A Method of Detection and Guidance for Surface Movement of Small Celestial Bodies
A technology for small celestial bodies and detectors, applied in the aerospace field, can solve problems such as the influence of uncertain dynamic characteristics and poor control accuracy, and achieve the effect of improving robustness and control accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
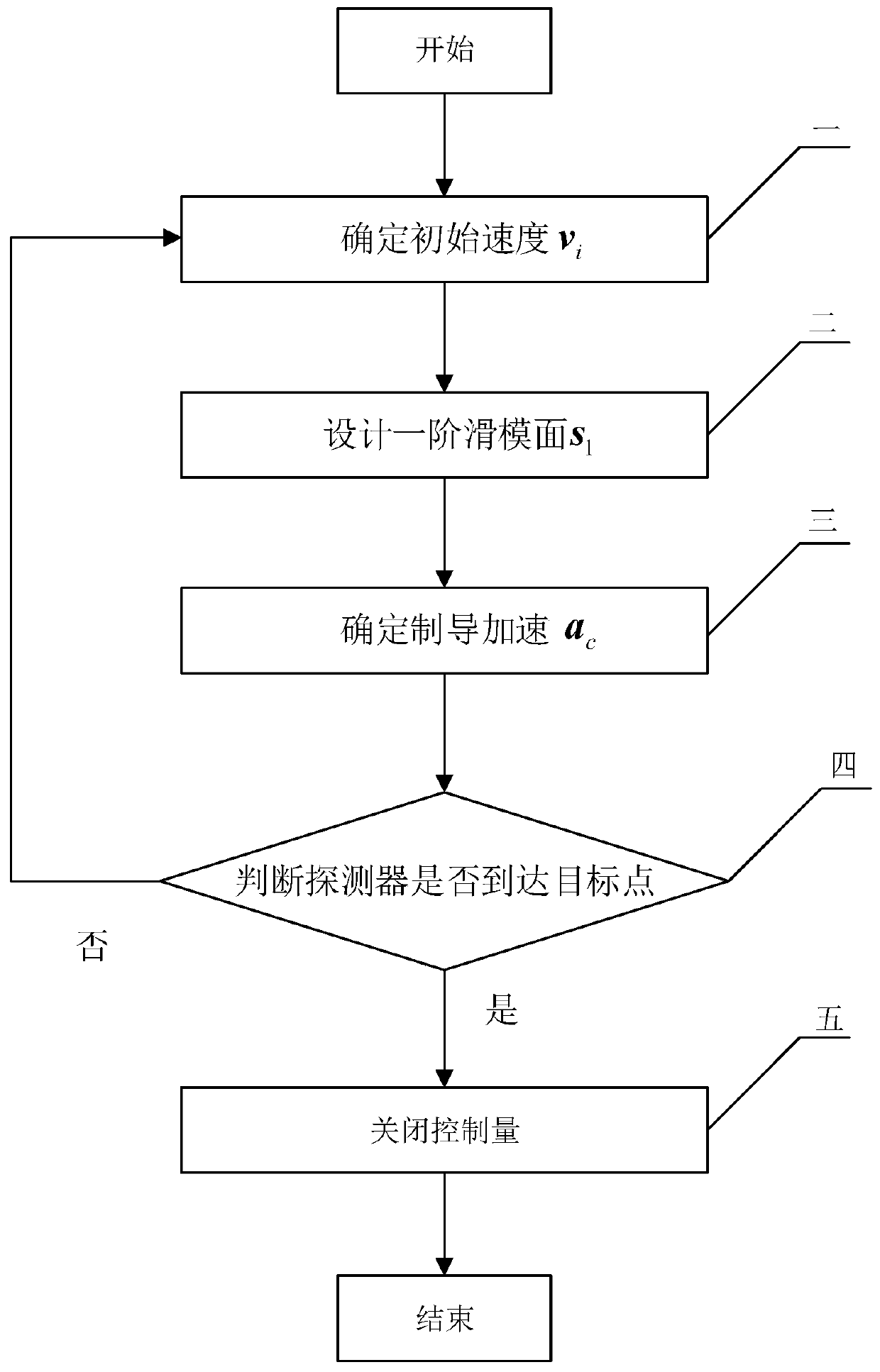
[0051] Step 1. Determine the initial velocity v i .
[0052] Use the three-axis ellipsoid model to construct small celestial bodies, the three semi-major axes are set to 3km, 2km and 1km respectively, and the density of the ellipsoid is 1200kg / m 3 , the spin angular velocity is 1.407×10 -4 rad / s.
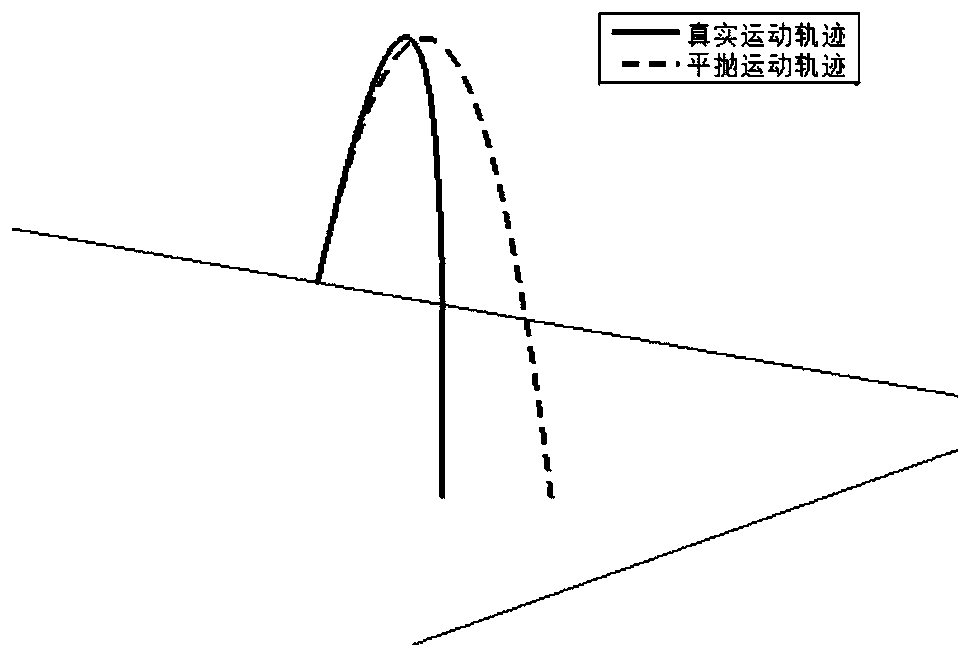
[0053]Define R as the vector from the starting point [2181,309,669]m pointing to the single bounce target point [1763,0,809]m, then the unit vector in the R direction is:
[0054]
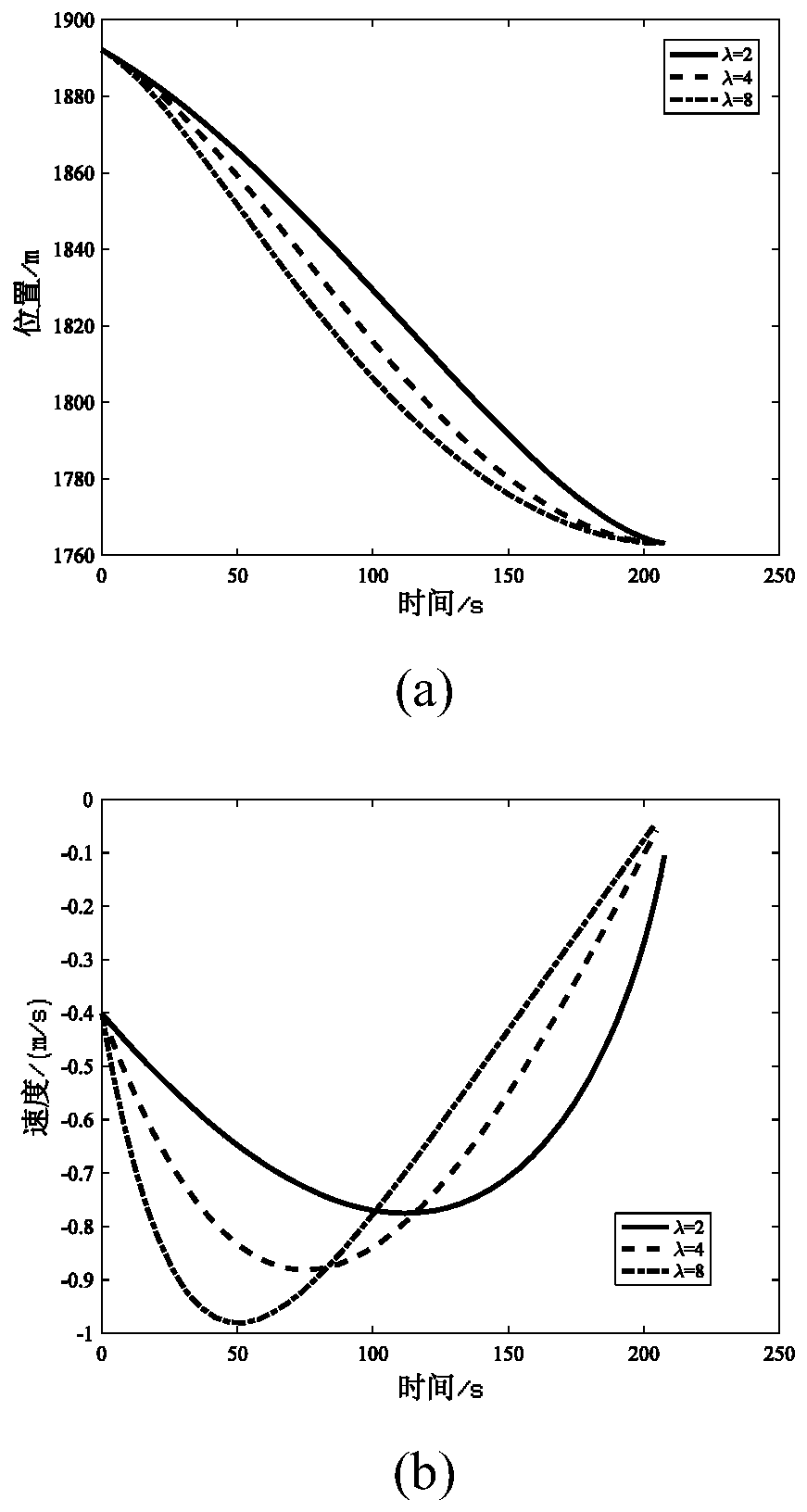
[0055] where R represents the modulus of the vector R. Define g as the gravitational acceleration vector at the starting point. In the R-g plane, let the vector l be perpendicular to R and point to the outside of the small celestial body. g l and g R are the components of the gravitational acceleration vector g along the l and R directions, respectively, and the expected bounce time t f Set to 1500s, then v i The velocity component along the l direction is:
[0056]
[0057] v i The velo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com