Method for monitoring grounding current of main transformer iron core
A technology of iron core grounding current and main transformer, applied in the direction of measuring current/voltage, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as transformer tripping, transformer oil performance degradation, burnout, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
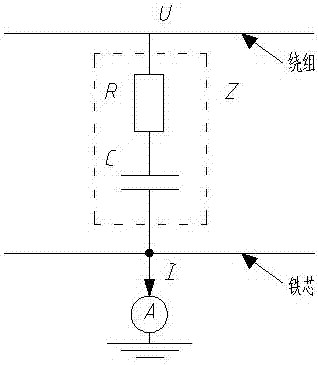
[0019] like figure 1 As shown, the main transformer includes a winding and an iron core, and an ammeter can be connected in series between the iron core and the ground. The voltage U on the winding is coupled to the iron core through a resistor R and a capacitor C, and then enters the ground through the ammeter, I=U / Z, The ground current of the iron core is monitored by an ammeter.
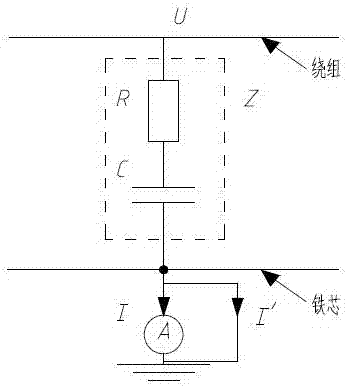
[0020] During normal operation, Z is very large, that is, the current passing through the ammeter is very small, generally tens of milliamperes. When the insulation between the winding and the iron core is damaged, that is, Z decreases and I increases. When the iron core is grounded at multiple points or the insulation between the iron core and the ground is reduced, the schematic diagram is as follows: figure 2 As shown, due to the shunting of the branch, the current flowing through the ammeter will decrease. Therefore, the reading of the ammeter can be used to judge whether the insulation ...
Embodiment 2
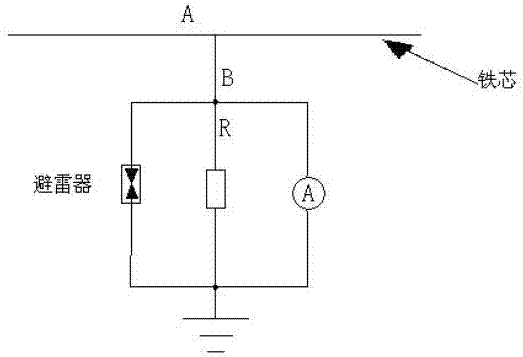
[0022] In the first embodiment, if figure 2 As shown, when the ammeter breaks inside, the iron core will lose its grounding, and a pair of ground potentials will be generated, and a floating discharge will occur at point B. In order to avoid this phenomenon, a resistor with a small resistance can be connected in parallel between the ammeters, the resistance value is close to the internal resistance of the ammeter, and a low-voltage arrester can be connected in parallel, such as image 3 shown.
[0023] The arrester presents a high-resistance state at low voltage, which is equivalent to an open circuit, that is, in normal operation, no current flows through the arrester, and the grounding current of the iron core is divided into two parts: one part passes through the parallel resistance R, and the other part passes through the ammeter, so as long as you know the parallel connection The resistance value and the internal resistance of the ammeter can accurately calculate the gr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com