Directed self-assembly of electronic components using diamagnetic levitation
A diamagnetic, component technology, applied in diamagnetic/paramagnetic materials, electric components, holding devices with magnetic attraction or thrust, etc., can solve problems such as slowness, impossible and impractical use of robots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
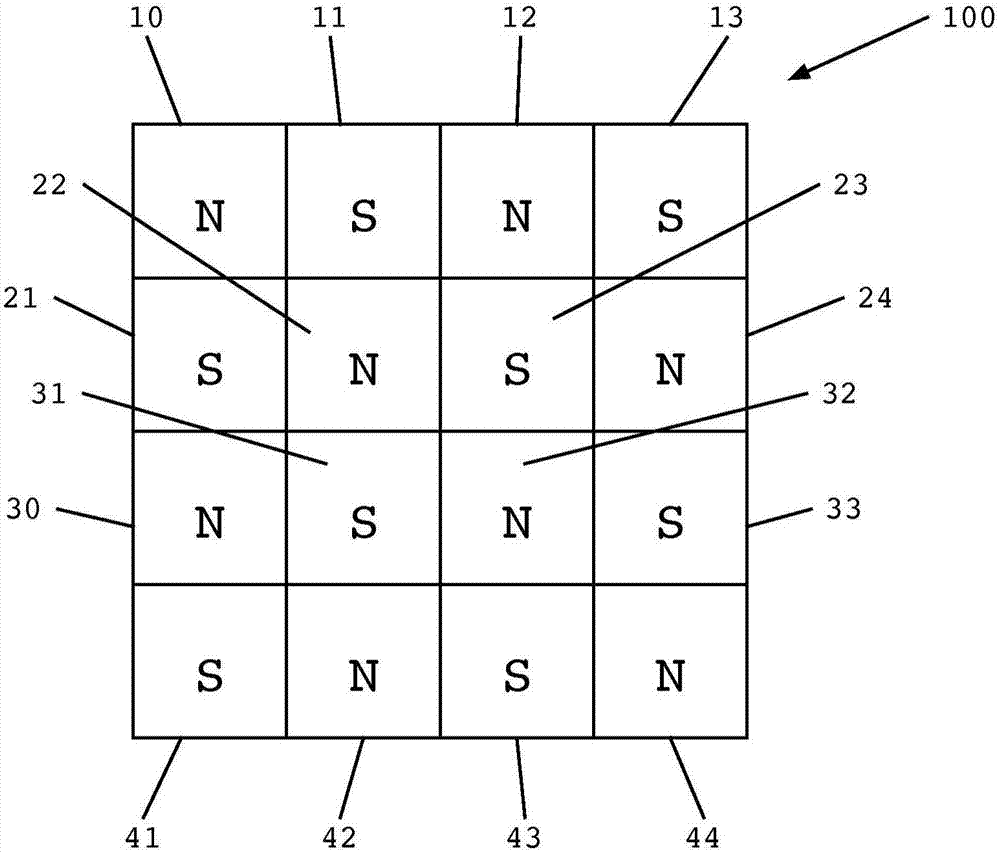
[0023] Referring now to the accompanying drawings, figure 1 A schematic top view of a magnetic table 100 suitable for use in accordance with various embodiments of the invention is shown. The magnetic table 100 includes a plurality of magnets arranged in rows and columns with alternating poles facing upward, similar to a checkerboard pattern. That is, the first row of magnets includes "northup" magnets 10 and 12 alternating with "south up" magnets 11 and 13, while the second row of magnets includes "northup" magnets 22 and 24 alternate "south up" magnets 21 and 23. The third and fourth rows of magnets repeat the pattern such that each pole on the surface of the magnetic table 100 adjoins with opposite polarity above, below, and on each side thereof, and with the same polarity diagonally. adjacent.
[0024] Such as figure 1 As shown, the magnetic table 100 comprises a "four by four" square. However, those skilled in the art will appreciate that the magnetic table 100 may b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com