Bus differential protection method and device using self-synchronization technology
A busbar differential protection and self-synchronization technology, applied in the direction of emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of occupying transmission channel resources and increasing construction costs, and achieves small distributed capacitance of the busbar, saving construction capital, and strong self-adaptation sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
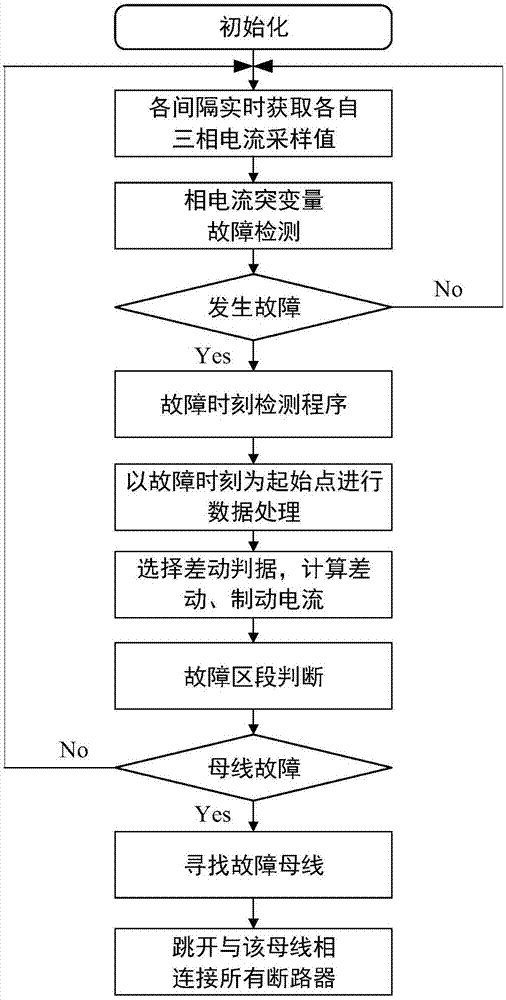
[0066] combine figure 1 The fault processing flow chart shown in the figure shows the implementation process of the bus differential protection method using self-synchronization technology by taking the A-phase ground fault of the II bus as an example:
[0067] Step 1: collect the three-phase instantaneous current at each bay protection installation place connected to the busbar, and calculate the sudden change of the three-phase instantaneous phase current at each bay in real time. In this step, according to domestic smart substation standards, the sampling frequency is 4 kHz, the number of sampling points per cycle is N=80, and the sampling time interval is 0.25 ms.
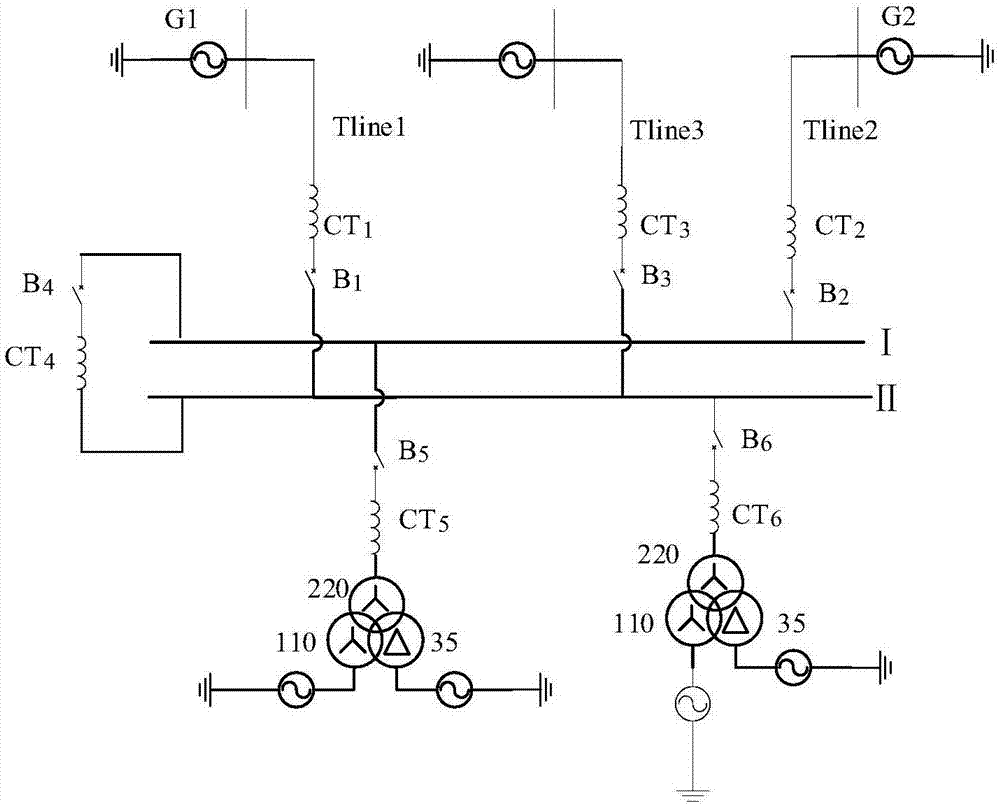
[0068] In the specific implementation process, the current transformers CT1, CT2, CT3, CT4, CT5, and CT6 are used to measure the instantaneous current of each interval three-phase in real time, the sampling frequency is 4kHz, and 80 points are collected per cycle; Current sudden change Δi φ .
[0069] In add...
Embodiment 2
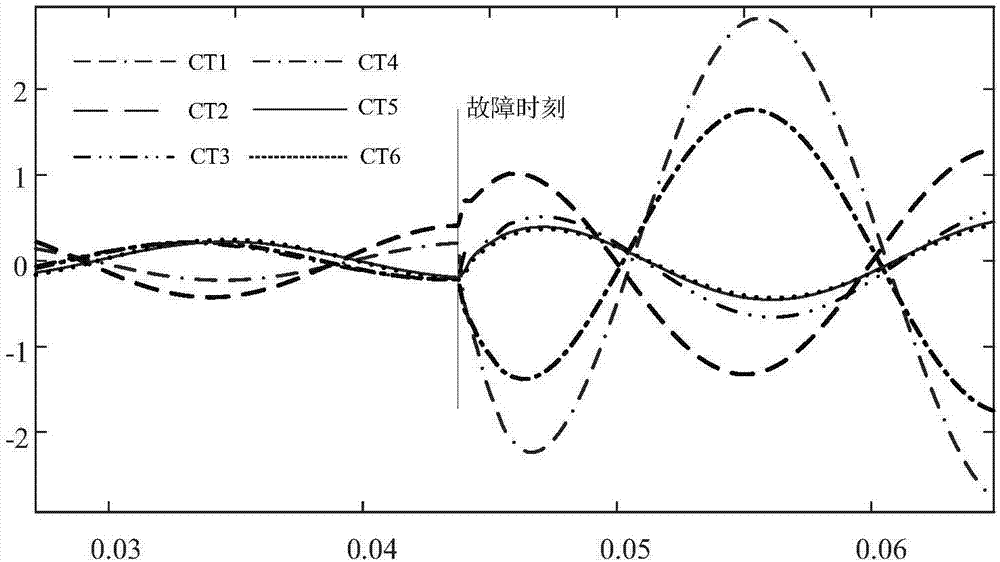
[0105] A phase-to-ground fault occurs on the line Tline3, and the fault handling process is the same as that in Embodiment 1. Table 2 shows the estimated fault times of each interval.
[0106] Table 2 The fault time obtained for each interval when the line is faulty
[0107]
[0108]
[0109] When a phase-A ground fault occurs on line Tline3, the protection action characteristics of the large bus difference, Ⅰ bus small difference, and Ⅱ bus small difference are as follows: Figure 5(a)-Figure 5(c) shown.
[0110] As shown in Table 1 and Table 2, the fault time calculated for each interval is very close to the actual fault occurrence time, the maximum error is only 0.25ms, and the phase angle error is only 4.5°, which is within the allowable range of differential protection. At a sampling frequency of 4kHz, there is only one sampling point difference from the real fault time, and the synchronization accuracy fully meets the synchronization requirements of differential p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com