Implementation method of spin lock as multi-core CPU accessing resources
A technology for accessing resources and implementing methods, which is applied to the implementation of multi-core CPU spin locks and can solve problems such as bus occupancy and overhead.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] For any n-core CPU system, its CPU number is 0~n-1, then any number such as the kth (0≤k≤n-1) CPU, the specific implementation process of obtaining resource access rights is as follows image 3 shown.
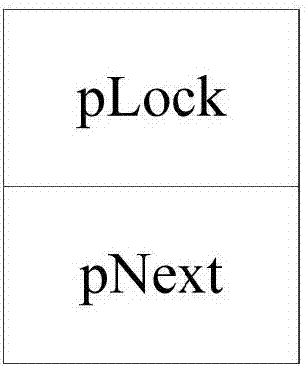
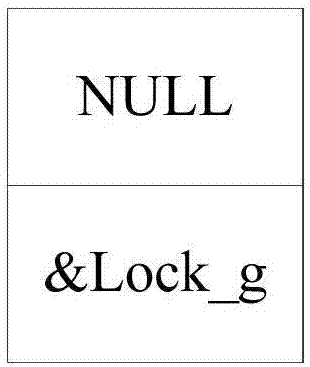
[0076] Before the kth CPU accesses the resource, initialize the resource lock and assign an initial value, such as figure 2 As shown, pLock is assigned a value of NULL, that is, the memory content is NULL, indicating that the current resource is not occupied. pNext is assigned a value of &Lock_g, that is, the next lock address of the resource lock is itself. Therefore, the initialized resource lock forms a one-way self-circulating list, such as figure 2 shown.
[0077] The kth CPU locks and unlocks when accessing resources.
[0078] Compared with the prior art, the method according to this embodiment allocates a resource lock for each shared resource, and each resource lock forms a one-way self-circular linked list when the right to use the shared resource is not oc...
Embodiment 2
[0080] In this embodiment, a specific implementation scheme of locking and unlocking in Example 1 is given. During the locking and unlocking process of this method, the CPU does not need to retain its own spin lock when using resources, specifically as Figure 4 shown.
[0081] S101: Set the first unit of the spin lock of the kth CPU to be non-empty, and set the second unit to be empty.
[0082] Wherein, the spin lock is formed in the running stack.
[0083] In programmatic operation, this can be achieved as follows:
[0084] When the CPU obtains access rights to shared resources, it first declares. Declare the type variable me of the spin lock LOCK, and assign the initial value to the spin lock, [pLock]=&me, [pNext]=NULL.
[0085] S103 The k-th CPU puts the spin lock at the end of the current queue for resource acquisition, and simultaneously acquires the last lock ID of the queue before the above-mentioned spin lock is placed in the queue, that is, the ID of the previous...
Embodiment 3
[0120] The above process of unlocking and unlocking does not provide an interface for trying to access resources. The method further includes a method of trying to obtain resource usage rights, that is, when resources are occupied, the CPU does not need to wait for resource locks to be acquired, and can perform other operations. The corresponding operation method is performed only when it is determined that the resource usage permission has been obtained.
[0121] When trying to access, the atomic operation of the bus hardware lock mode can be used, and the operation flow is shown in Figure 5:
[0122] Assuming that the kth CPU is trying to obtain access to resources, that is, the initialization return value pRet=&Lock_g, the step goes to S201.
[0123] S201 locks the resource access queue of the CPU before the kth CPU acquires the access resource, and the CPUs not in the queue can access the resource only when the queue lock is unlocked.
[0124] In programmatic operation, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com