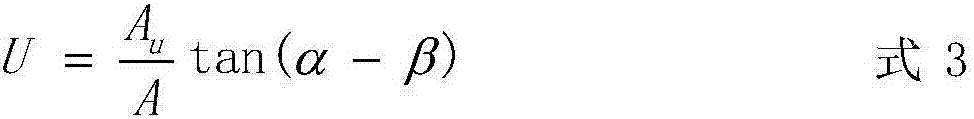Method for predicting slope debris flows of red bed area and application thereof
A technology for red-bed areas and debris flow, applied in data processing applications, forecasting, ICT adaptation, etc., can solve the problems of different thicknesses of landslides, forecast hysteresis, and the relationship between topographic conditions and rainfall conditions, etc., to improve disaster prevention and application. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
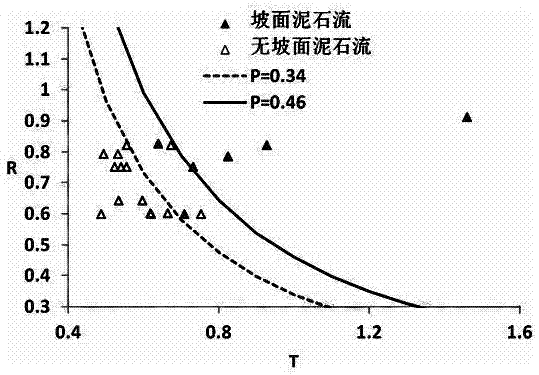
[0045] A method for forecasting debris flow on a slope in a red bed area, comprising the following steps:
[0046] a. Take the slope debris flow that has occurred in the red bed area and the surrounding slopes that are favorable in topography but have not occurred as the investigation object, and determine the slope α and the debris flow area A, upper part of the debris flow and the slope where no debris flow occurs Slope β and upper area A u , Lateral left slope θ 1 , Lateral right slope θ 2 , horizontal left area A L , horizontal right area A R and whether there is an air surface, consult the hydrology manual to determine the annual average rainfall R of the survey object 0 , 1h rainfall variation coefficient C V , arranging rain gauges to measure real-time pre-precipitation rainfall B and excitation hour rainfall I;
[0047] b. Taking the predictor P as the monitoring value, calculate and determine the predictor P through formula 1;
[0048] P=R * (S+1.8U+0.8C+F) 1...
Embodiment 2
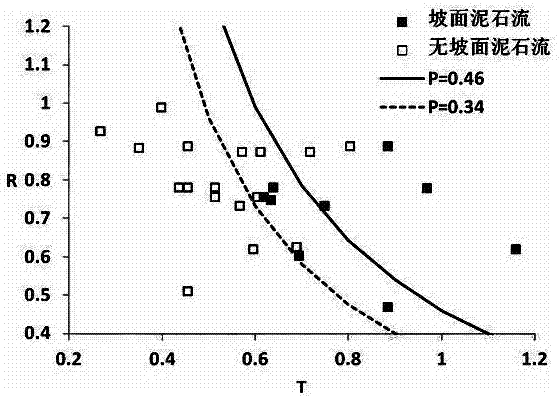
[0065] A method for forecasting debris flow on a slope in a red bed area, comprising the following steps:
[0066] a. Take the slope debris flow that has occurred in the red bed area and the surrounding slopes that are favorable in topography but have not occurred as the investigation object, and determine the slope α and the debris flow area A, upper part of the debris flow and the slope where no debris flow occurs Slope β and upper area A u , Lateral left slope θ 1 , Lateral right slope θ 2 , horizontal left area A L , horizontal right area A R and whether there is an air surface, consult the hydrology manual to determine the annual average rainfall R of the survey object 0 , 1h rainfall variation coefficient C V , arranging rain gauges to measure real-time pre-precipitation rainfall B and excitation hour rainfall I;
[0067] b. Taking the predictor P as the monitoring value, calculate and determine the predictor P through formula 1;
[0068] P=R * (S+1.8U+0.8C+F) 1...
Embodiment 3
[0086] A method for forecasting debris flow on a slope in a red bed area, comprising the following steps:
[0087] a. Take the slope debris flow that has occurred in the red bed area and the surrounding slopes that are favorable in topography but have not occurred as the investigation object, and determine the slope α and the debris flow area A, upper part of the debris flow and the slope where no debris flow occurs Slope β and upper area A u , Lateral left slope θ 1 , Lateral right slope θ 2 , horizontal left area A L , horizontal right area A R and whether there is an air surface, consult the hydrology manual to determine the annual average rainfall R of the survey object 0 , 1h rainfall variation coefficient C V , arranging rain gauges to measure real-time pre-precipitation rainfall B and excitation hour rainfall I;
[0088] b. Taking the predictor P as the monitoring value, calculate and determine the predictor P through formula 1;
[0089] P=R * (S+1.8U+0.8C+F) 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com