GPU-based parallel generation method for stochastic models of two-phase media, electronic devices
A stochastic model and medium technology, applied in the direction of concurrent instruction execution, machine execution device, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve problems such as expensive hardware, reduced parallel efficiency due to communication traffic, difficult to build and popularize computing platforms, etc., to achieve efficient parallelism Generative, versatile, and computationally inexpensive effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0047] It should be noted that all expressions using "first" and "second" in the embodiments of the present invention are to distinguish two entities with the same name but different parameters or parameters that are not the same, see "first" and "second" It is only for the convenience of expression, and should not be construed as a limitation on the embodiments of the present invention, which will not be described one by one in the subsequent embodiments.
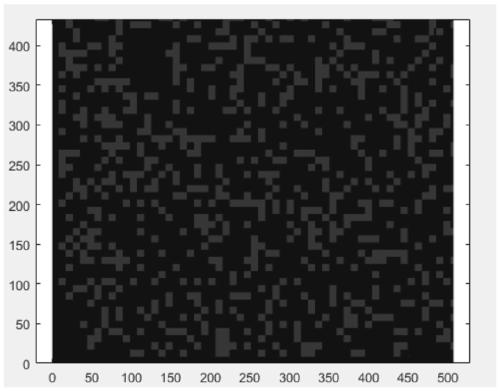
[0048] An embodiment of the present invention provides a GPU-based method for generating a random model of a two-phase medium in parallel. refer to figure 1 , is a flow chart of a GPU-based parallel generation method for a stochastic model of a two-phase medium accor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com