A quality control method for dna ploidy analysis equipment
A quality control method and technology of analysis equipment, applied in the direction of analyzing materials, material analysis by optical means, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate analysis results, and achieve the effect of accurate and error-free analysis of samples
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
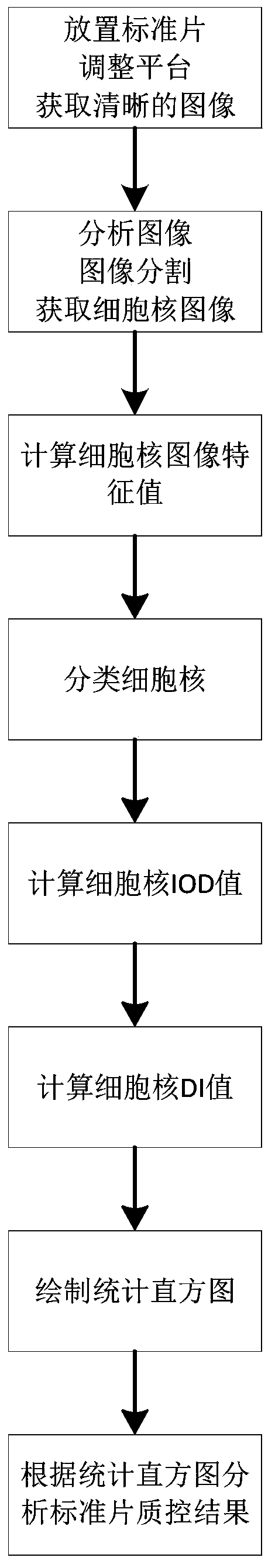
[0032] Specific embodiment one: a kind of quality control method of DNA ploid analysis equipment comprises the following steps:
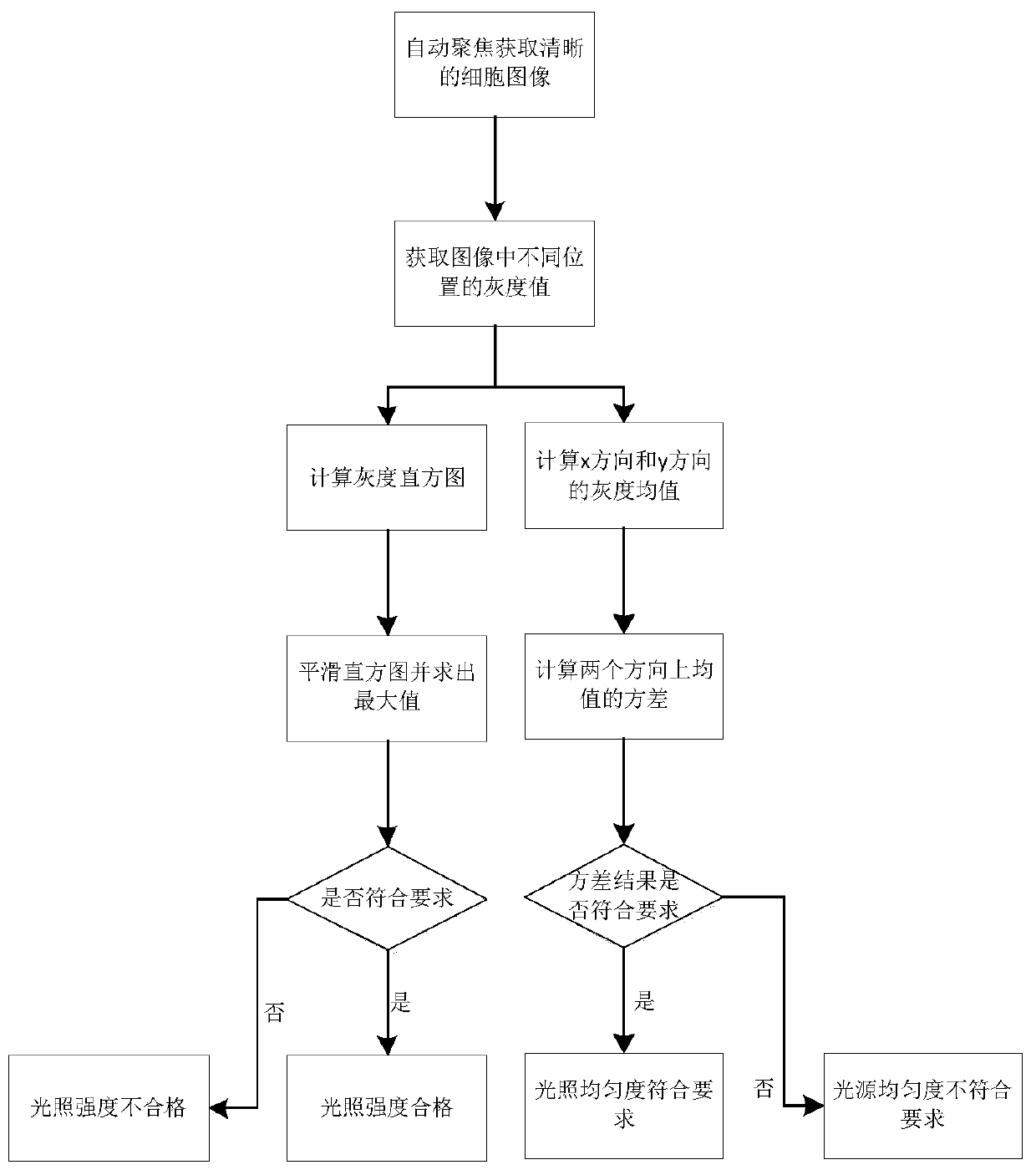
[0033] Step 1: By analyzing the pictures under the microscope field of view, adjust the light source in the microscope to make the light intensity and light uniformity meet the requirements;
[0034] If T low ≤p max ≤T high Then the light intensity meets the requirements, where T low , T high Respectively represent the minimum and maximum values of the light source intensity that meet the requirements, T low , T high After many experiments and theoretical explorations, it can make the equipment operate normally, keep the image from being too dark or too bright, which will affect the analysis of cells, and the results are within the allowable range of error, which will not lead to misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis. p max for p(p k ), the maximum value in p(p k ) is the mean value of the number of pixels corresponding to the gray level in th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0045] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in the step 1, by analyzing the pictures under the microscope field of view, the specific process of judging the intensity of illumination and the uniformity of illumination is as follows:
[0046] Step 11: Place the sample piece on the platform, and adjust the platform up and down to make a clear cell image under the camera field of view (the collected cell image has a clear outline, not blurred, not blurred, that is, the focus of the microscope objective lens coincides with the edge of the cell screen) ;
[0047] Step 1 and 2: Use the camera to capture the picture. Under the microscope, the black and white picture of the cell is represented by A0, and A0(i, j) represents the gray level at the image position (i, j), 1≤i≤M, 1≤j≤ N; M is the number of pixels in the horizontal direction in the captured image, and N is the number of pixels in the vertical direction in the captur...
specific Embodiment approach 3
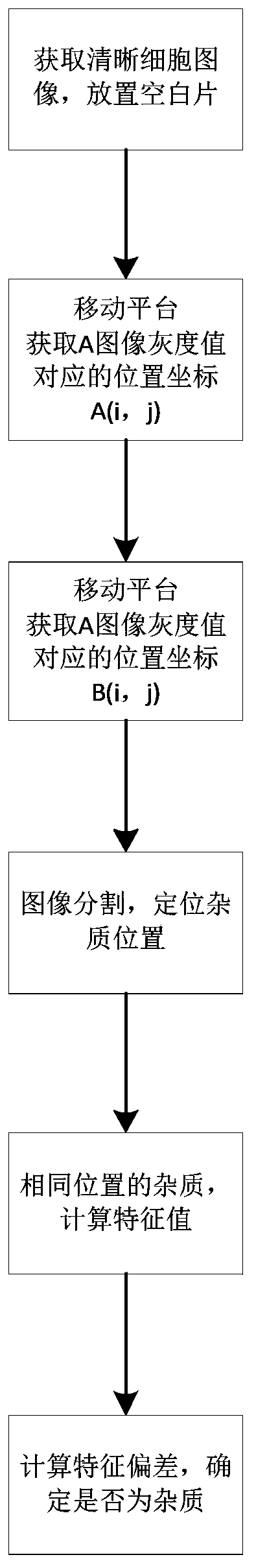
[0066] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that: in said step two, the specific process of determining the impurities in the optical path by analyzing the picture of the blank sheet under the microscope is:
[0067] Step 21: Place a blank slide and adjust the platform up and down to make a clear cell image in the camera field of view;
[0068] Step 2 and 2: Use the camera to capture the black and white picture under the microscope, represented by A, A(i, j) represents the gray value at the image position (i, j), 1≤i≤M, 1≤j≤N;
[0069] Step two and three: control the electric platform to move a field of view, and use the camera to collect picture B;
[0070] Step 2 and 4: Segment images A and B, and locate the impurity position; here the impurity may come from the optical path or from the blank film.
[0071] Step 25: Locate the position of the impurity on A and B. For the impurity at the same position on A an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com