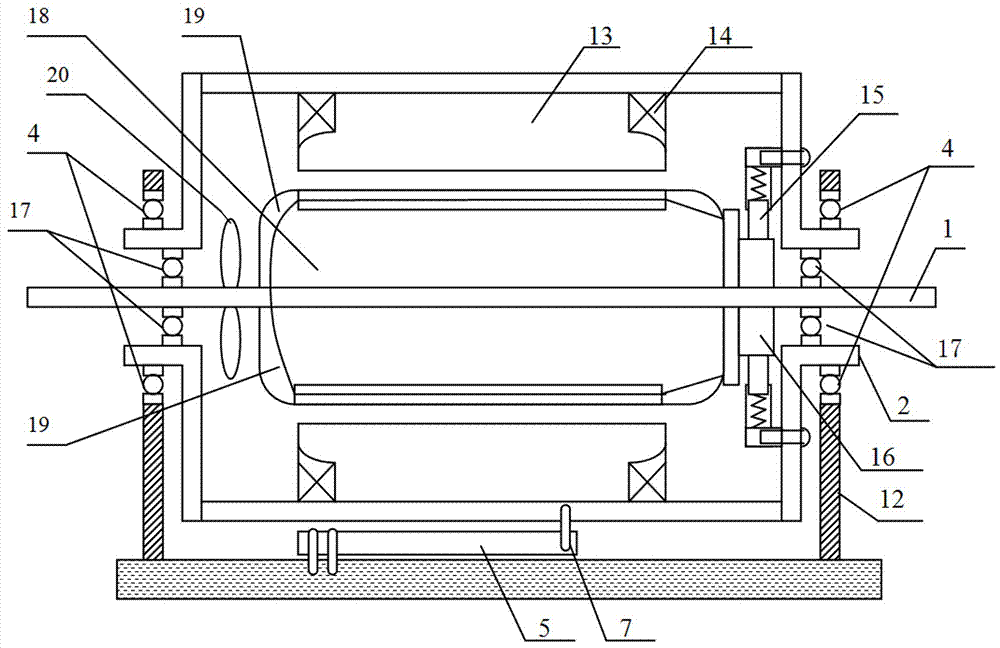
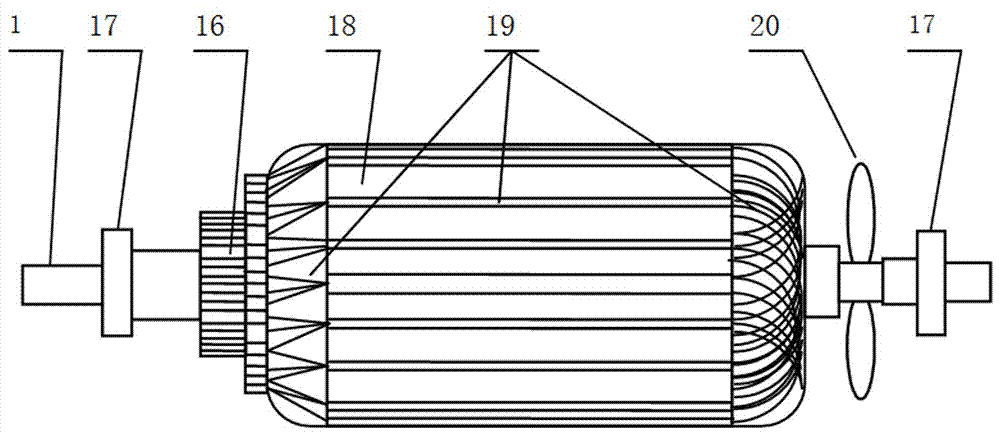
[0017] like figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the three-dimensional view and the cross-sectional view of the theoretical zero-error dynamometer of the present invention are respectively provided. The dynamometer shown is composed of a rotor, a stator 13, a rotating shaft 1, a casing 3, an end cover cover 2, a rotor bearing 17, and a casing bearing 4. The supporting plate 12 and the force sensor 11 are composed. The rotor is composed of the rotor core 18 and the rotor winding 19. The rotor core 18 is fixed on the rotating shaft 1 so that the rotor core 18 follows the rotating shaft 1 to rotate. The stator 13 shown is located on the periphery of the rotor, and the stator 13 is provided with an excitation winding 14, and the stator 13 is stipulated to be able to be connected to the casing 3; both ends of the rotating shaft 1 are fixed on the casing 3 throu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com