Structure and manufacturing method of a micro light-emitting diode display
A technology of light-emitting diodes and displays, applied in static indicators, instruments, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of unstable, comparable, and uneven display of organic materials, reducing production costs, simplifying production processes, and long service life. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] The micro light-emitting diode display of the present invention includes one or more display units, each display unit is composed of several pixels, and each pixel includes two or more sub-pixels.
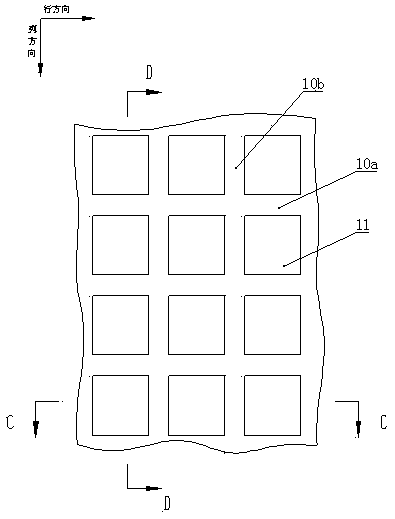
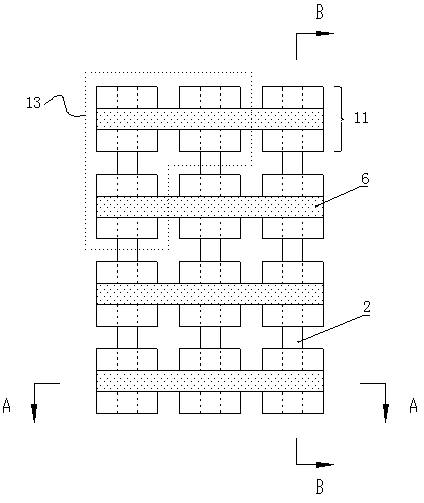
[0058] figure 1 It shows a partial top view of the same unit containing 3*4 sub-pixels. There is an etching gap between adjacent sub-pixels, and the sub-pixels 11 of the same column in a unit are connected to the same electrode A, and the electrode A is defined as One of the N electrode or the P electrode, the sub-pixels in the same row in one unit are connected to the same electrode B, the electrode B is defined as the other of the N electrode or the P electrode, and the P electrode is used as the address scanning electrode, The N electrodes are used as data driving electrodes to realize row and column driving. In this embodiment, the electrode A is the N electrode 2 , the electrode B is the P electrode 6 , and three sub-pixels 11 constitute one pixel 13 . The diameter of...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Figure 12 It shows a partial top view of the same unit containing 3*4 sub-pixels. There is an etching gap between adjacent sub-pixels, and the sub-pixels 11 of the same column in a unit are connected to the same electrode A, and the electrode A is defined as One of the N electrode or the P electrode, the sub-pixels in the same row in one unit are connected to the same electrode B, and the electrode B is defined as the other of the N electrode or the P electrode, and the row and column driving is realized. In this embodiment, the electrode A is the N electrode 2 , the electrode B is the P electrode 6 , and three sub-pixels 11 constitute one pixel 13 . The diameter of the sub-pixel is 200nm-500 um, and the etching gap is 20nm-100 um.
[0079] In this example, if Figure 13 , 14 As shown, the basic structure of the sub-pixel 1 includes a toning layer 1, an N-type semiconductor layer 3, an active light-emitting region 4, a P-type semiconductor layer 5, a P electrode 6, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com