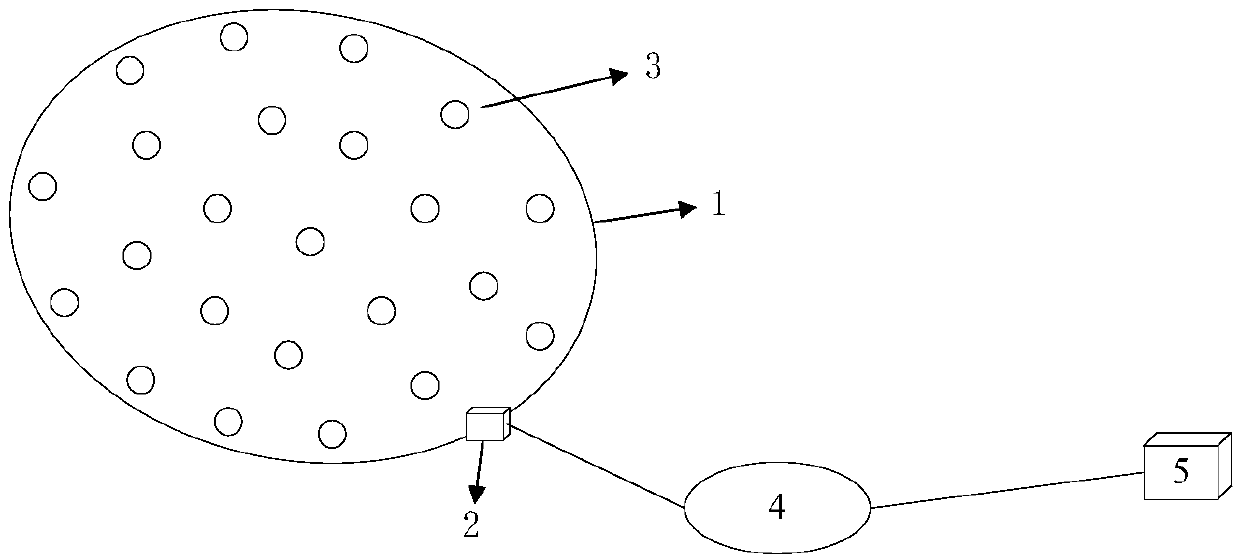
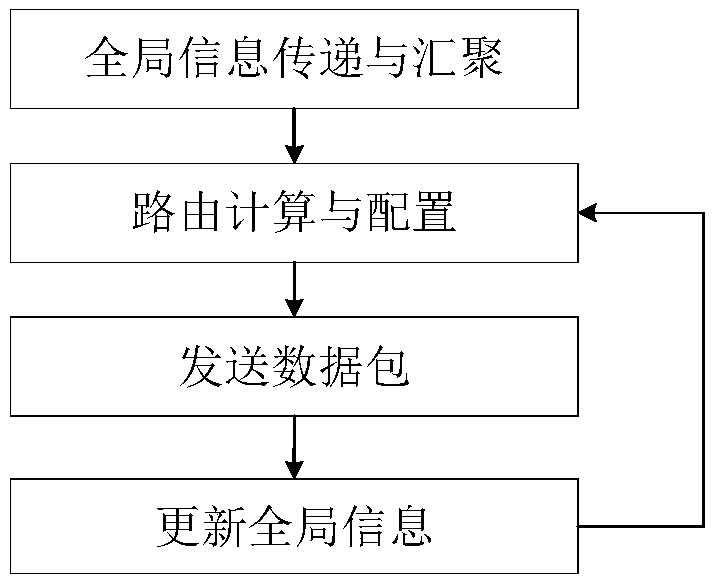
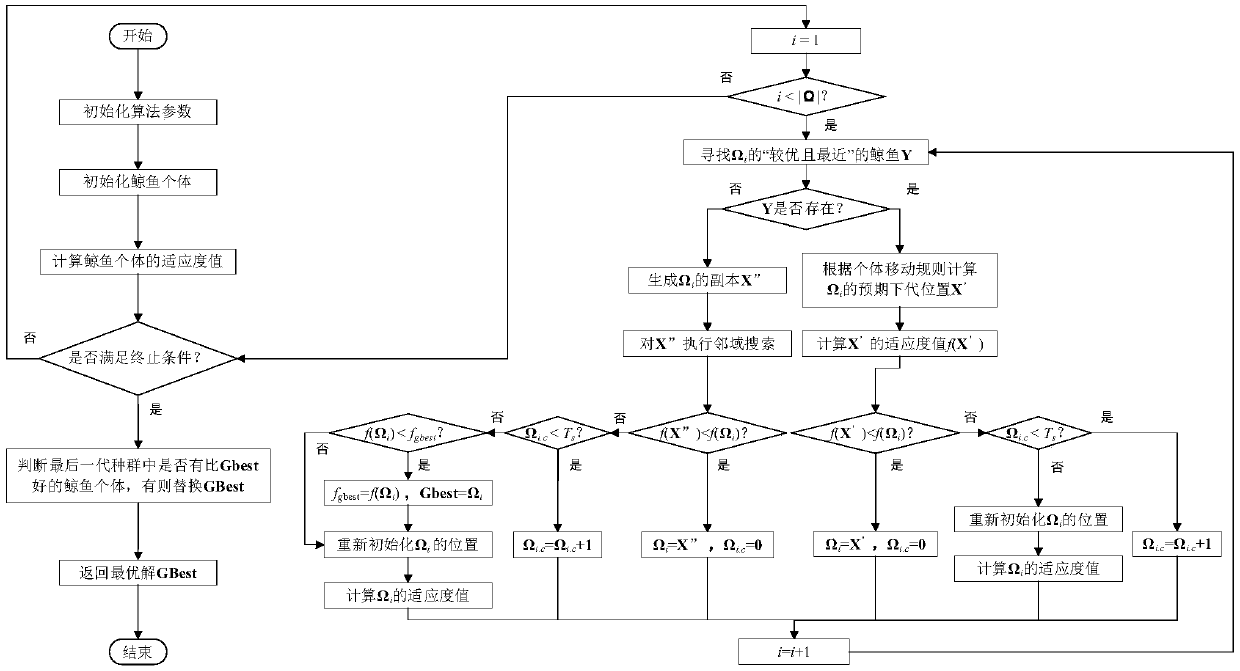
A Routing Method for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Improved Whale Swarm Algorithm
A wireless sensor and swarm algorithm technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, advanced technology, etc., can solve the problem that the number of sensor nodes cannot be determined, and the number of design variables cannot be determined.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0302] In Embodiment 1, the routing method of the present invention operates in the wireless sensor network of Fig. 9(b), Fig. 9(d), Fig. 9(f) and Fig. 9(h), wherein the initial energy of each node is from 6J to 12J And randomly selected in 18J. When the sink node in each wireless sensor network is the source node to calculate the path for the first time, the fitness convergence of the WSA-ICR algorithm and the IHSBEER algorithm is as follows: Figure 10(a) ~ 10(d) shown. In this embodiment, in order to facilitate the comparison of the performance of each algorithm in terms of other evaluation indicators, the performance of routing algorithms in terms of fitness convergence is firstly compared. Since the ACORC algorithm and the EEABR algorithm are distributed routing algorithms based on the ant colony algorithm and do not need to calculate the fitness value, only the WSA-ICR algorithm is compared with the IHSBEER algorithm in terms of fitness convergence. from Figure 10(a)...
Embodiment 2
[0304] In Example 2, for 3 evaluation indicators (average residual energy, residual energy standard deviation, minimum residual energy), the initial energy of each sensor node in 10 networks is initialized to 6J, and all data packets are sent from fixed source nodes , forwarded to the sink node by other nodes, until each sink node receives 6000 data packets, the calculation stops; for the fourth evaluation index (that is, the network life cycle), when the energy of any sensor node in the network is exhausted Just stop counting. Figure 11(a) ~ 11(d) is the experimental result when the initialization energy of each sensor node is the same. Figure 11(a) , 11(b) , 11(c) are the 10 running averages of the average residual energy, standard deviation of residual energy and minimum residual energy of each sensor node in the network after the sink node in each network receives 6000 data packets. Figure 10(d) is the mean value of 10 runs in the network life cycle when the energy of ...
Embodiment 3
[0309] In Example 3, for the three evaluation indicators (average remaining energy, standard deviation of remaining energy, and minimum remaining energy), the initial energy of each sensor node in the 10 networks is initialized to 6J, and the nodes in each scene periodically Send data packets to the sink nodes, and stop the calculation until each sink node receives 26,000 data packets; for the fourth evaluation index (that is, the network life cycle), stop when any sensor node in the network runs out of energy calculate.
[0310] Figure 12(a) ~ 12(d) is the experimental result when the initialization energy of each sensor node is the same. Figure 12(a) , 12(b) , 12(c) are respectively the average residual energy, standard deviation of residual energy and 10 running averages of the minimum residual energy of each sensor node in the network after the sink node in each network receives 26,000 data packets. Figure 12(d) is the mean value of 10 runs in the network life cycle w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com