Drug repositioning method based on low-rank matrix completion
A low-rank matrix and repositioning technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve the problems of inapplicable drugs-target diseases-gene association data unavailable, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] Concrete realization process of the present invention is as follows:
[0041] In the standard dataset adopted, a drug set, a disease set, and known drug-disease associations were included, which were obtained from the dataset collected by Gottlieb et al. The similarity between drugs is calculated based on the SMILES chemical structure information of drug molecules; the similarity between diseases is calculated based on the phenotype information of the disease.
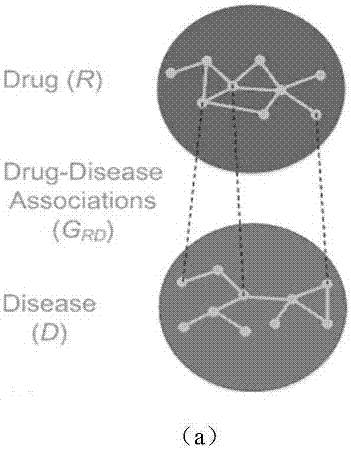
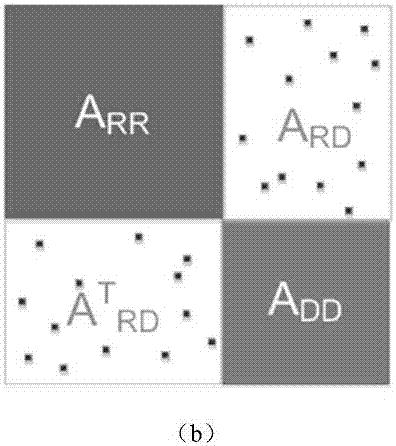
[0042] 1. Construction of drug-disease heterogeneous network
[0043] First, based on the similarity between drugs, the similarity between diseases, and known drug-disease associations, drug networks, disease networks, and drug-disease networks are constructed, respectively. In the drug network, the drug node set R={r 1 ,r 2 ,...,r m} represents m kinds of drugs, and the weight of the edge between two drug nodes is equal to the chemical structure similarity between these two drugs; in the disease network, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com