A metabolically modified Bacillus subtilis biotransformation cell and its preparation method and application
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and biotransformation, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering metabolic transformation and microorganisms, can solve problems such as accumulation of by-products, side reactions, degradation of substrates or products, etc., so as to increase the conversion rate, increase the effective conversion rate, and improve the conversion rate. efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Construction of recombinant Bacillus subtilis:
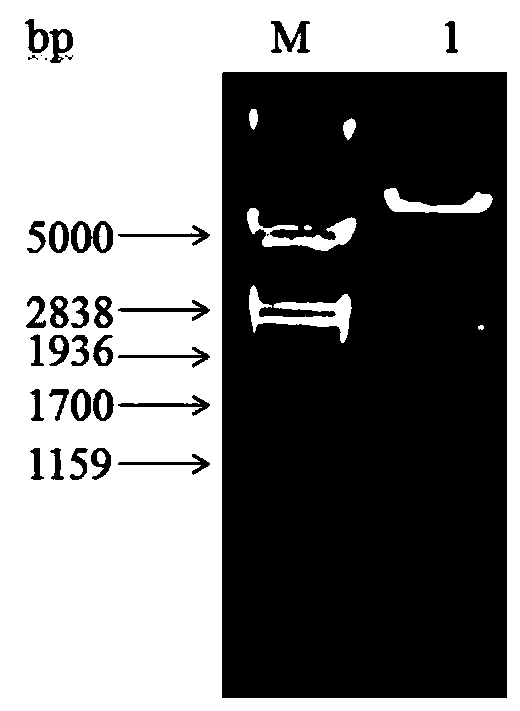
[0038]The gene sequence of L-glutamic acid oxidase (LGOX) derived from Streptomyces sp.X-119-6 was synthesized through codon optimization (the amino acid sequence of L-glutamic acid oxidase is shown in SEQ ID No.1. shown; the gene sequence of the L-glutamic acid oxidase is shown in SEQ ID No.2), and BamH Ⅰ and EcoR Ⅰ restriction sites were added to the 5' end and 3' end respectively, and the above-mentioned enzyme was synthesized by the company The LGOX gene was cloned into the pUC57 vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pUC57-LGOX. Then, the above-mentioned LGOX gene was connected to the pHY-Bs.xyl inducible expression vector through molecular cloning to obtain a recombinant plasmid containing the L-glutamic acid oxidase gene. Plasmid pHY-Bs.xyl-LGOX, verified by double digestion with BamH Ⅰ and EcoR Ⅰ ( figure 1 ) to obtain target fragments of corresponding size.
[0039] Transform the inducible expressio...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Knockout of gene glnA and integration of target gene
[0041] (1) Using primers GlnA-F and GlnA-R as upstream and downstream primers, amplify the gene glnA (glutamine synthetase) from Bacillus subtilis WB600 by PCR, and connect it to the pMDT19-simple plasmid vector by T-A cloning , to construct recombinant plasmids, respectively marked as pMD-glnA, select two suitable restriction sites Nco Ⅰ and Pst Ⅰ in the above-mentioned amplified gene, respectively, after double digestion, remove the 818bp part of the glnA gene fragment, and recover from the gel Obtain a fragment of 3210bp, that is, use the remaining part as a homology arm;
[0042] (2) Using the B. subtilis WB600 genome as a template, P43-Nco Ⅰ-F, P43-R-LGOX as upstream and downstream primers to amplify the P43 promoter with a size of 426bp, using pUC57-LGOX as a template, P43-LGOX-F , LGOX-Pst Ⅰ-R as upstream and downstream primers to amplify the LGOX gene, using the amplified LGOX and P43 as templat...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Construction of embodiment 3 recombinant strain WB604
[0050] The expression plasmid pHY-Bs.xyl-LGOX was transformed into WB603 according to the transformation method, and the recombinant bacterium WB604 was constructed. The specific implementation method is as follows:
[0051] Medium: Bacillus subtilis B. subtilis WB600 transformation medium:
[0052] SP Ⅰ-a solution (g·L -1 ): (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 4,K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 28, KH 2 PO 4 12. Sodium citrate dihydrate 2;
[0053] SP Ⅰ-b solution (g·L -1 ): MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.4;
[0054] 500g·L -1 glucose solution;
[0055] 100×CAYE solution (g·L -1 ): casamino acids 20, yeast powder 100;
[0056] CaCl 2 Solution: 50mmol·L -1 ;
[0057] MgCl 2 Solution: 250mmol·L -1 ;
[0058] 100×EGTA solution: Weigh 3.8g of EGTA (ethylene glycol ditetraacetic acid) and dissolve it in 1L of deionized water, adjust the pH to 8.0 with NaOH, filter and sterilize, and store at -20°C for later use;
[0059] Sterilize the reagent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com