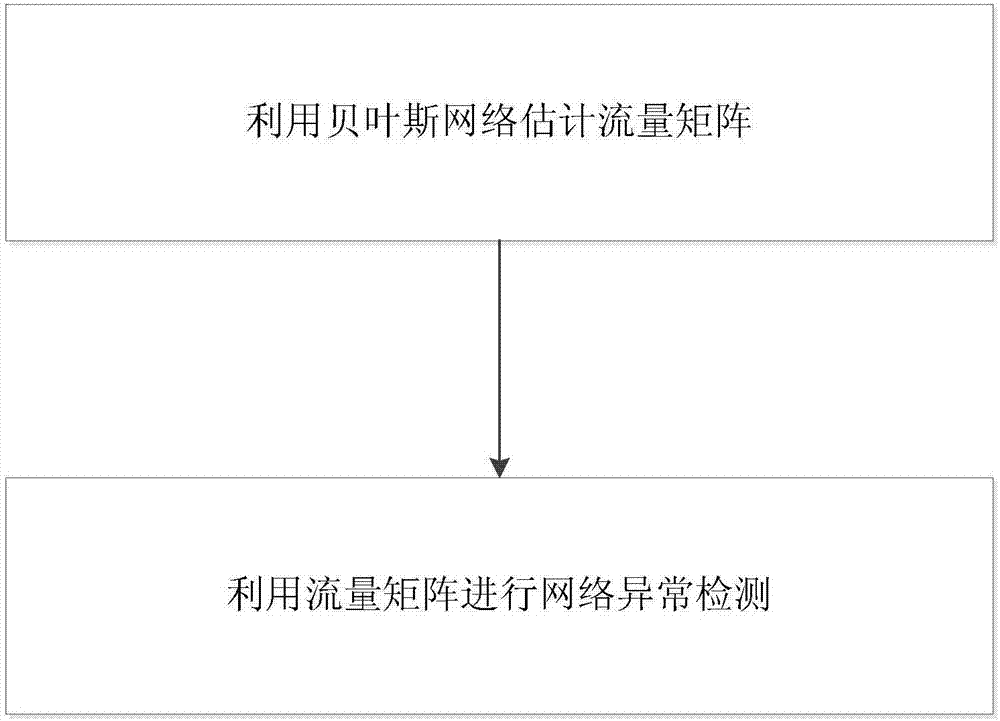
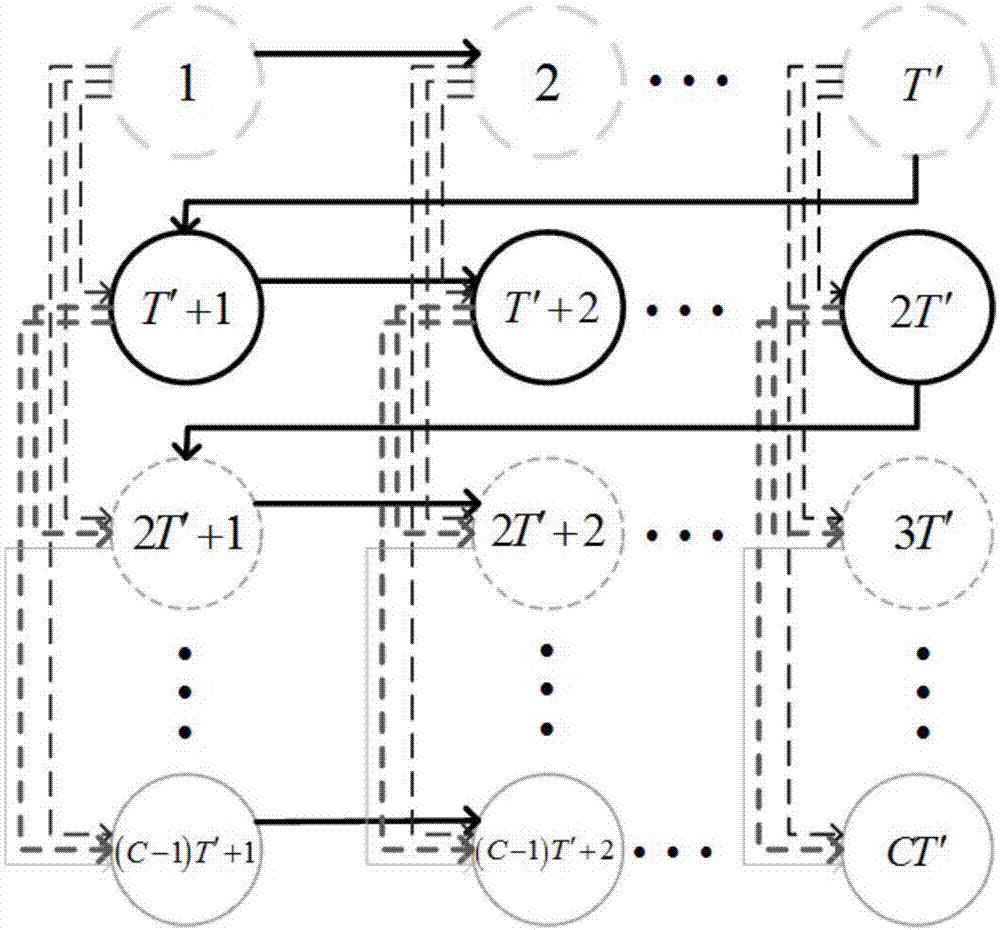
Network service anomaly detection method based on distributed probe monitoring
A technology for network services and network anomalies, which is applied in the field of network service anomaly detection based on distributed probe monitoring, and can solve the problems of complex network traffic statistics characteristics and characterization of network traffic statistics characteristics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
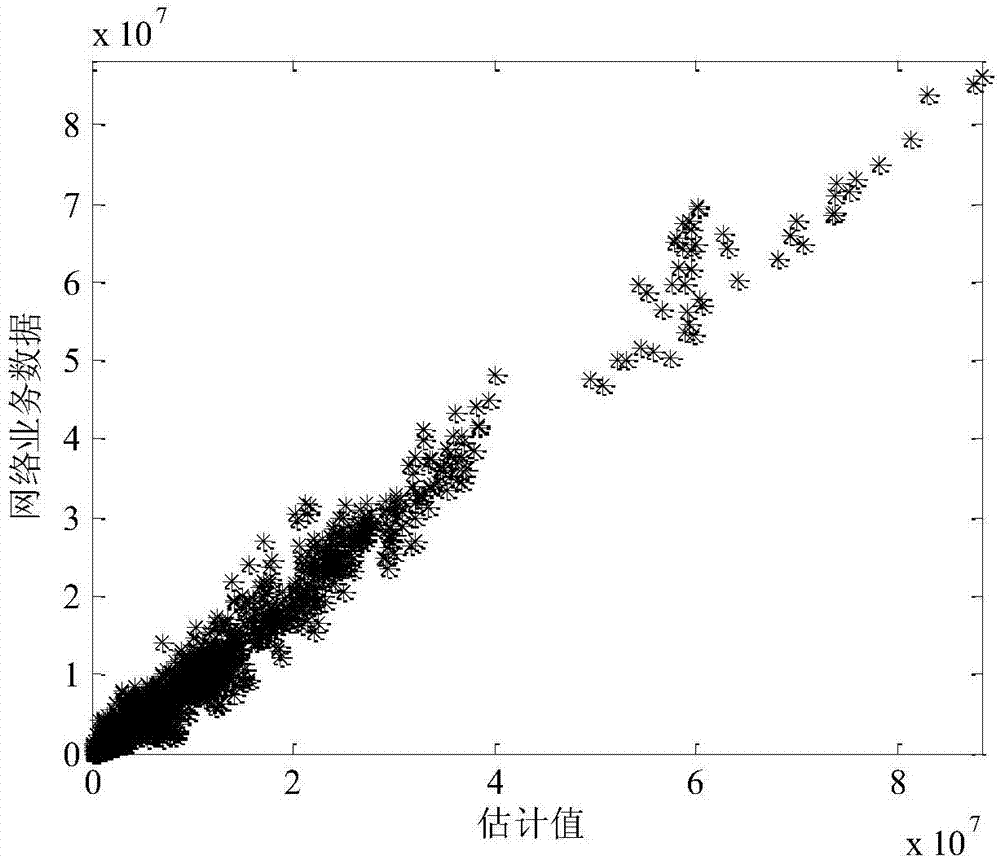
[0103] Directly compare Abilene and The actual flow of the backbone network and the estimated value obtained by the network service anomaly detection method based on distributed probe monitoring of the present invention.
[0104] image 3 with 4 shows Abilene and The comparison between the actual values of the two network data flows and the estimated value of the network data flows obtained by using the method for estimating the flow matrix of the present invention. The x-axis and y-axis respectively represent the estimated value and the real value of network data traffic, from image 3 It can be seen that the BN algorithm can accurately estimate the Abilene network data flow, but there are still a small amount of negative estimates. For network data, such as Figure 4 As shown, the BN algorithm has a large estimation error, especially a more obvious negative estimation.
Embodiment 2
[0106] Evaluate the effectiveness of the algorithm;
[0107] In the simulation, compare the BN algorithm with the SRSVD algorithm, TomoGravity algorithm and PCA algorithm. First compare the estimated bias of the four algorithms, the estimated bias of the algorithm is defined as
[0108]
[0109] Among them, X(n,t) and represent real network traffic and its estimated value, respectively.
[0110] Figure 5 It is the estimated deviation of the four algorithms for Abilene network data. The x-axis represents the ID of the OD flow, and is arranged in descending order according to the average traffic value. The y-axis represents the estimated deviation of the algorithm. It can be seen that as the average value of the OD flow decreases, the BN algorithm and The estimated deviation of the SRSVD algorithm gradually decreases, and compared with the SRSVD algorithm, the BN algorithm has a smaller estimated deviation. In addition, the estimated deviations of the TomoGravity algorit...
Embodiment 3
[0116] Evaluate the overall performance of the algorithm;
[0117] The performance improvement ratio of the algorithm is used as a measure to evaluate the overall performance of the algorithm, and the performance improvement ratio of the algorithm is defined as
[0118]
[0119] in, with Represent the estimated value of the flow matrix obtained by algorithm a and algorithm b, respectively. Such as Figure 9 As shown, for Abilene network data, the performance improvement rates of BN algorithm compared with SRSVD algorithm, TomoGravity algorithm and PCA algorithm are 57.61%, 53.14% and 54.94%, respectively. Such as Figure 10 shown, for Network data, the performance improvement rate is 46.91%, 44.71% and 71.70%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com