De novo diploid genome assembly and haplotype sequence reconstruction
A genome assembly and haplotype technology, applied in genomics, sequence analysis, proteomics, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
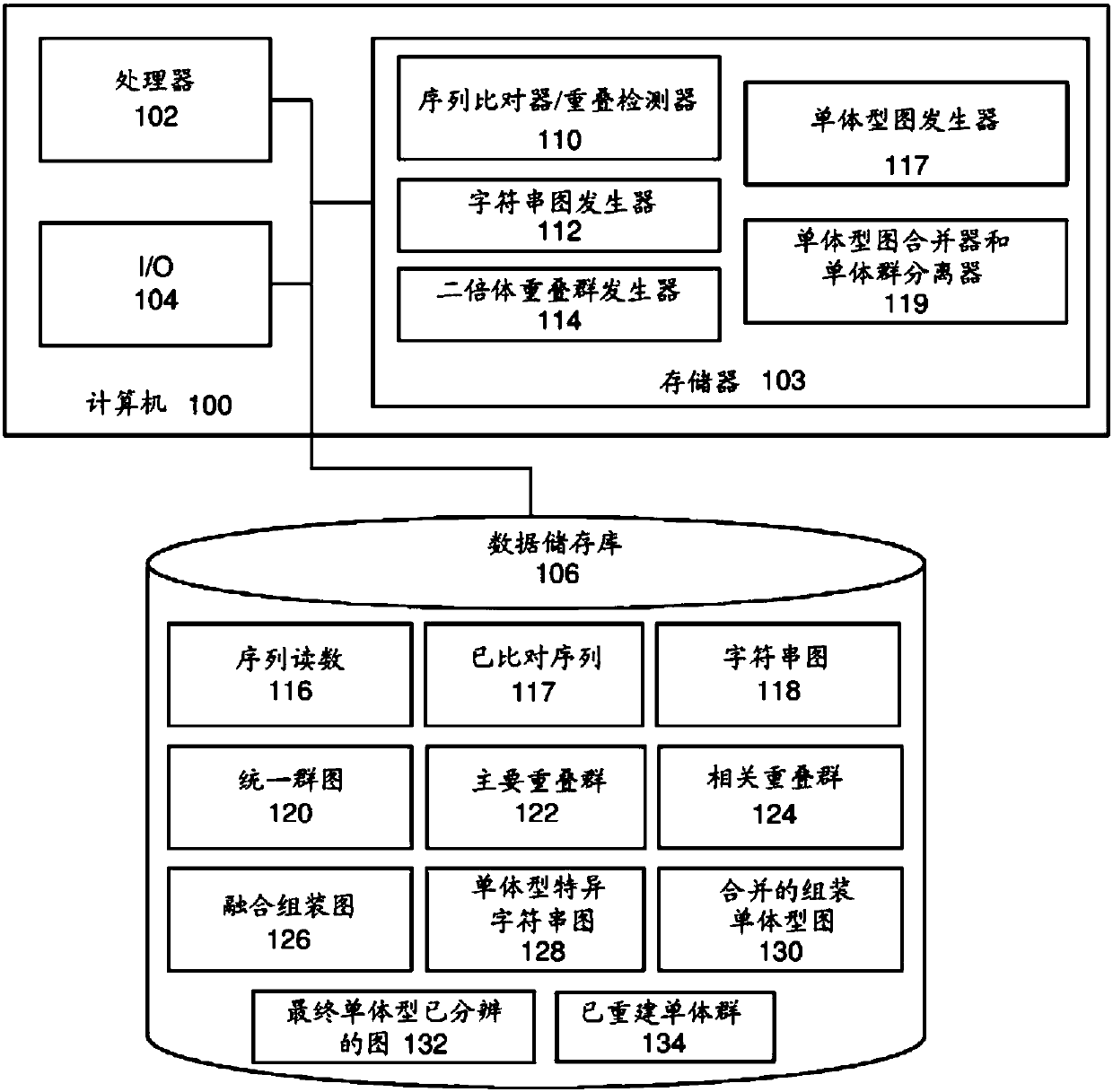
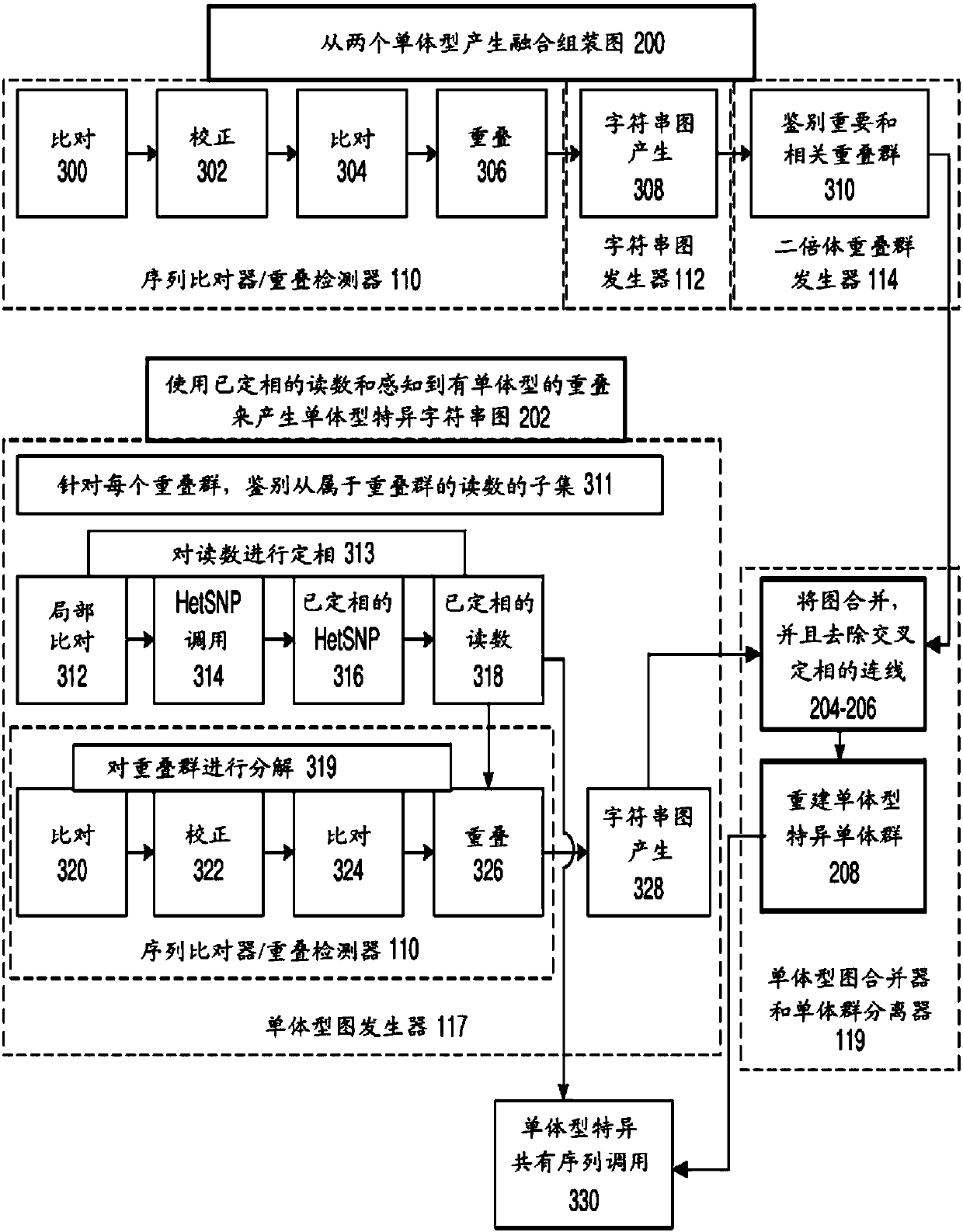
[0096] Figure 11A is a flowchart illustrating the process of string graph assembly performed by the diploid contig generator 114 on a polyploid genome, according to an exemplary embodiment. The process may begin by receiving a string map and a unified group map generated from sequence reads of length at least 0.5 kb, more preferably at least 1 kb (block 1100). According to an exemplary embodiment, the diploid contig generator 114 uses long reads to generate a string map from which a unified group map is constructed, rather than just identifying simple paths without branches in the unified group map. In one embodiment, the unified group graph may be generated by the string graph generator 112 . Alternatively, the unified group map can be generated by the diploid contig generator 114 .
[0097] String bundles are identified in the unified group graph or string graph (block 1102). In one embodiment, a bundle of character strings may include a set of unbranched wires that form...
Embodiment approach 2-
[0112] Embodiment 2 - Identification of bundles of strings and determination of primary and related contigs
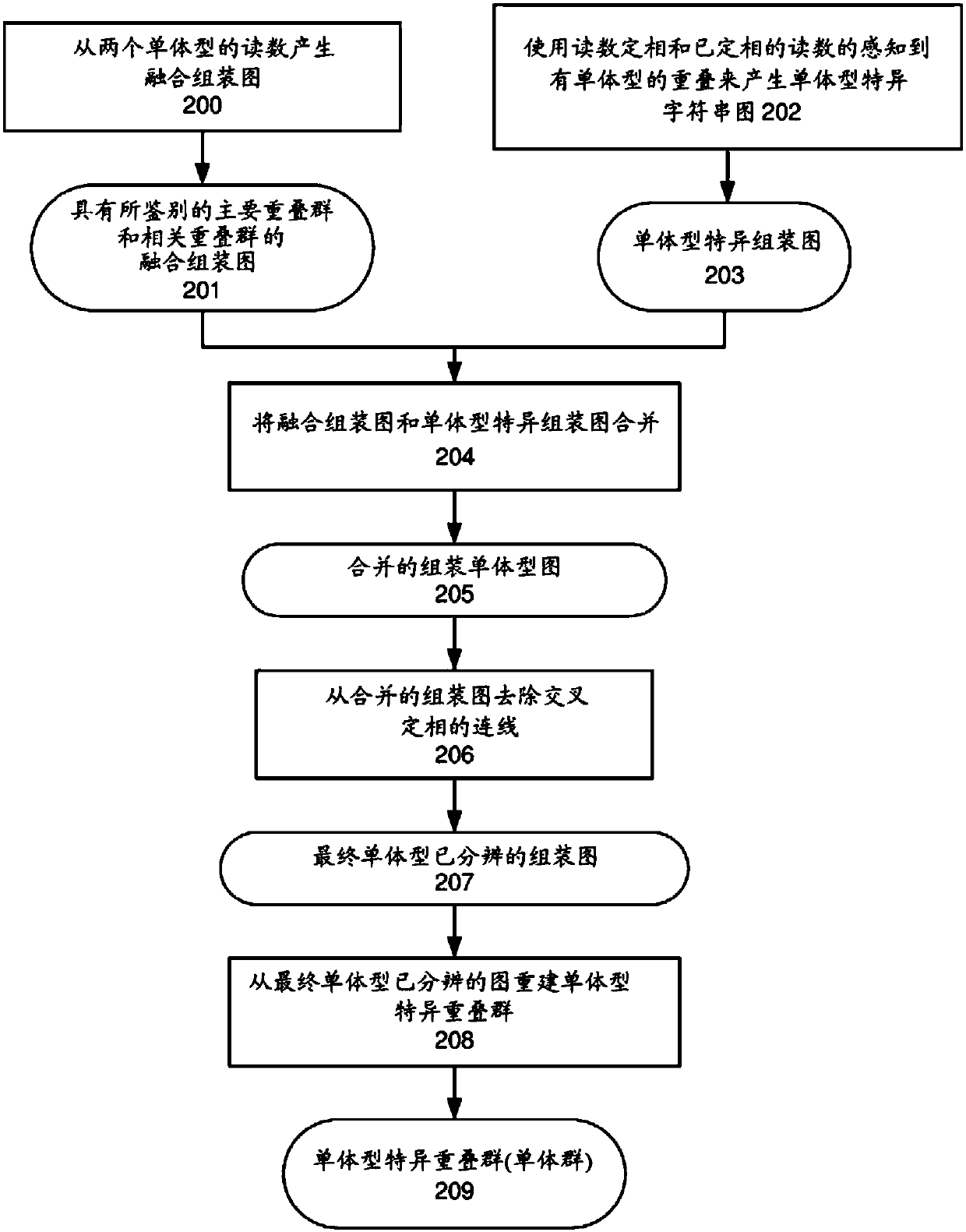
[0113] Figure 12B is a graphical diagram showing processing of a character string bundle according to the second embodiment. In a second embodiment for identifying string bundles and determining primary and related contigs, the goal is to first identify bubble regions as compound pathways. One purpose of this is to try to decompose the string graph into simple paths and simple bubbles. However, the string graph of diploid genomes with complex heterozygous structural variants or repeat structures cannot be easily decomposed into simple paths and simple bubbles due to possible subgraph motifs.
[0114] For example, it is possible to have nested bubbles, loops, intertwined bubbles, and long branches between source and sink nodes, in which case instead of between haplotypes Local structural variation, some duplication of bubbles may be caused at branch points. The fol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com