High-observability optical pulsar hybrid navigation method for deep space probe
A deep-space detector and hybrid navigation technology, applied in the field of deep-space detector navigation, can solve the problems of unobservable systems, achieve the effects of enhancing observability, improving navigation accuracy, and reducing convergence time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the drawings and embodiments.
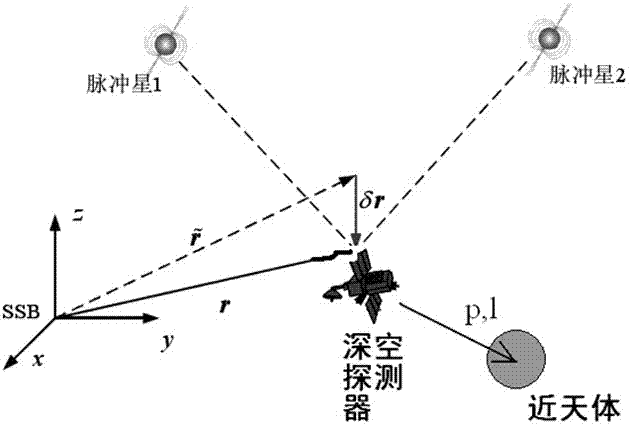
[0041] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of the optical pulsar hybrid measurement scheme of the present invention, wherein SSB refers to the solar system barycenter (Solar System Barycenter, which is the origin of the coordinate system in the figure, and the r of the deep space probe is calculated relative to this point), Pulsar 1 and Pulsar 2 are used for pulsar observations of near celestial bodies (such as Mars). When deep space probes approach large celestial bodies, they introduce optical observations of nearby celestial bodies as a supplement.
[0042] The optical pulsar mixing highly observable deep space navigation method described in the present invention has the following steps:
[0043] Step 1: When the detector is close to the large celestial body, the optical observation of the adjacent celestial body is introduce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com