Discrimination method for power system transient stability based on phase trajectory and relative kinetic energy change rate
A transient stability, power system technology, applied in circuit devices, AC network circuits, reducing/preventing power oscillations, etc., can solve problems such as low accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
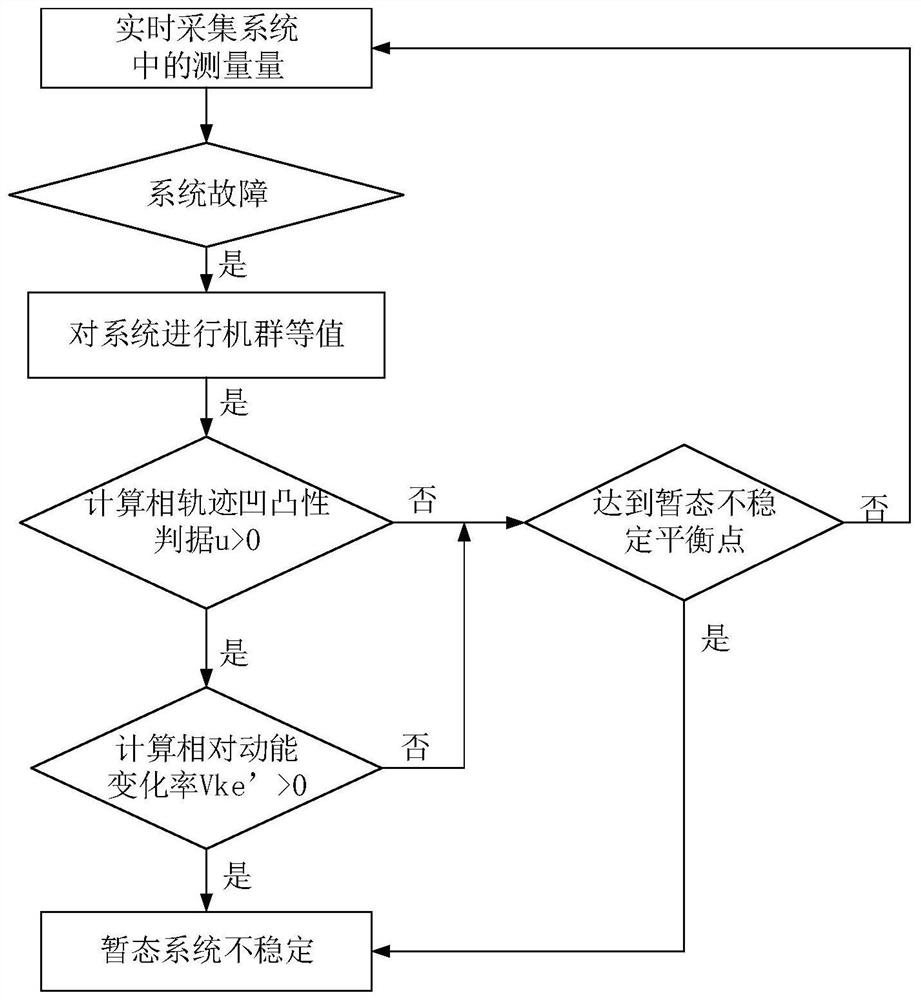
[0062] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-10 As shown, the power system transient stability discrimination method based on phase trajectory and relative kinetic energy change rate, the specific steps of the discrimination method are as follows:
[0063] Step S1. At time t, collect the power angle δ of the i-th generator in the power system in real time through the WAMS system i , Angular velocity Δω i , Electromagnetic power P ei , mechanical power P mi , i=1, 2, 3...n, n is the number of all generators in the power system;
[0064] Step S2. According to the generator information extracted in step S1, judge whether there is a fault in the power system. If there is no fault, return to step S1. If there is a fault, sort all generators according to the power angle from large to small, and calculate the adjacent two The power angle difference of each unit is selected, and the two generator sets corresponding to the largest power angle difference are selected as the dividing line. The ...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Embodiment 2: as Figure 1-10 As shown, the power system transient stability discrimination method based on phase trajectory and relative kinetic energy change rate,
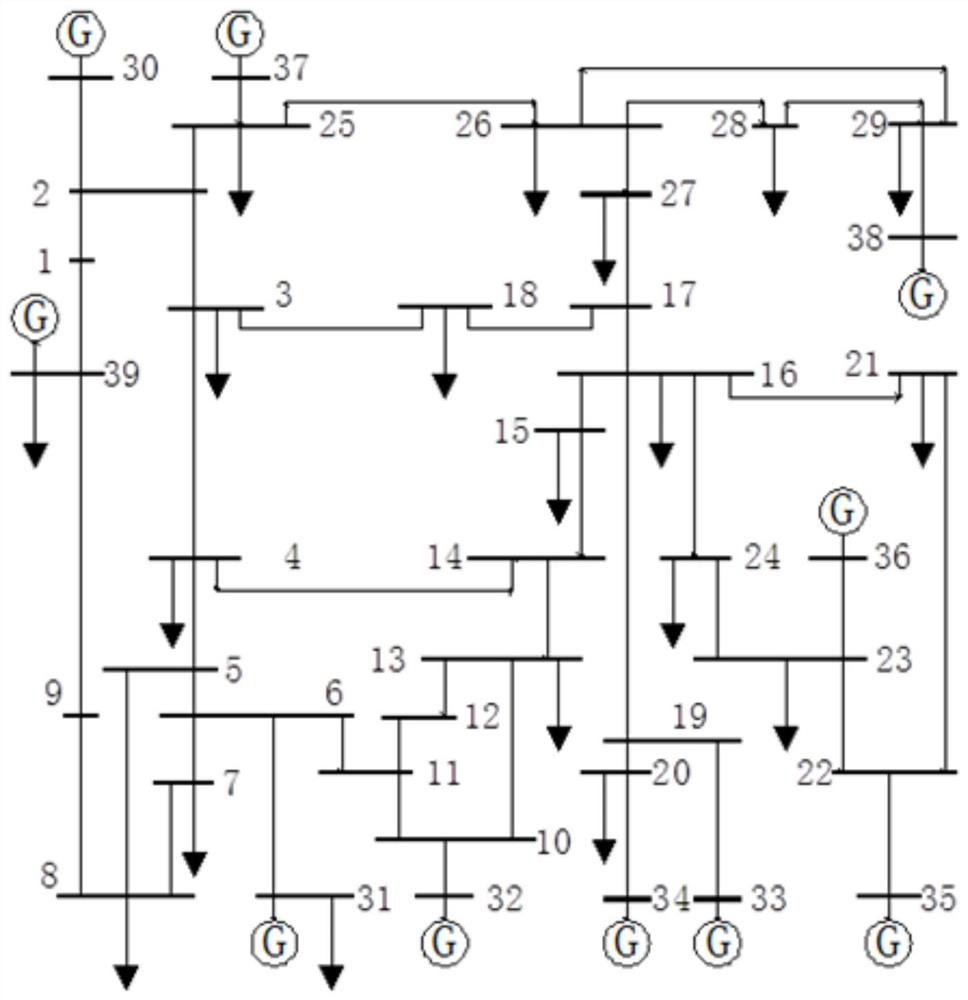
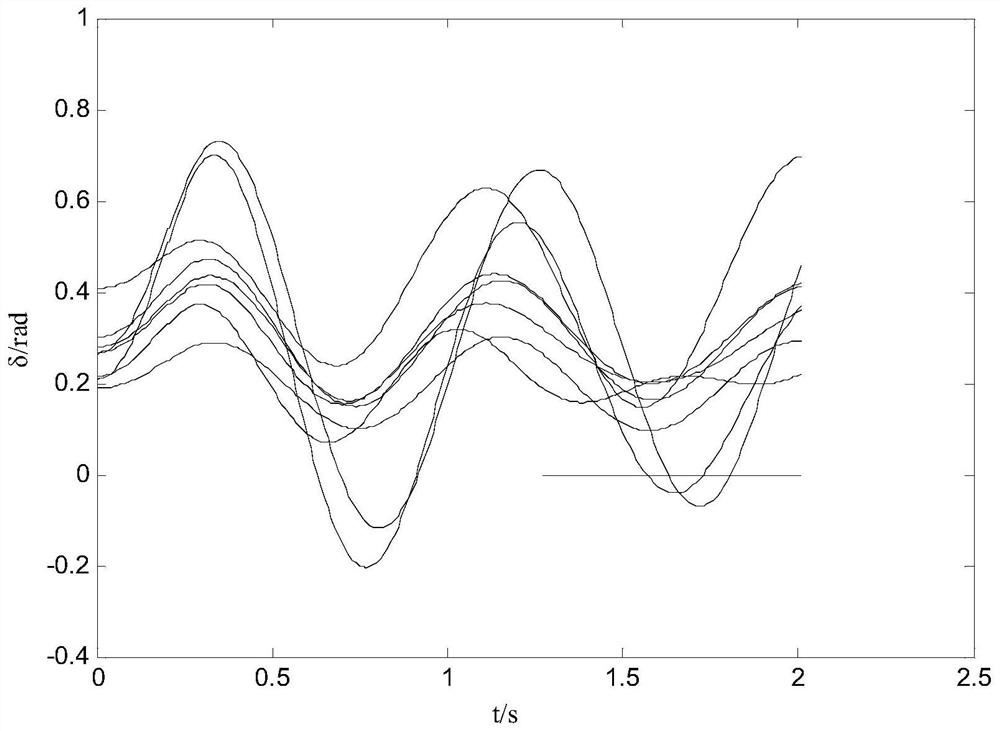
[0094] In order to verify the stability identification method based on phase trajectory and transient energy proposed in this paper, the BPA program is used to simulate the same fault at different locations and the same fault duration is different on the IEEE10 machine 39 node system, and the calculation step size is 0.01s, E for generator q 'Model, load with constant load model. The parameters such as power angle, mechanical power, angular velocity and electromagnetic power of the generator obtained through simulation calculation are used as the corresponding measurement input, and a MATLAB program is written to analyze and calculate the data.
[0095] Case 1
[0096] Set fault 1 as a three-phase ground short circuit between busbars 4 and 14. After 0.2s, the fault disappears, and the system will be in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com