A numerical representation method and system for the stress-strain constitutive relationship of materials
A technology of constitutive relationship and numerical characterization, applied in the direction of analyzing materials, using stable tension/pressure to test the strength of materials, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as large performance deviations and inability to meet design refinement requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] According to the method of the present invention, the materials with different properties are specifically measured, and the numerical model is used to simulate them, and the parameters in the model are obtained to obtain the mechanical properties of the measured materials.
[0040] According to the classification of metal materials into materials with obvious yield stage and materials without obvious yield stage, select the corresponding numerical model. When the material is a material with obvious yield stage, the corresponding stress-strain numerical model for,
[0041] where T s Indicates the minimum temperature at which the yield plateau of the tensile curve disappears, and a and b are parameters in the stress-strain numerical model. By calculating the parameters a and b, the mechanical properties of a material with an obvious yield stage can be characterized.
[0042] When the material is a material without obvious yield strength, the corresponding stress-strain ...
Embodiment 2
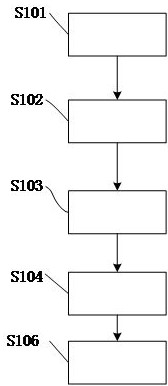
[0076] Such as figure 1 As shown, the numerical characterization method of the material stress-strain constitutive relationship in this embodiment of the present invention includes, S101 setting test parameters, and the test parameters include the sample temperature.
[0077] S102 Perform a tensile test on the material according to the test parameters, and acquire tensile test data of the material, where the tensile test data includes stress data and strain data.
[0078] S103 establishing a stress-strain curve according to the stress data and the strain data.
[0079] S104 Select a corresponding stress-strain numerical model according to the properties of the material, fit the stress-strain curve of the material, and obtain parameters in the stress-strain numerical model. The numerical characterization method in the embodiment of the present invention is close to the reality. The stress-strain data of the tensile test is used as the fitting basis, and the numerical model cor...
Embodiment 3
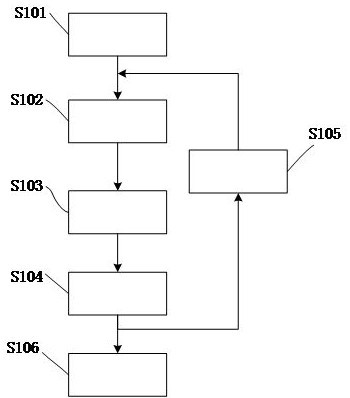
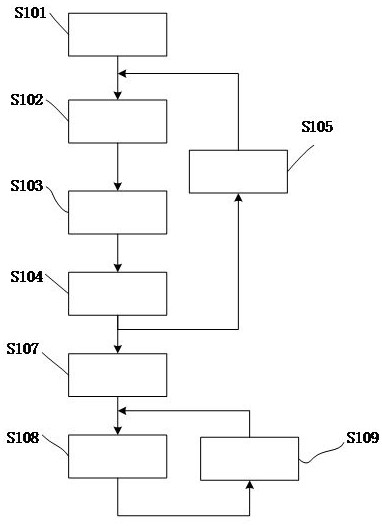
[0094] Such as Figure 5 As shown, one embodiment of the numerical characterization method of the material stress-strain constitutive relationship of the present invention adopts a tensile test to obtain the test data of the material, specifically, S201 formulates the test method according to the material, and sets the sample of the material sample Require, set the strain rate, set the frequency of data and financial resources, set the strain range, set the stretch rate, set the temperature of the test, the sample used in this embodiment of the present invention is as follows Image 6 As shown, a sample with a diameter of 10mm is selected, and the stretching time is divided into room temperature stretching and high temperature stretching, and the stretching rate is set in two cases. When stretching at room temperature, that is, stretching at room temperature, stretching The stretching temperature is between 10°C and 35°C. The stretching temperature can also be set at 23°C±5°C....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| reduction of area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com