Optoelectronic Devices
A technology of optoelectronic devices and Faraday rotators, applied in instruments, optics, nonlinear optics, etc., can solve the problems of high production cost, high production cost, and large area of optical hybrid devices, achieve flexible design of electronic circuits, and facilitate small the effect of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
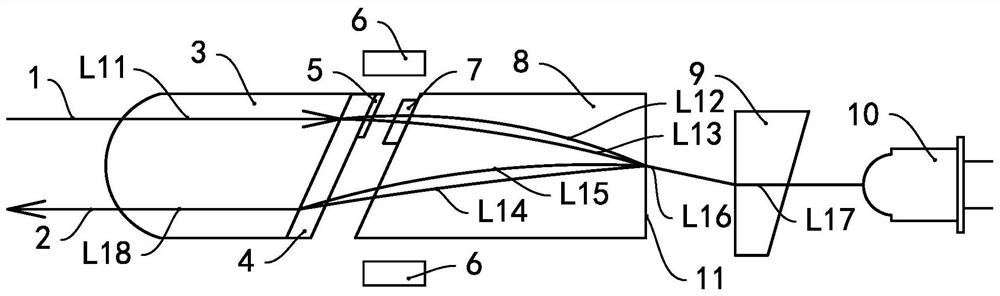
[0035] see figure 1 , The optoelectronic device of this embodiment has a fiber head 3 , a beam splitting crystal 4 , a half-wave plate 5 , a Faraday rotator 7 , a self-focusing lens 8 , an angle wedge plate 9 and a photoelectric converter 10 . Wherein, the fiber head 3 is provided with two optical fibers, which are fiber 1 and fiber 2 respectively. Therefore, the fiber head is a dual-fiber fiber head, and an externally input light beam can enter the optoelectronic device through the fiber 1 .
[0036] In this embodiment, the optical fiber 1 and the optical fiber 2 both extend outward from the first end of the optical fiber head 3, the light splitting crystal 4 is attached to the second end of the optical fiber head 3, and the half-wave plate 5 is attached to the light splitting crystal 4 away from the optical fiber. 3 side of the head. In this embodiment, the half-wave plate 5 is only arranged on the optical path of the optical fiber 1 .
[0037] The self-focusing lens 8 is ...
no. 2 example
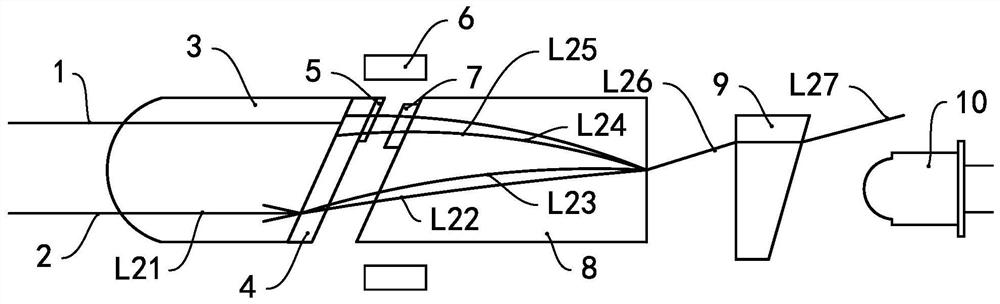
[0051] see image 3 , The optoelectronic device of this embodiment has an optical fiber head 23 , a beam splitting crystal 24 , a half-wave plate 25 , a Faraday rotator 27 , a self-focusing lens 28 , an angle wedge plate 29 and a photoelectric converter 30 . Wherein, two optical fibers are arranged in the optical fiber head 23 , namely an optical fiber 21 and an optical fiber 22 , and an externally input light beam can enter the optoelectronic device through the optical fiber 21 .
[0052] In this embodiment, both the optical fiber 21 and the optical fiber 22 extend outward from the first end of the optical fiber head 23, the light splitting crystal 24 is attached to the second end of the optical fiber head 23, and the half-wave plate 25 is attached to the light splitting crystal 24 away from the optical fiber. 23 side of the head. In this embodiment, the half-wave plate 25 is only arranged on the optical path of the optical fiber 21 .
[0053] The self-focus lens 28 is arra...
no. 3 example
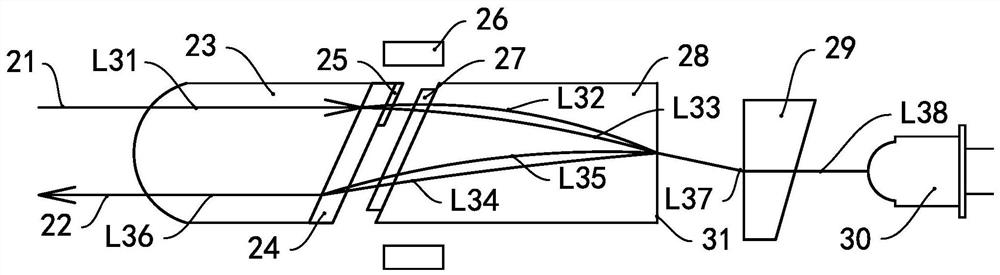
[0062] see Figure 5 , In this embodiment, the optoelectronic device has a fiber head 43 , a beam splitting crystal 44 , a half-wave plate 45 , a Faraday rotator 47 and a self-focusing lens 48 . Wherein, two optical fibers are arranged in the optical fiber head 43 , namely an optical fiber 41 and an optical fiber 42 , and the light beam input from the outside can enter the optoelectronic device through the optical fiber 41 .
[0063] In this embodiment, both the optical fiber 41 and the optical fiber 42 extend outward from the first end of the optical fiber head 43, the light splitting crystal 44 is attached to the second end of the optical fiber head 43, and the half-wave plate 45 is attached to the light splitting crystal 44 away from the optical fiber. 43 side of the head. In this embodiment, the half-wave plate 45 is only arranged on the optical path of the optical fiber 41 .
[0064] The self-focus lens 48 is arranged opposite to the fiber head 43 , and the Faraday rota...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com